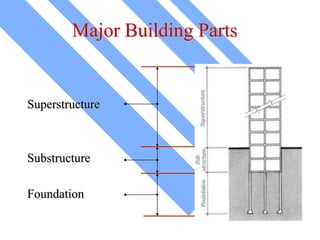
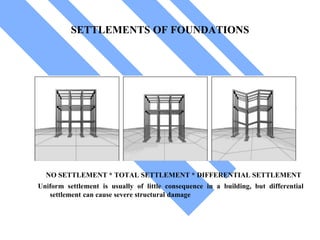
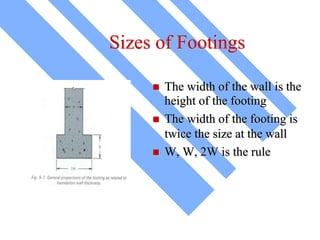
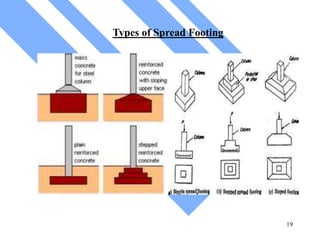
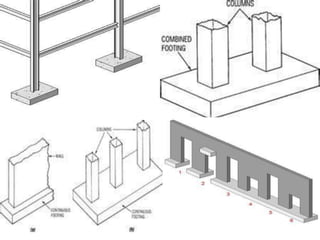
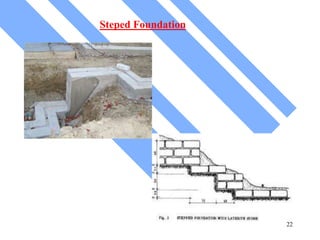
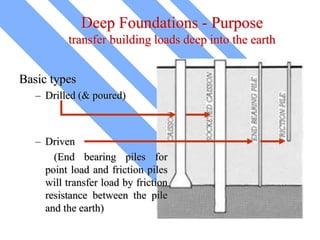
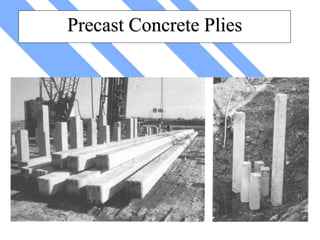
The document discusses foundations for buildings. It states that foundations transfer structural loads from a building safely into the ground, reaching below the frost line into competent soil or rock. Foundation design depends on factors like subsurface soil, loading intensity, and groundwater. Shallow foundations like spread footings are used when soils can support loads near the surface, while deep foundations like piles are needed in weak soils. Foundation selection involves considering soil strength, loads, construction methods, and effects on neighboring properties.