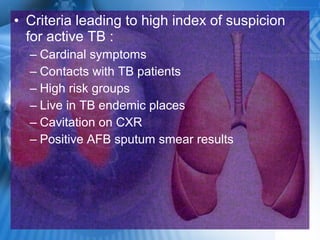
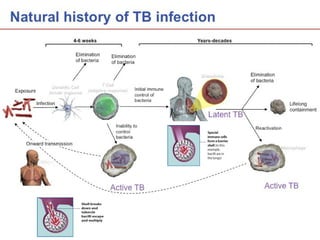
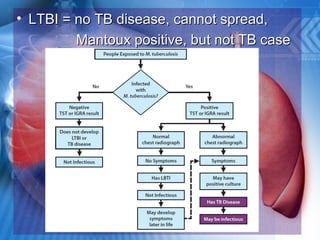
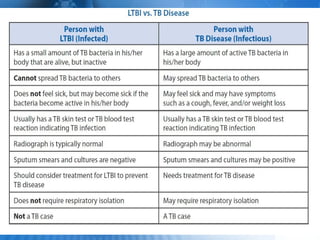
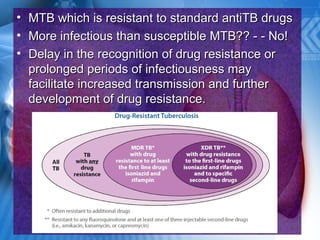
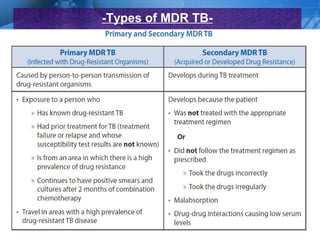
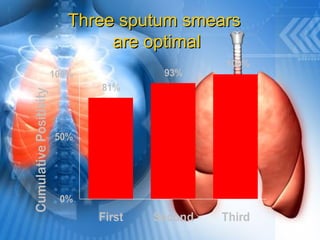
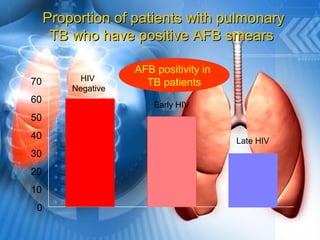
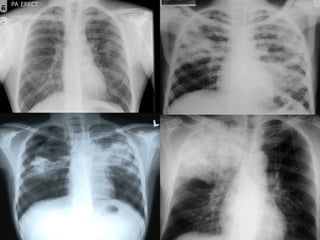
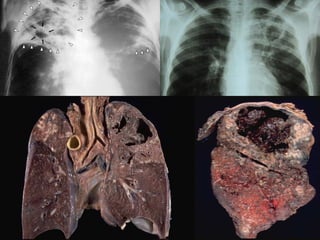
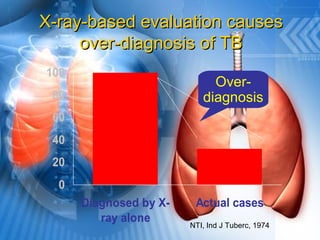
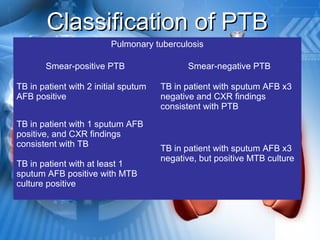
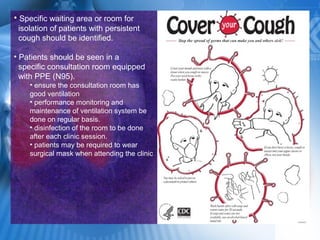
Pulmonary tuberculosis is caused by the airborne bacterium Mycobacterium tuberculosis. It is highly contagious and spreads through air droplets from infected individuals. While over 1 in 3 people worldwide are infected with TB, only a small portion (5-10%) will develop active disease. The lungs are the most common site of infection. Symptoms include cough, night sweats, weight loss and fever. Diagnosis involves sputum smear, culture and chest x-ray. Treatment requires a multi-drug regimen to prevent drug resistance. Health facilities should take precautions like isolating coughing patients and providing protective equipment to staff.