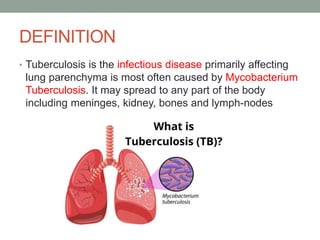
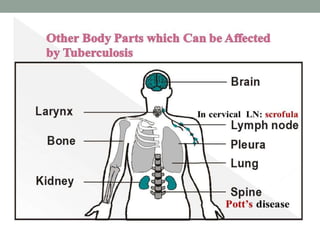
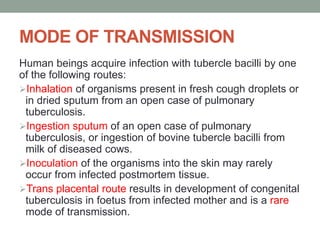
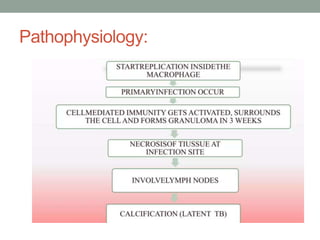
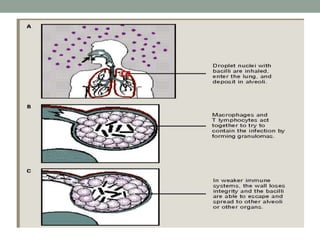
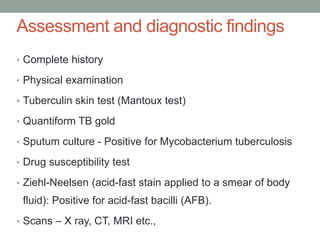
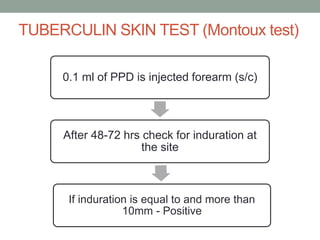
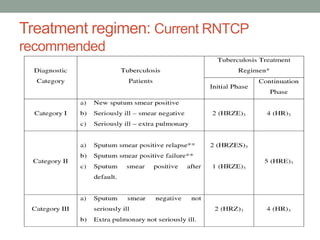
Tuberculosis (TB) is a contagious infection primarily affecting the lungs, caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis, with significant annual impacts, including 10 million new cases and 1.5 million deaths worldwide. It spreads through airborne droplets and can affect various body parts; risk factors include close contact with infected individuals, compromised immunity, and inadequate healthcare. Diagnosis involves clinical evaluation, laboratory tests, and a recommended treatment regimen consisting of first-line anti-TB drugs and directly observed therapy to ensure adherence.