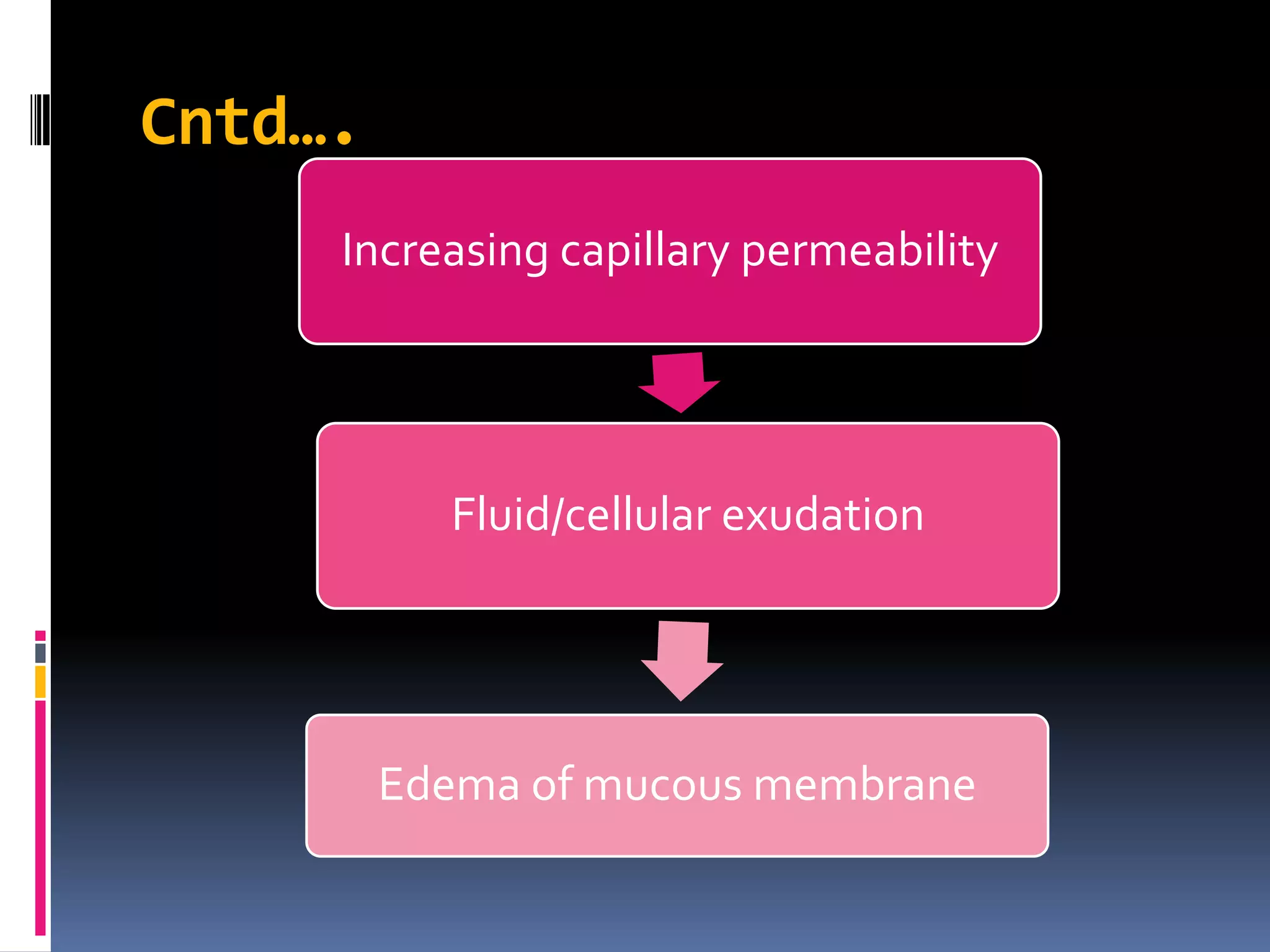
Respiratory tract infections are classified as either upper respiratory tract infections (URTI) that involve the areas above the vocal cords such as the nose, sinuses and throat, or lower respiratory tract infections (LRTI) that involve the areas below the vocal cords such as the trachea and lungs. Common causes of URTI include viruses and bacteria while LRTI are usually caused by bacteria or viruses with pneumonia being the most common LRTI. Symptoms vary depending on the location of the infection but may include cough, sore throat, runny nose and fever. Treatment involves medications to reduce symptoms and antibiotics if caused by bacteria.