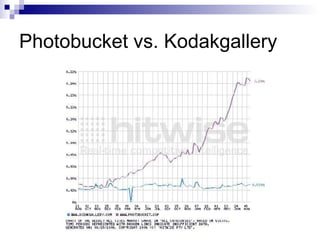
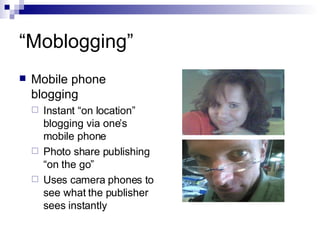
The document discusses trends in online journalism, including opportunities for web editors and producers. Some of the highest paying jobs include web editors and producers. Skills valued for these roles include writing, technical abilities, news judgment, and multimedia skills. Online journalism is evolving with new forms of storytelling using multimedia and participation from readers. Citizen and mobile journalism are emerging trends.