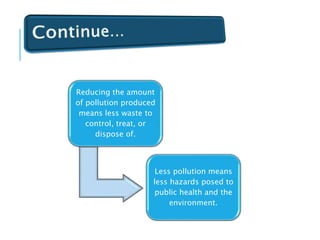
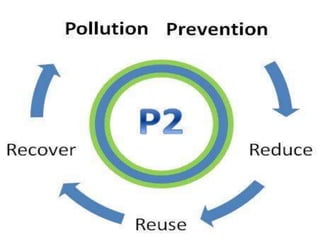
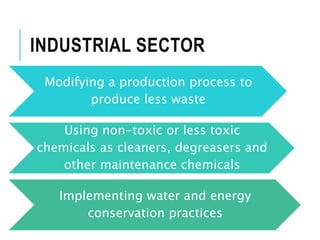
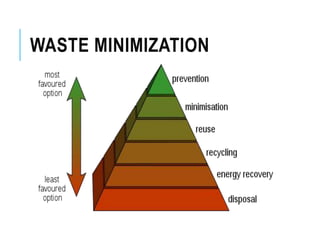
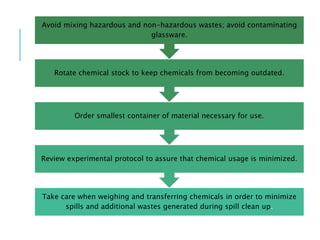
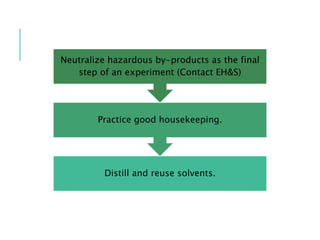
Pollution prevention (P2) aims to reduce or eliminate pollution at its source through practices like increasing energy efficiency, using renewable fuels, reducing agricultural inputs, and modifying industrial processes to produce less waste. P2 benefits the environment by lowering pollution hazards and conserving resources, and benefits financial costs by reducing waste management expenses. Waste minimization also aims to reduce hazardous wastes through practices like careful chemical handling, solvent reuse, and neutralizing byproducts. While waste minimization focuses specifically on hazardous waste, pollution prevention more broadly addresses reducing all toxic releases to air, water and land.