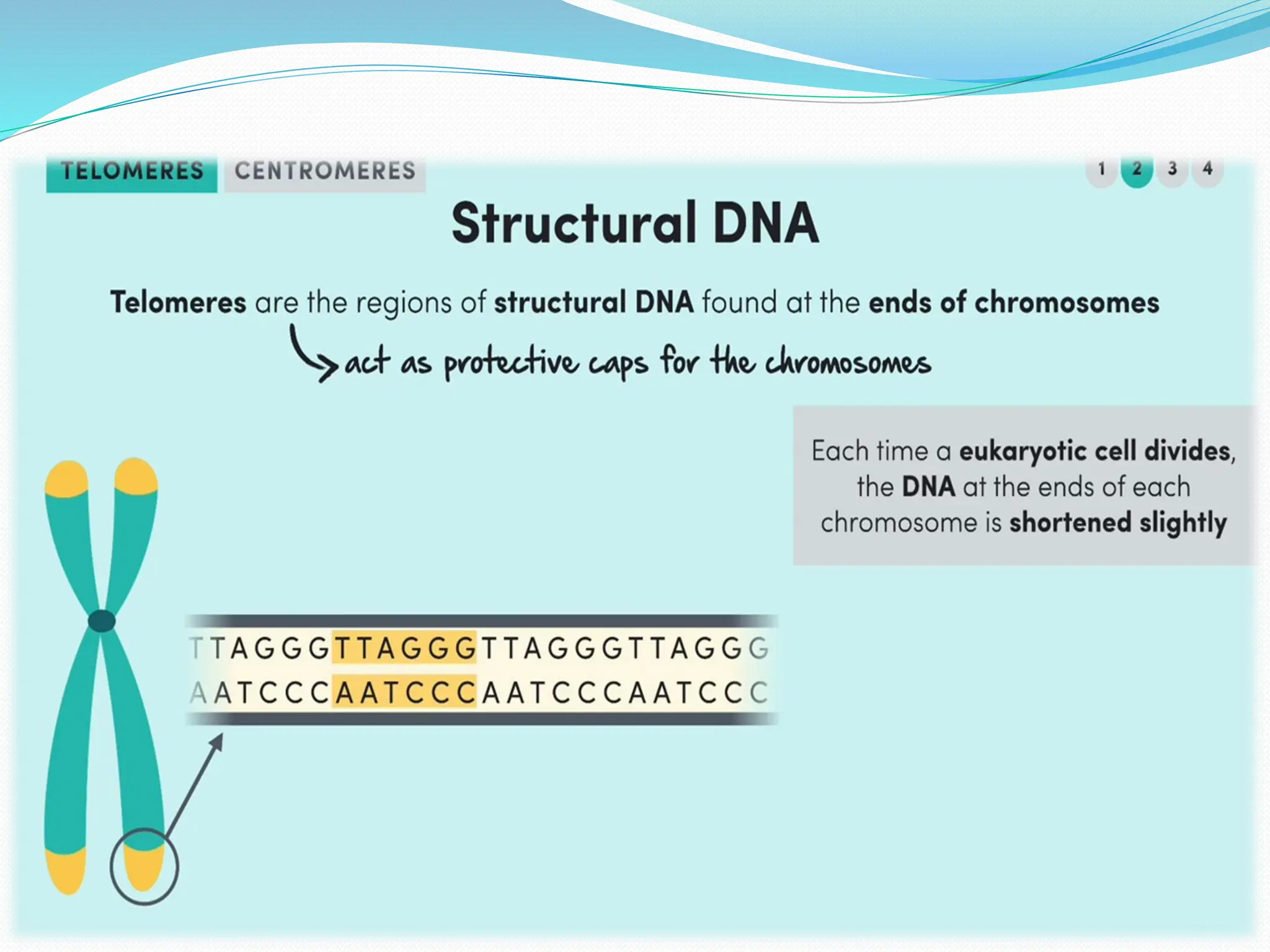
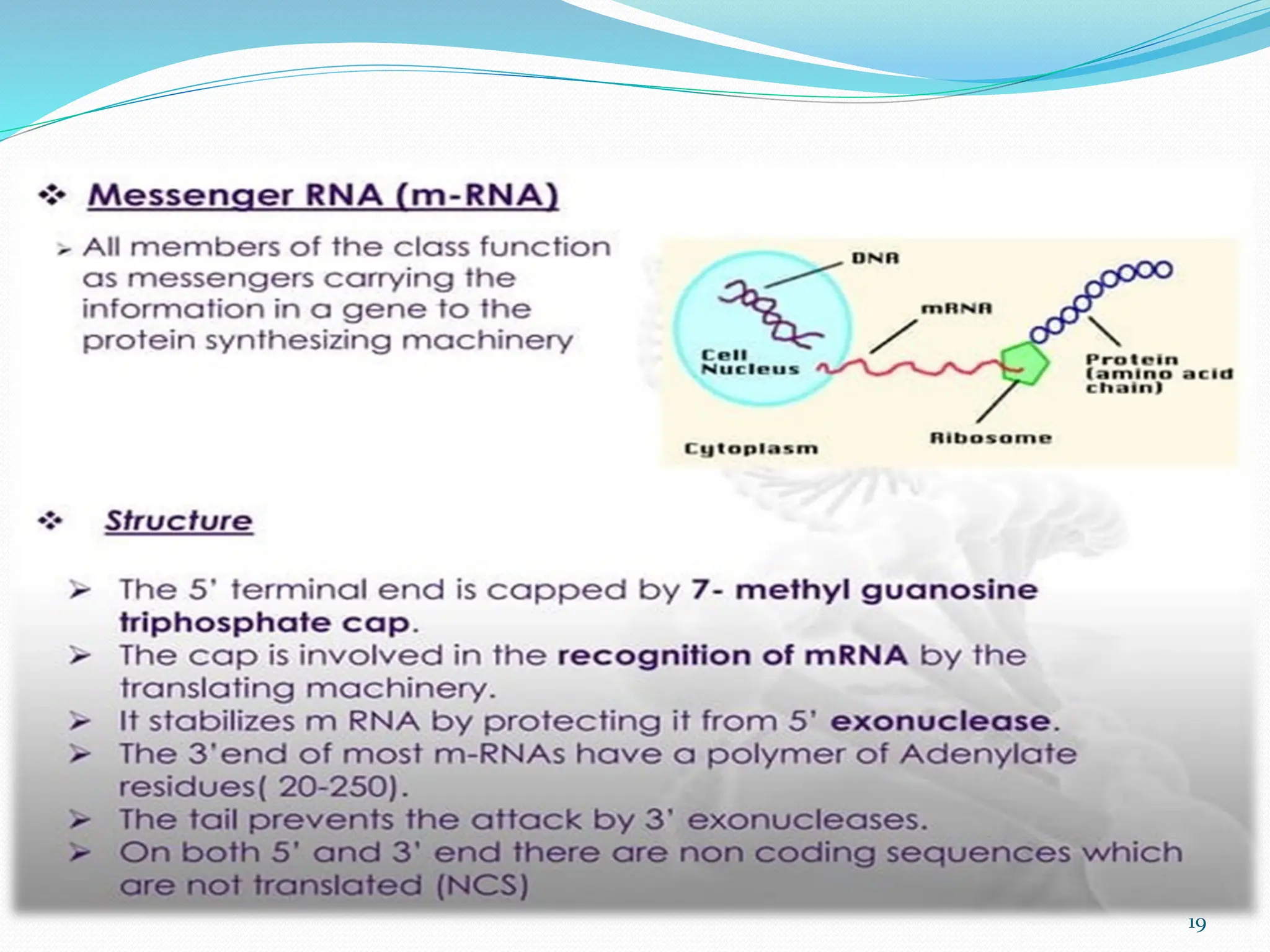
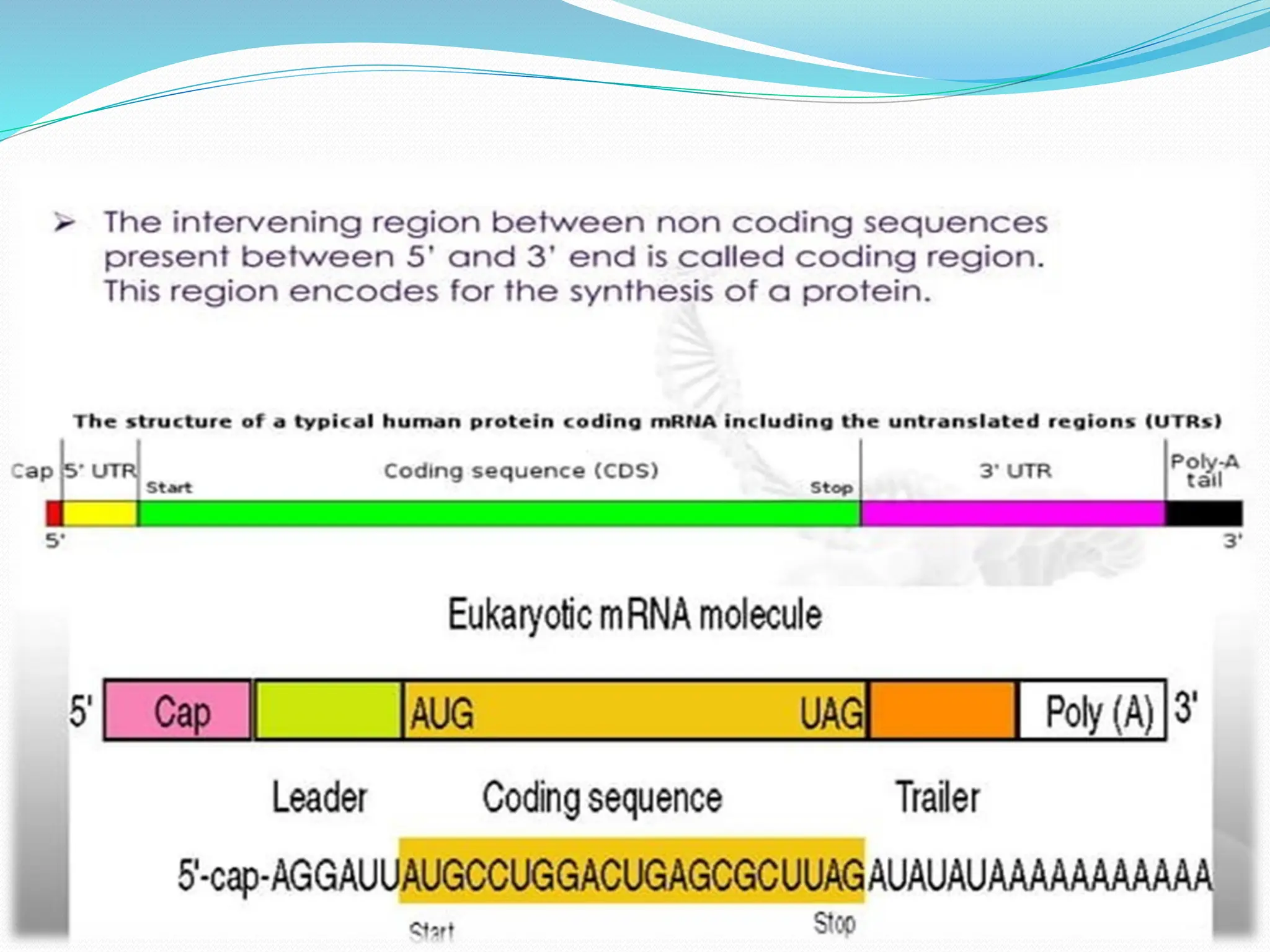
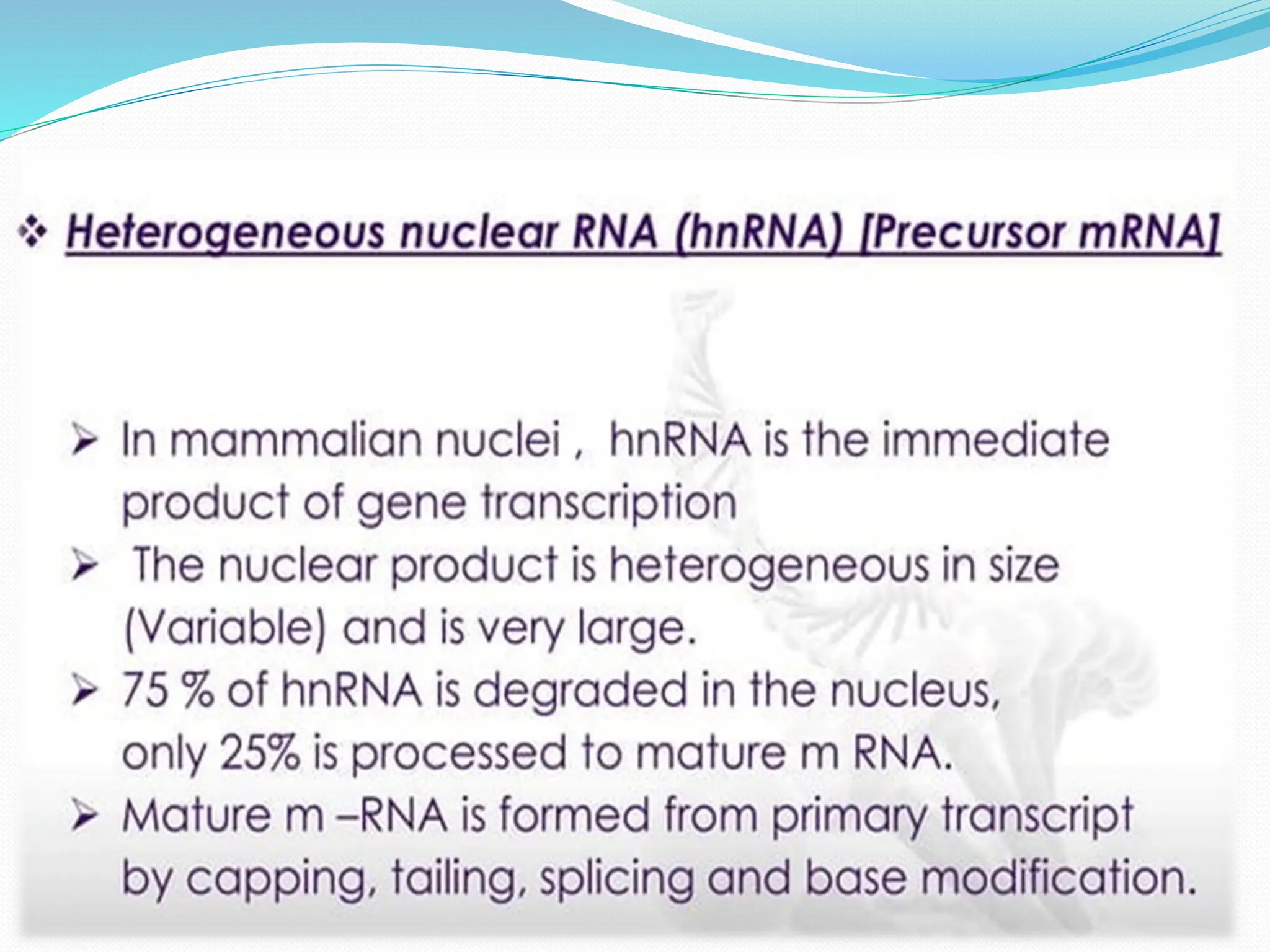
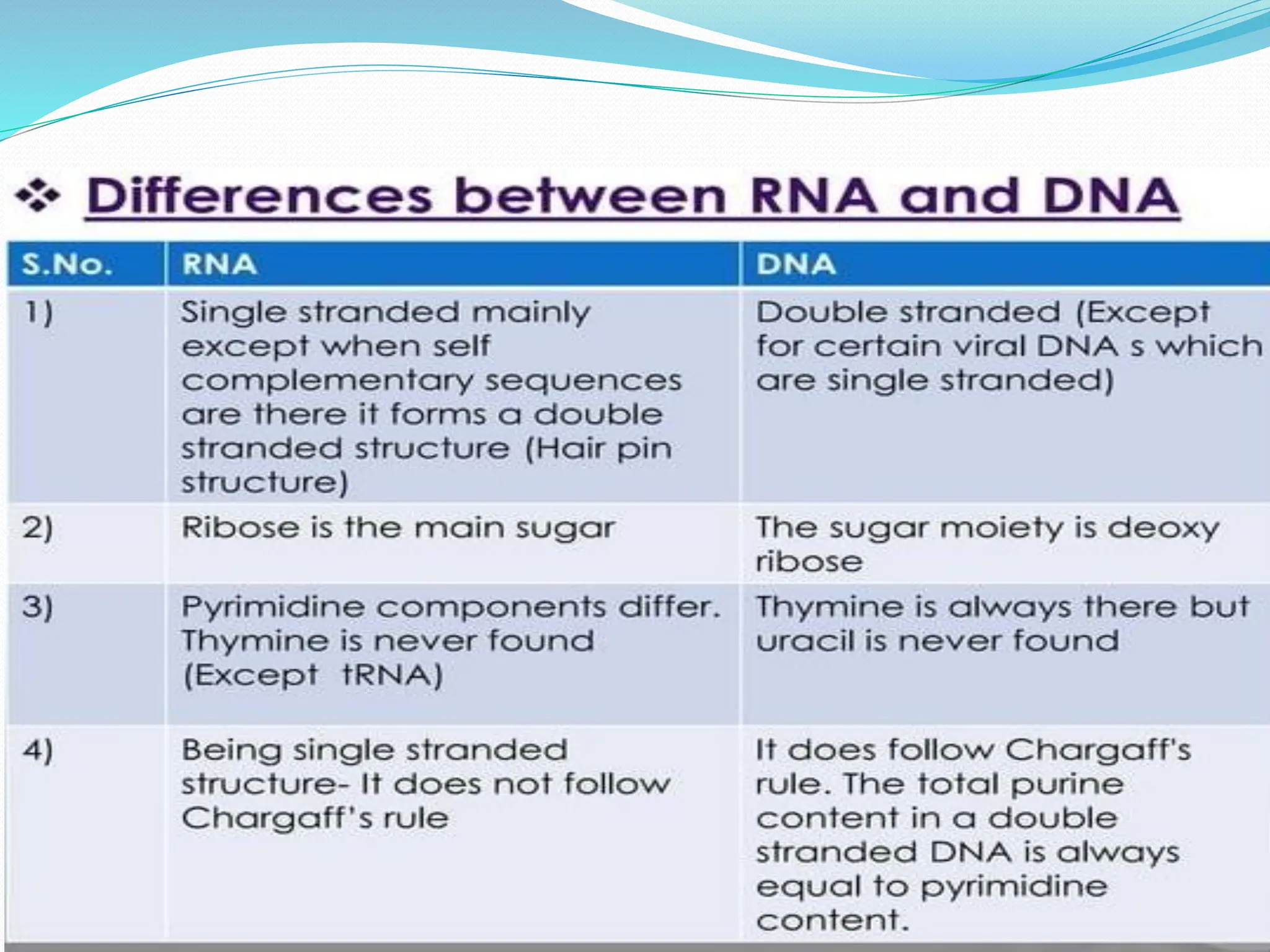
Coding DNA makes up about 2% of the human genome and contains genes that encode proteins. Noncoding DNA, which is about 98% of the genome, does not encode proteins but can be transcribed into noncoding RNAs. Noncoding DNA includes noncoding genes, promoters, introns, telomeres, satellite DNA, and mobile genetic elements like transposons. Promoters are DNA segments near genes that initiate transcription, while introns are parts of genes that are transcribed but later removed from mature RNA. Telomeres, satellite DNA, and mobile elements help preserve chromosome structure and regulate genes.