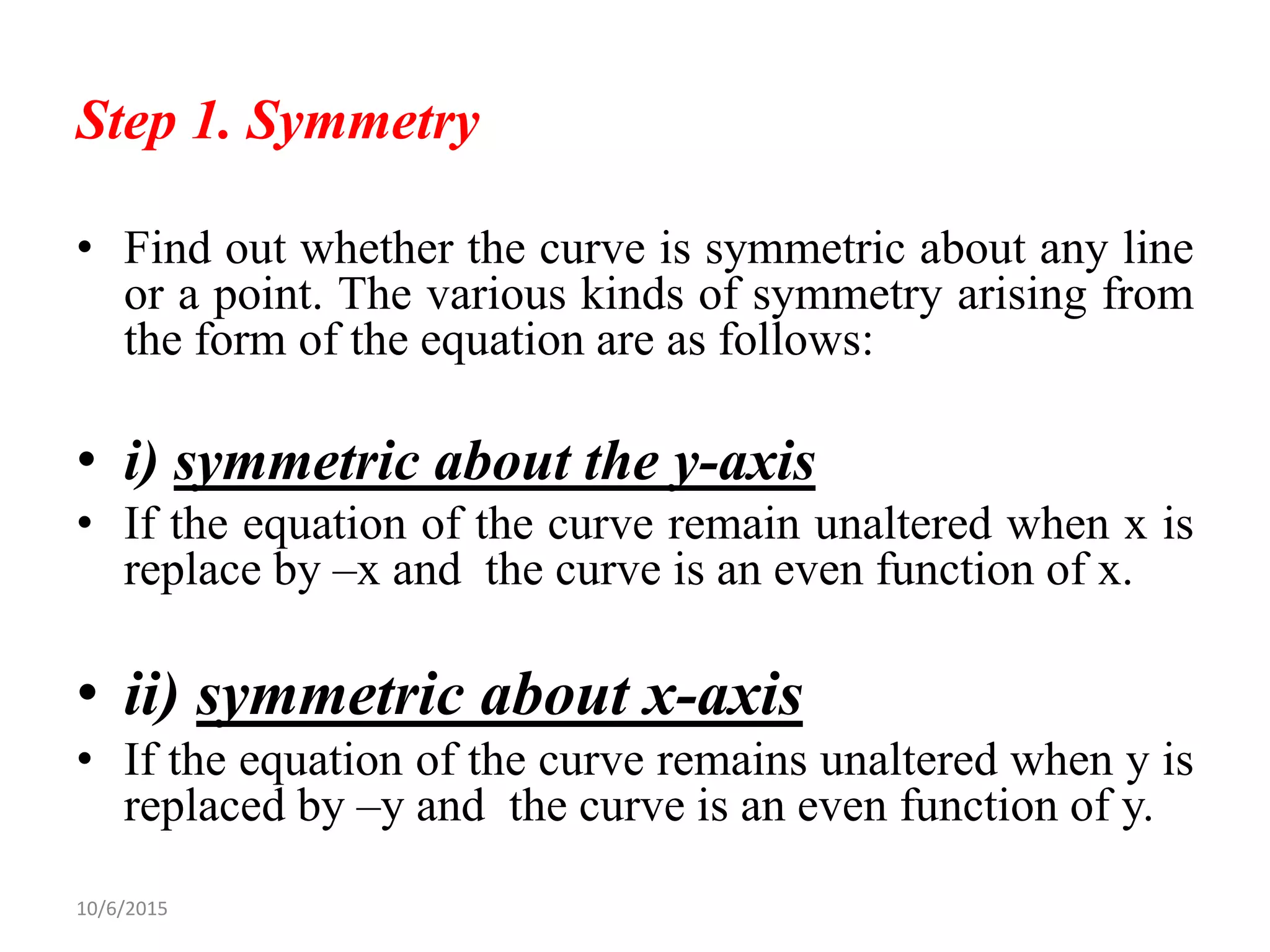
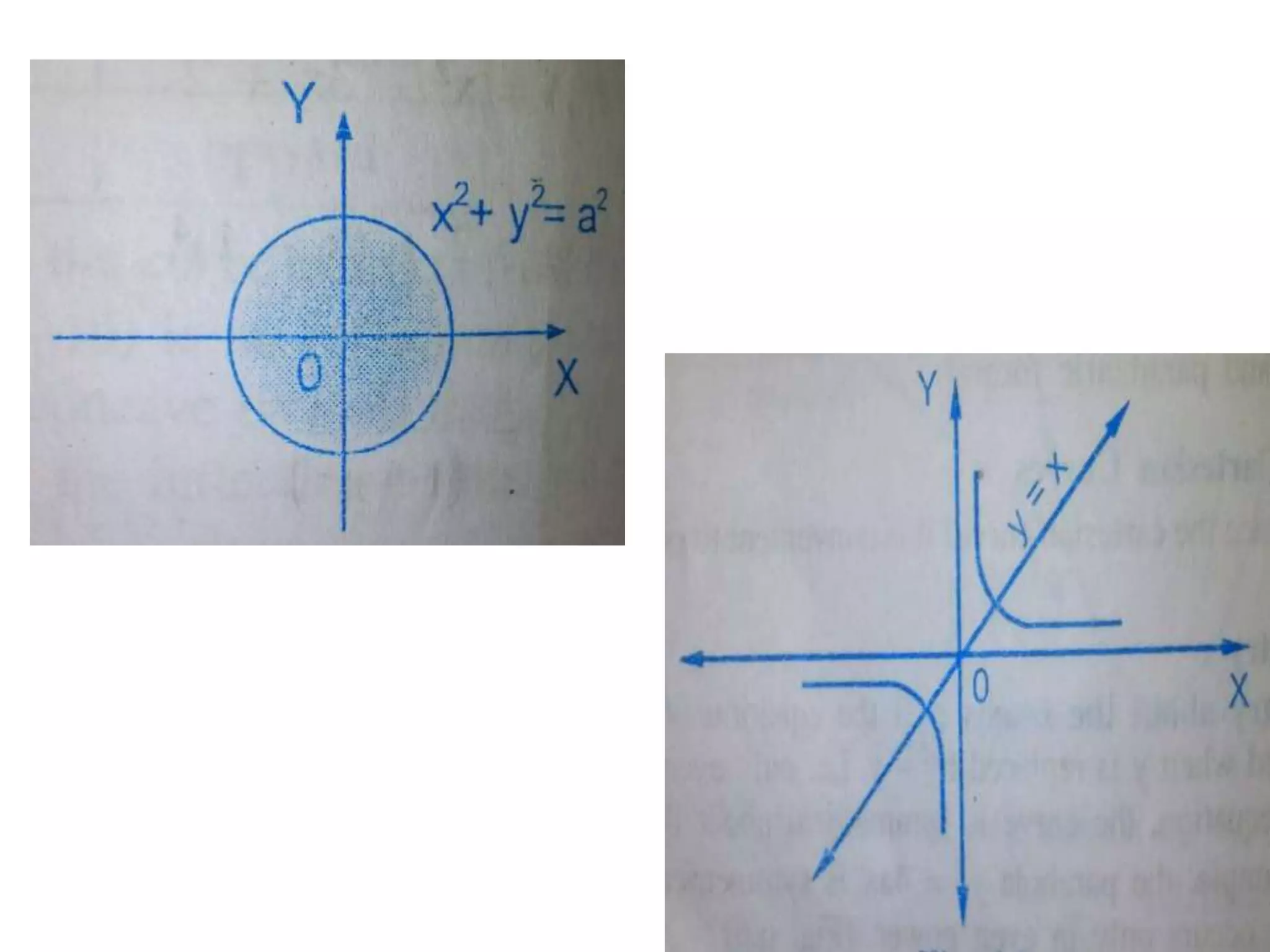
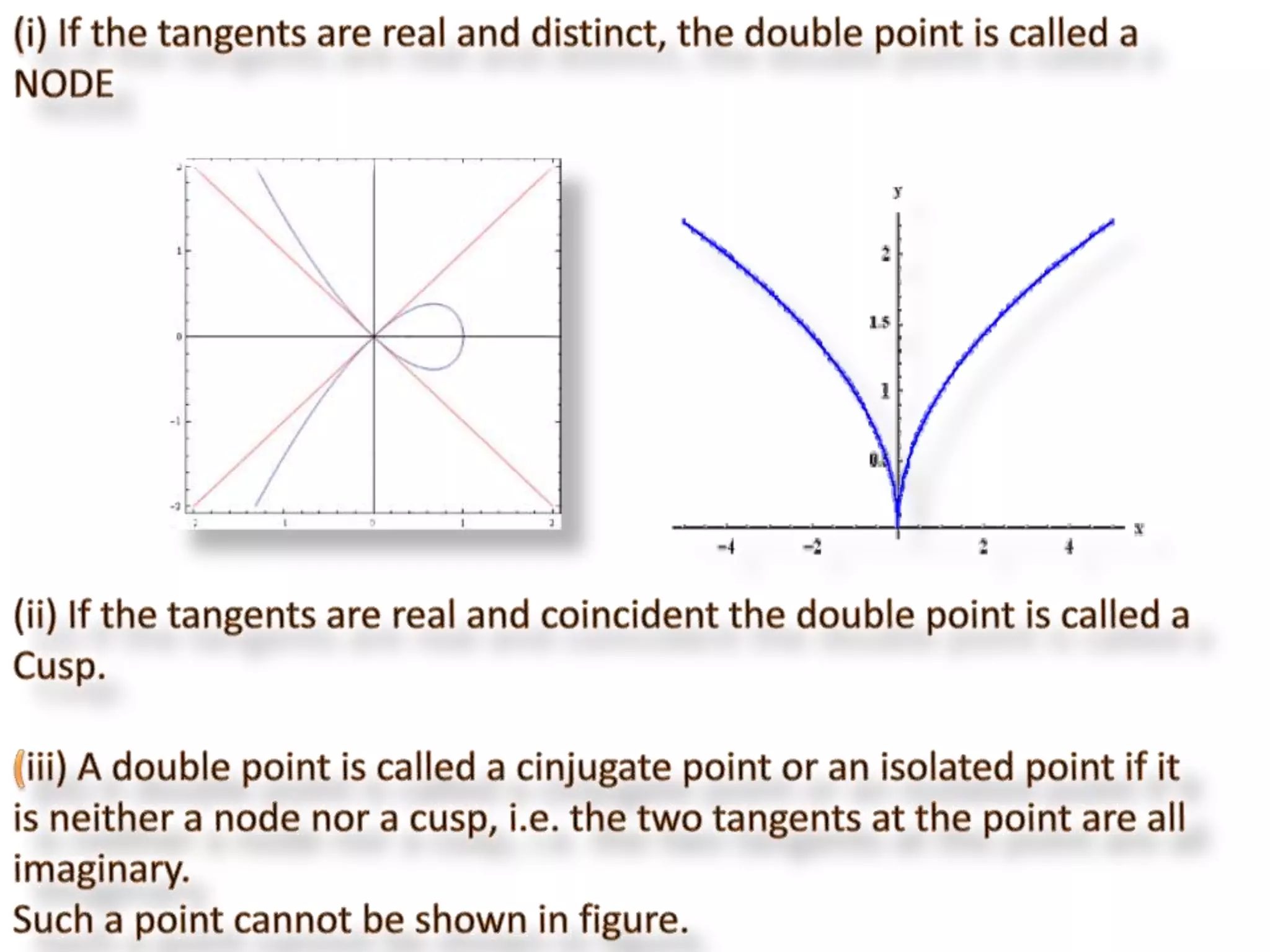
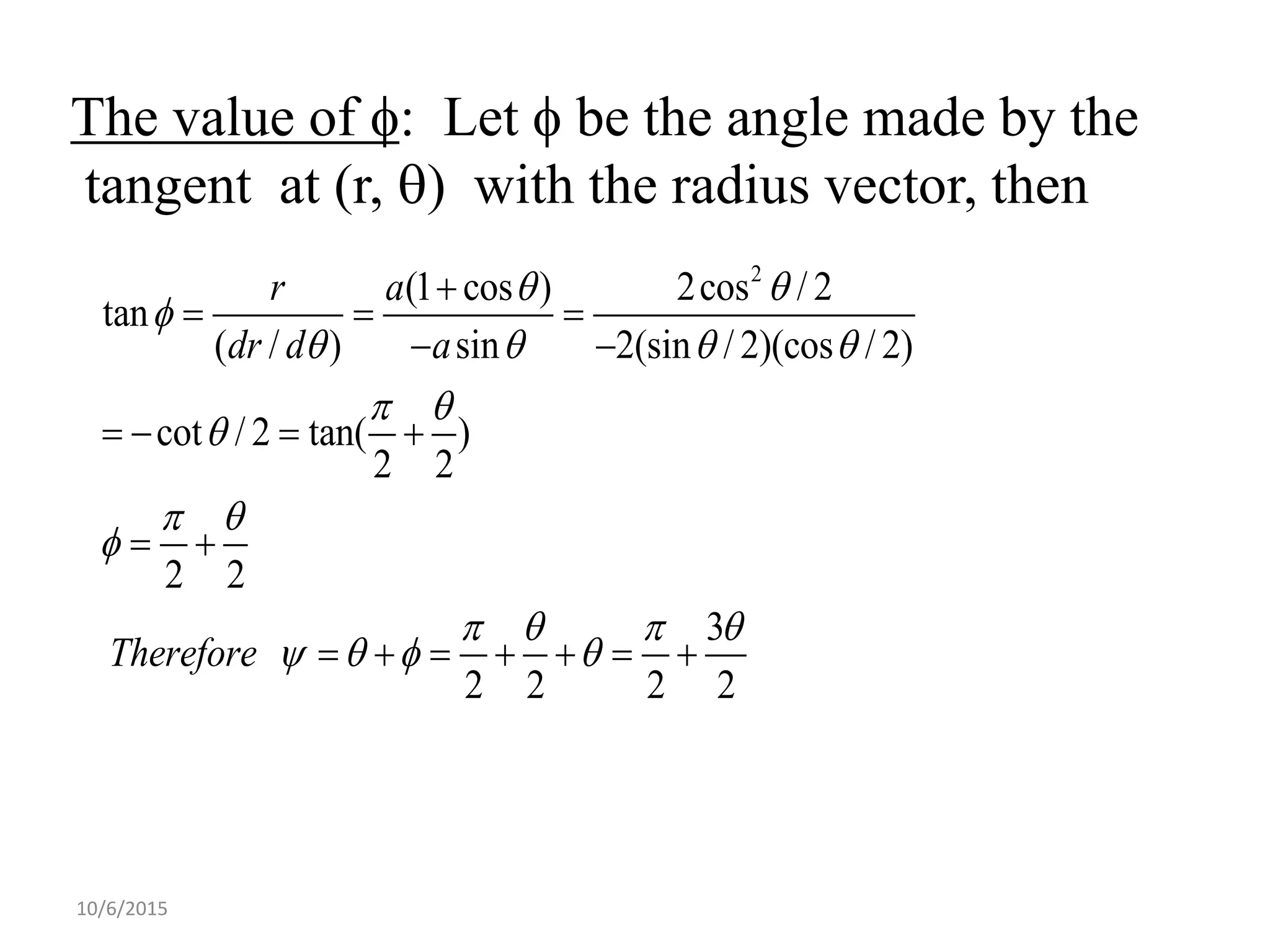
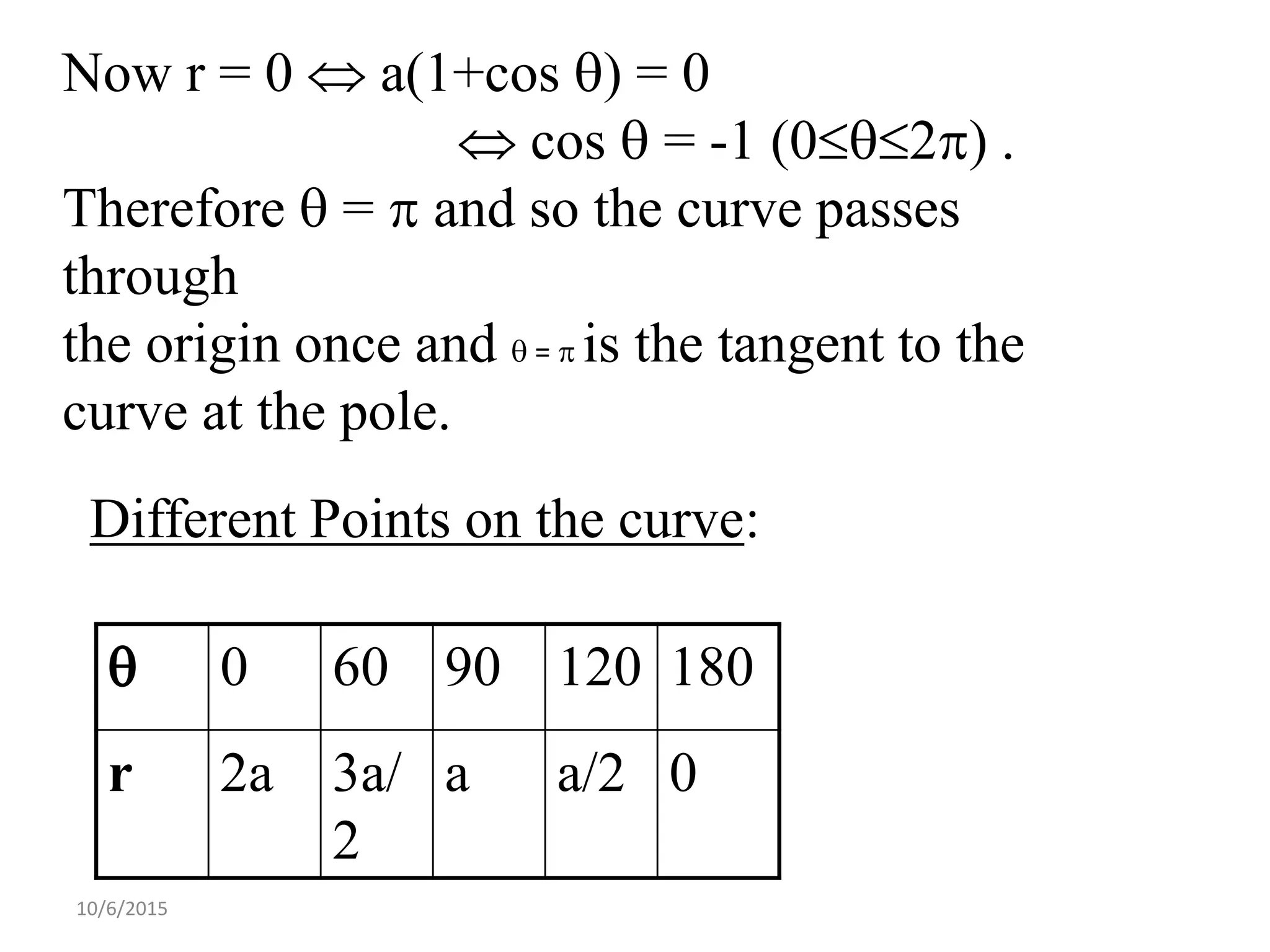
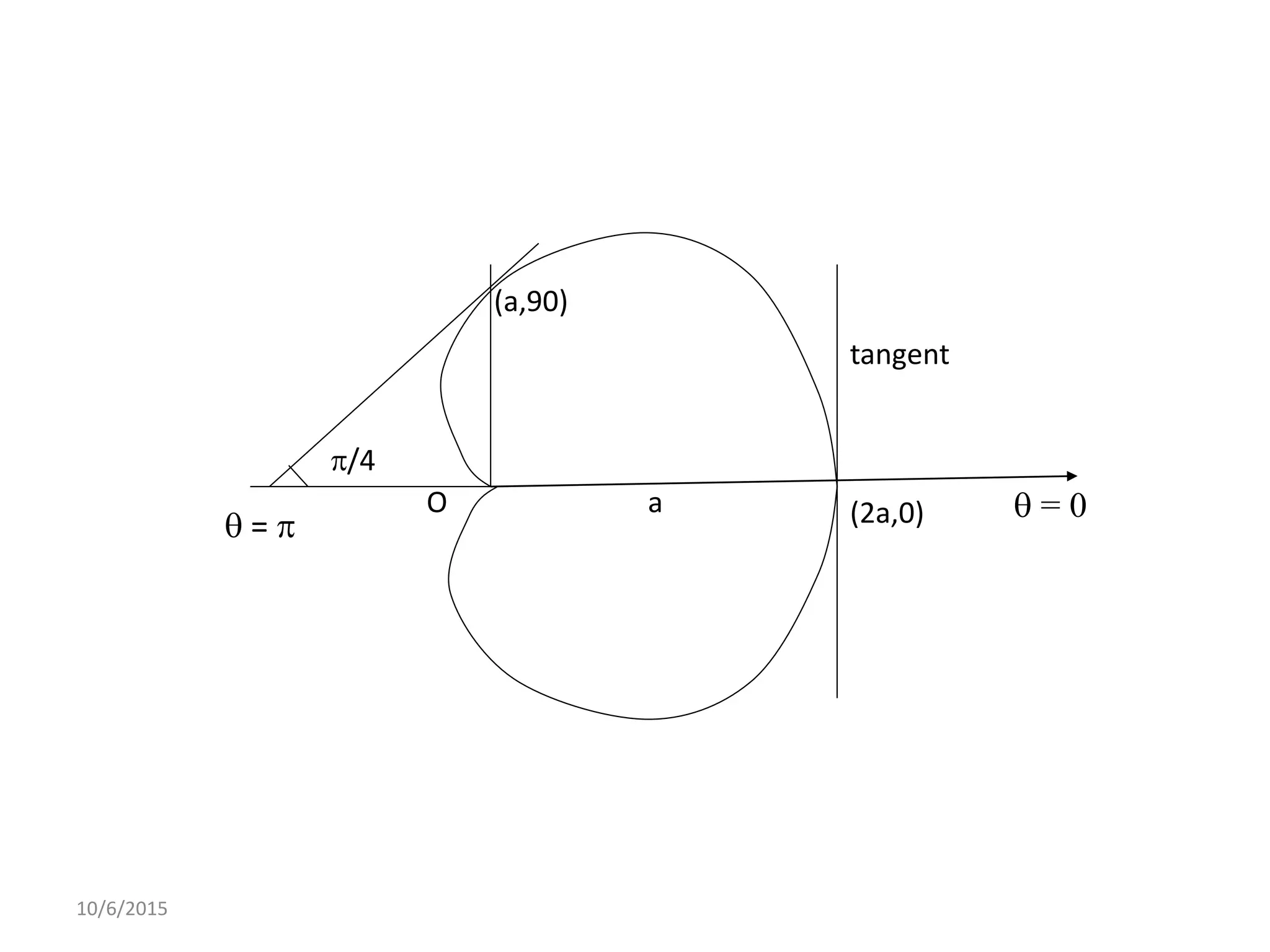
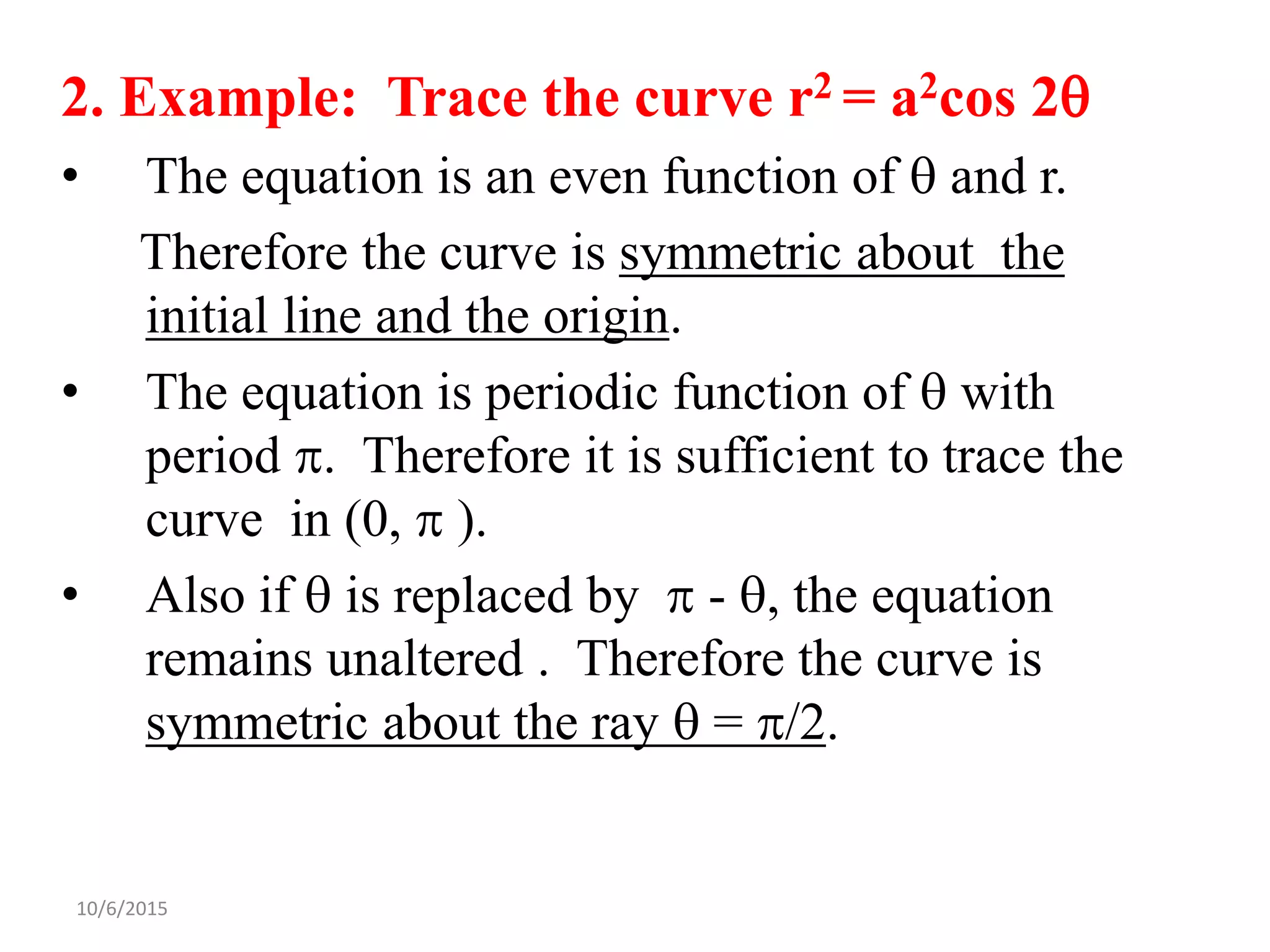
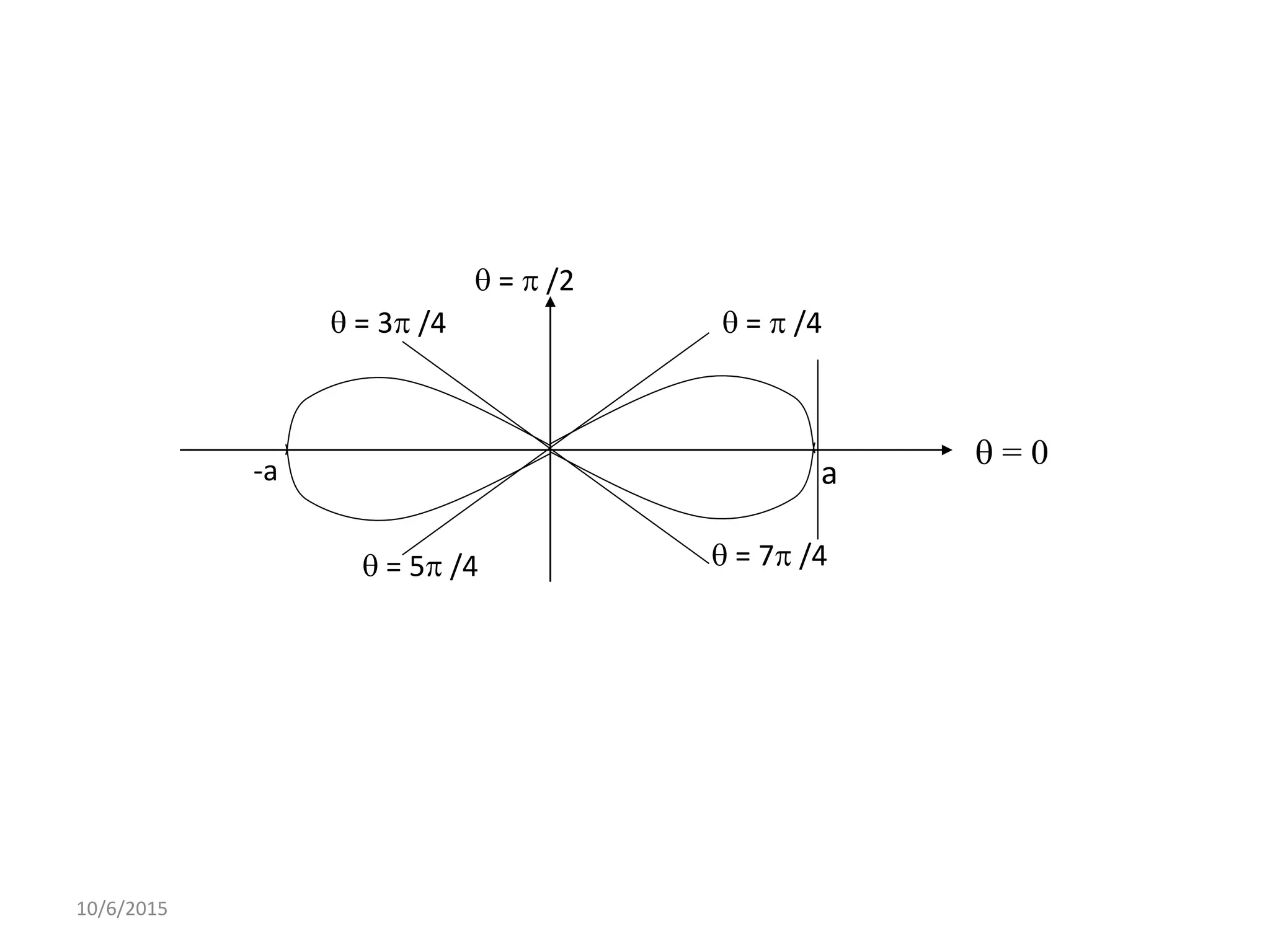
This document discusses procedures for tracing polar curves. It explains how to determine symmetry properties, the region over which the curve is defined, tabulation of points, finding the angle between the radius vector and tangent, and identifying asymptotes. Two examples are provided to demonstrate the tracing process. The first example traces the curve r=a(1+cosθ) and finds it is symmetric about the initial line, lies within a circle, and passes through the origin. The second example traces r2=a2cos2θ, finding its symmetries and that the curve exists between 0<θ<π/4 and 3π/4<θ<π.