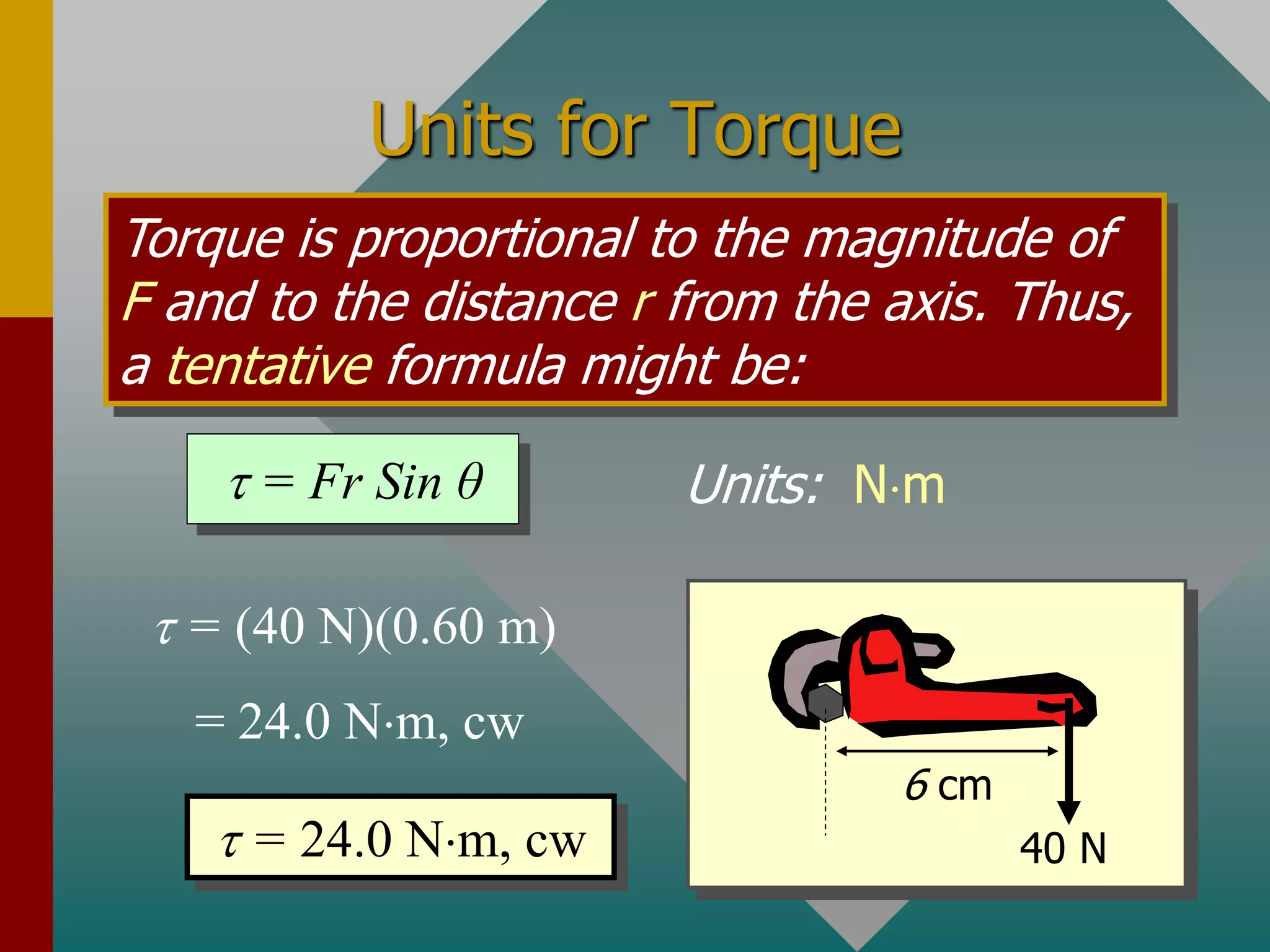
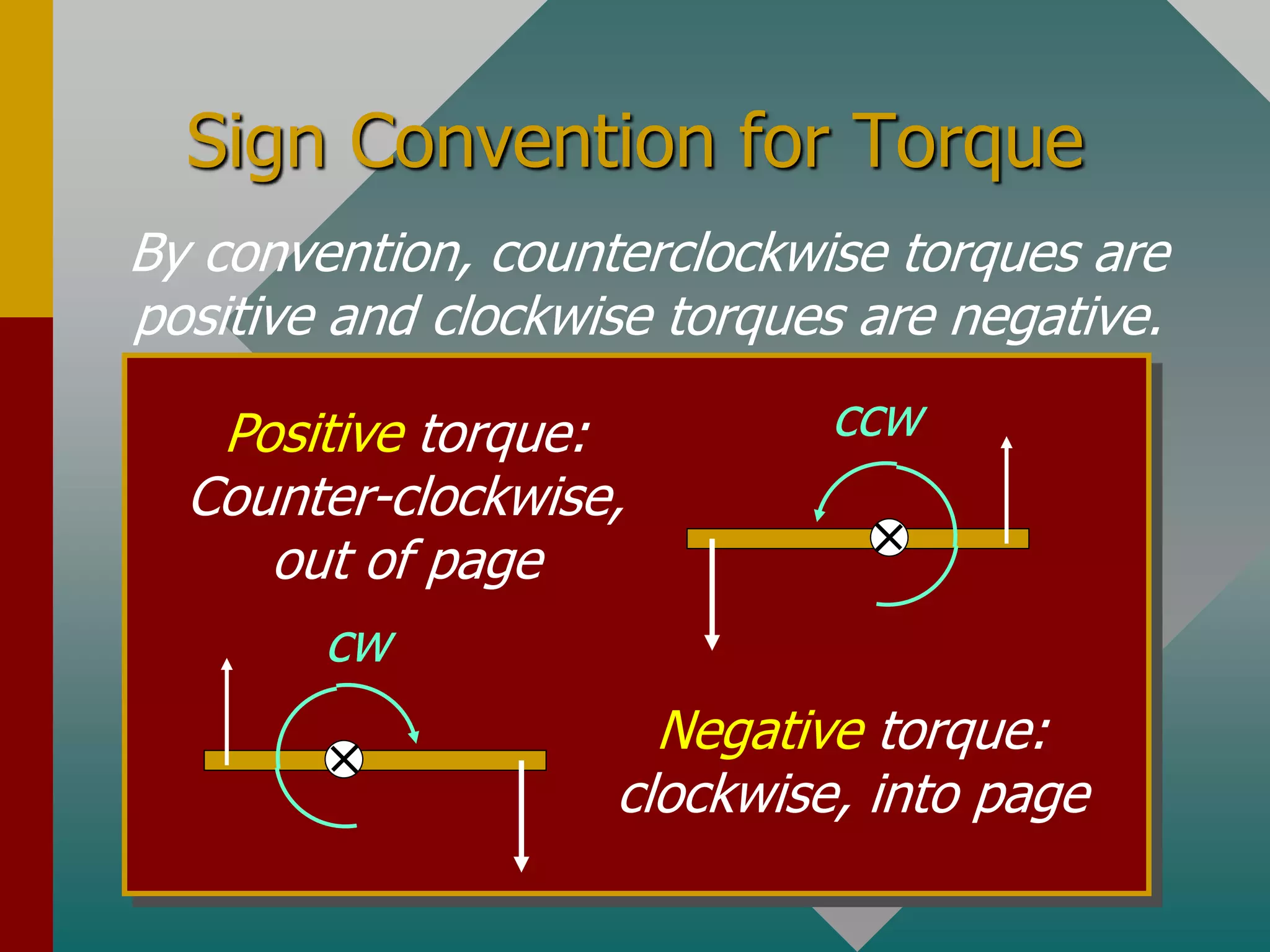
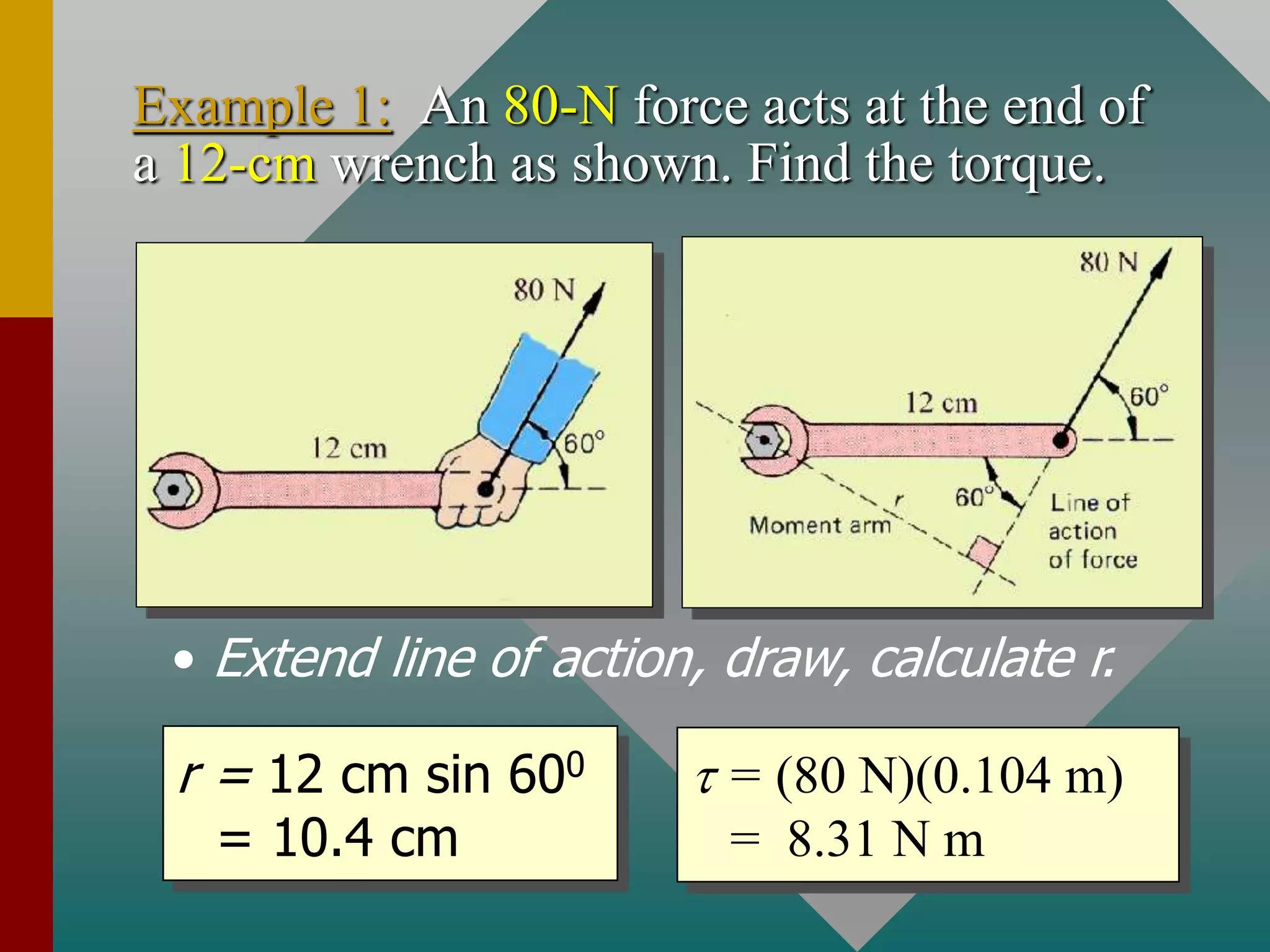
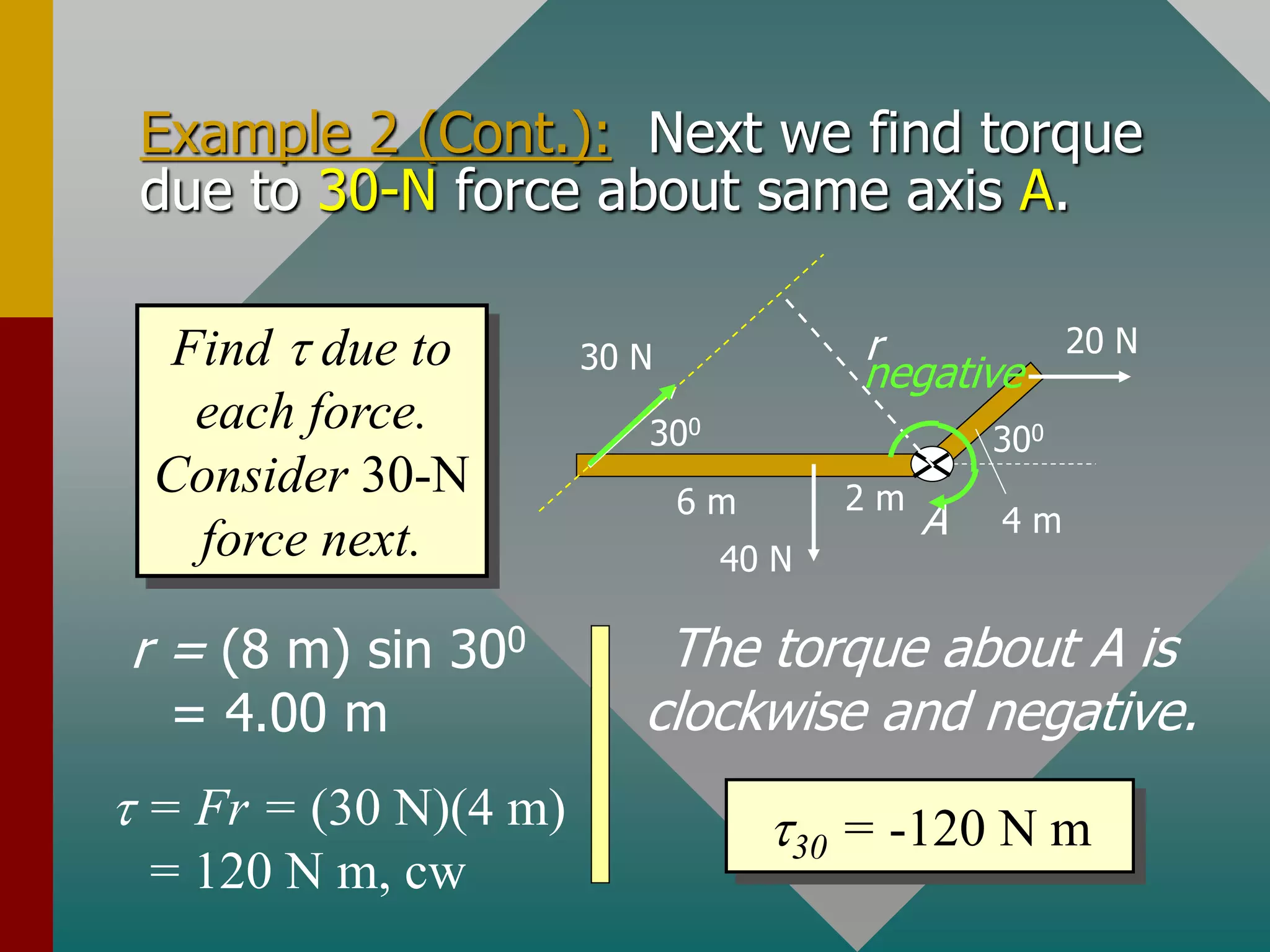
Torque is a measure of the tendency to cause rotation and is determined by three factors: the magnitude of an applied force, the direction of the force, and the location where the force is applied. Torque is calculated as the product of the force and the perpendicular distance from the axis of rotation, known as the moment arm. Newton's second law of motion can be applied to rotational systems by considering torque as the rotational analogue of force and angular acceleration as the rotational analogue of linear acceleration. The rotational inertia, which depends on the mass and how it is distributed relative to the axis of rotation, determines how difficult it is to change an object's rotational motion and is analogous to linear mass.