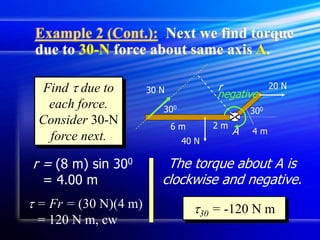
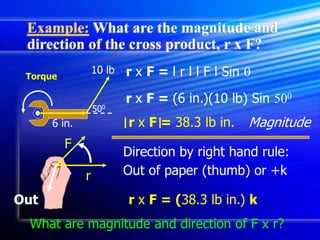
Torque is a twist or rotation produced by a force. It is calculated by multiplying the force by the perpendicular distance (moment arm) from the line of action of the force to the axis of rotation. Torque can be found using the cross product of the force and position vectors. The direction of the torque is given by the right-hand rule. The resultant torque is calculated by finding the individual torques of each force and taking their sum, with clockwise torques having a negative sign and counterclockwise torques having a positive sign.