Embed presentation
Download to read offline
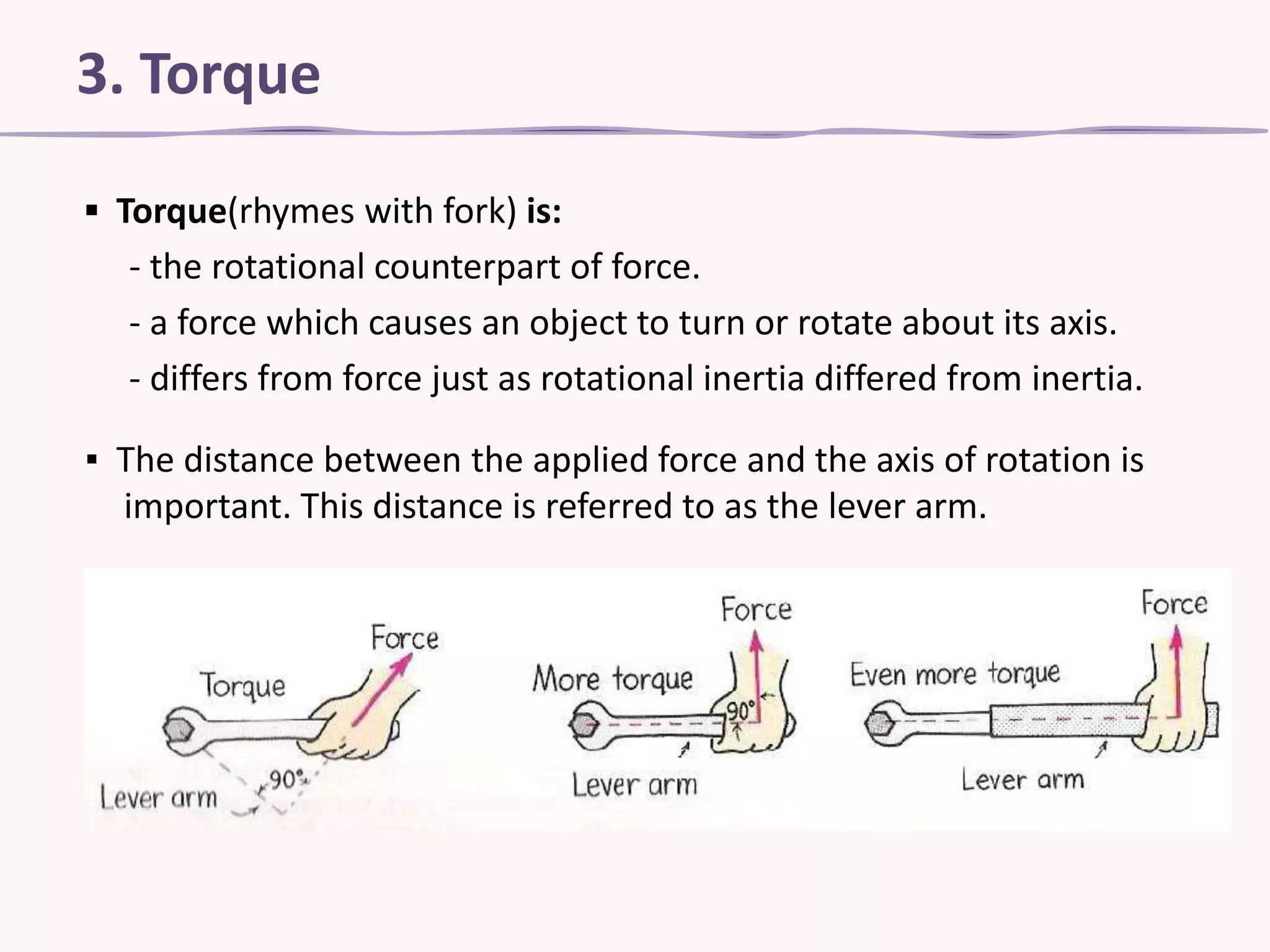
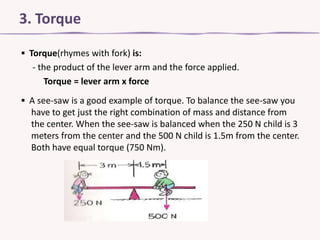


Torque is the rotational counterpart of force that causes an object to rotate about its axis. Torque is calculated as the product of the lever arm, or distance from the axis of rotation, and the applied force. A seesaw provides an example where balancing requires the right combination of mass and distance from the center to equalize the torque. Torque is calculated in the example of a 500 Newton force applied to a 25 cm wrench at a right angle, yielding a torque of 125 Newton-meters.


