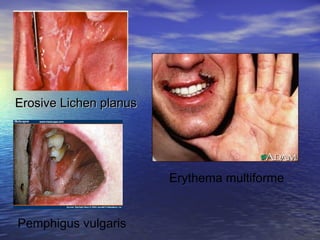
This document discusses topical keratolytics and topical steroids. It defines keratolytics as drugs that cause mild peeling of the skin or mucous membrane when applied locally by removing the pathologic desquamated keratin layer. Common keratolytics include salicylic acid, urea, benzoyl peroxide, and tretinoin. Topical steroids are defined as medicines used to treat skin conditions like eczema and psoriasis. They are anti-inflammatory and immunosuppressive. Common indications for topical steroids include recurrent aphthous ulcers, Behcet's syndrome, and pemphigus vulgaris. Potent topical steroids like bet