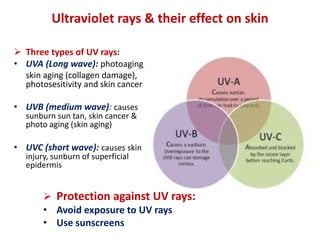
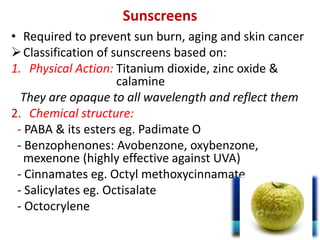
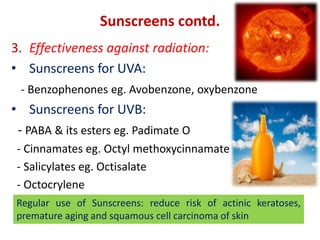
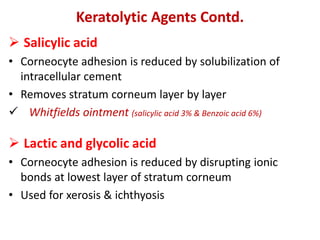
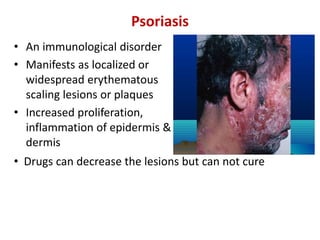
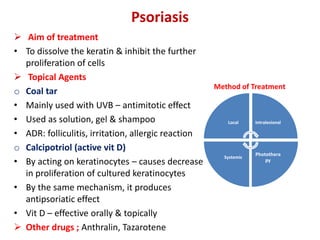
This document provides information on the structure and function of skin, treatment of various skin disorders, and drugs used for different skin conditions. It discusses:
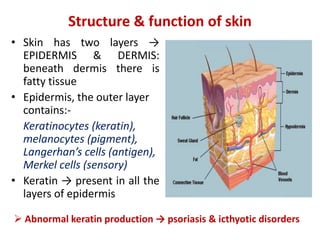
- The structure of the epidermis and dermis layers of skin and their functions.
- Topical, systemic, and other modes of treating skin disorders.
- Factors affecting absorption of topical drugs and examples of transdermal patches.
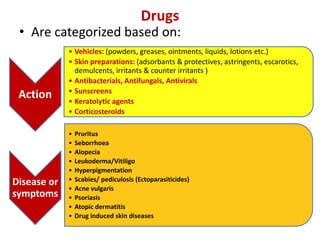
- Classes of drugs categorized by action, vehicles, and skin preparations.
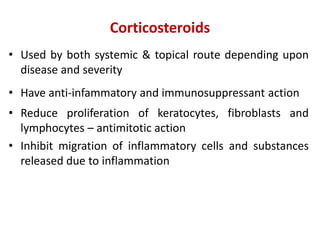
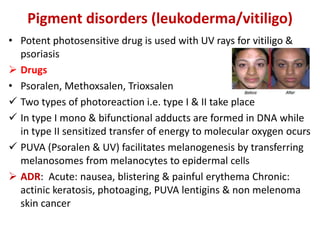
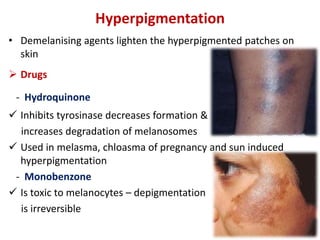
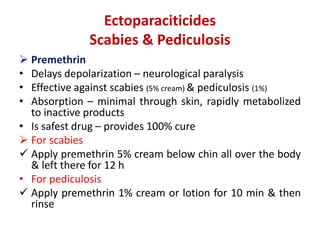
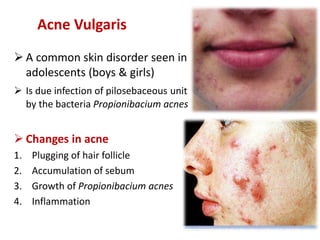
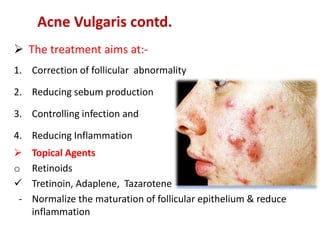
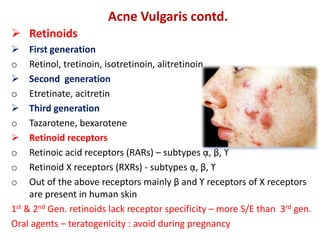
- Specific drugs and classes used to treat conditions like pruritus, seborrhea, alopecia, pigment disorders, ectoparasitic infections, acne, and others.