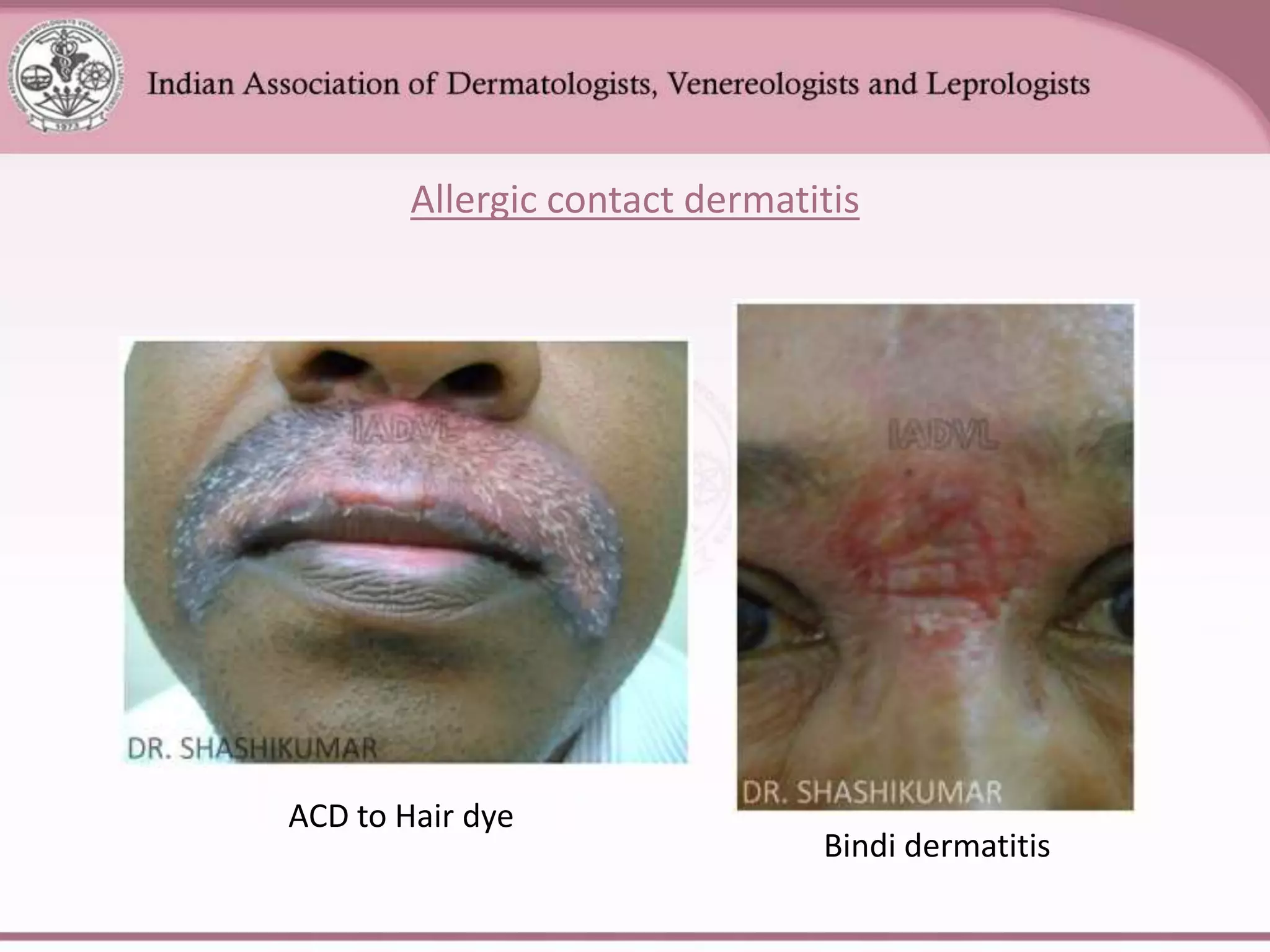
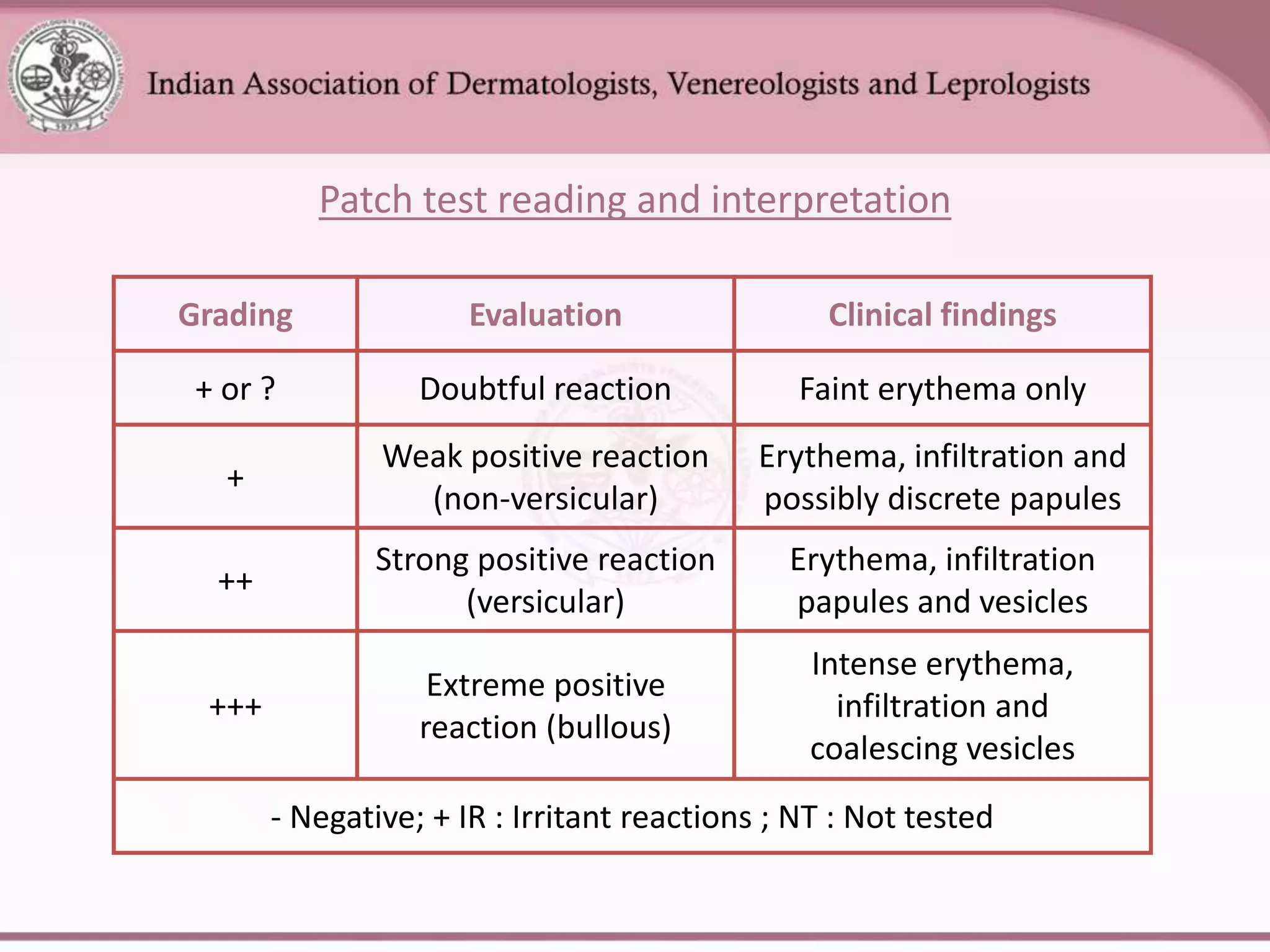
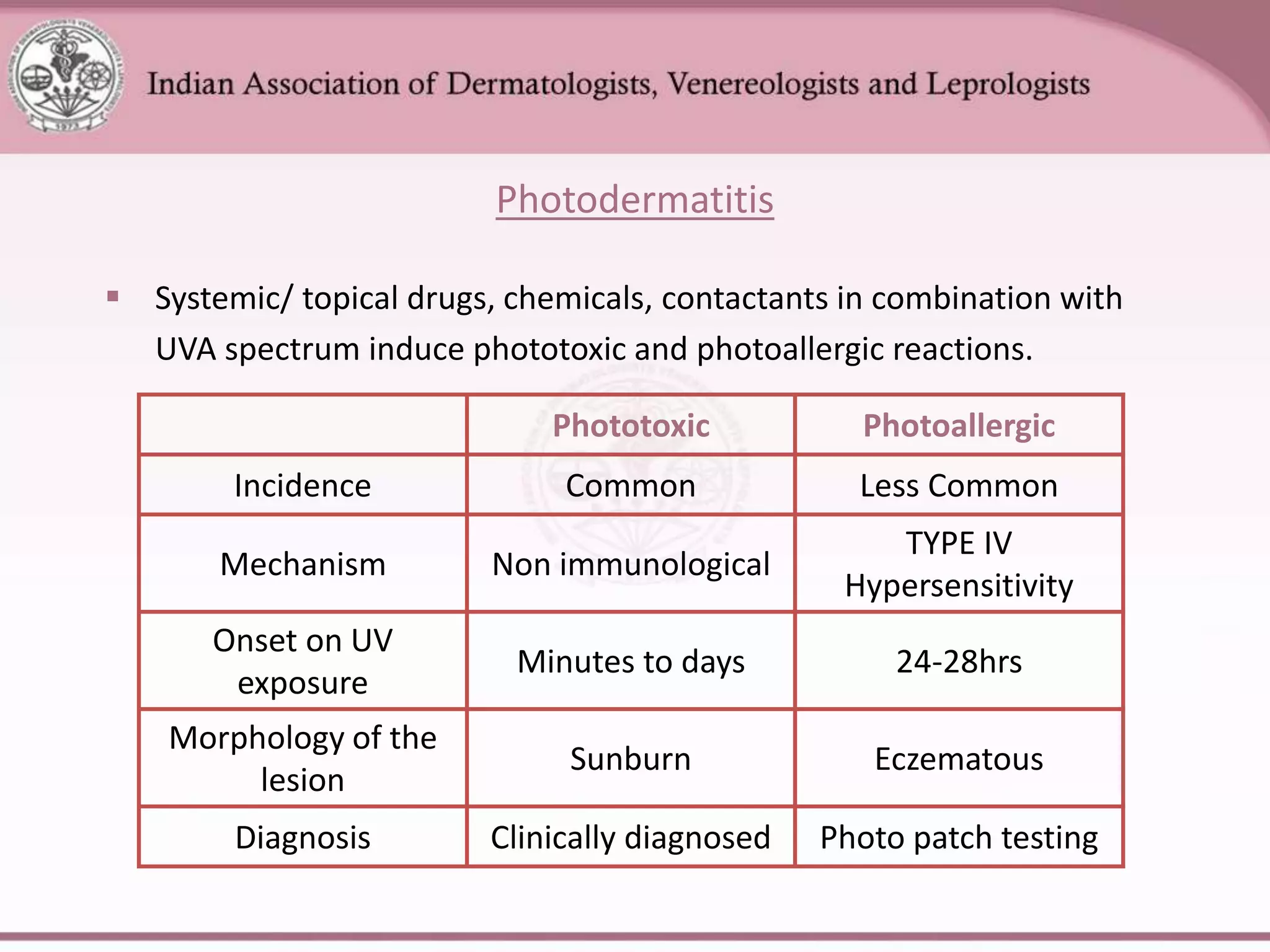
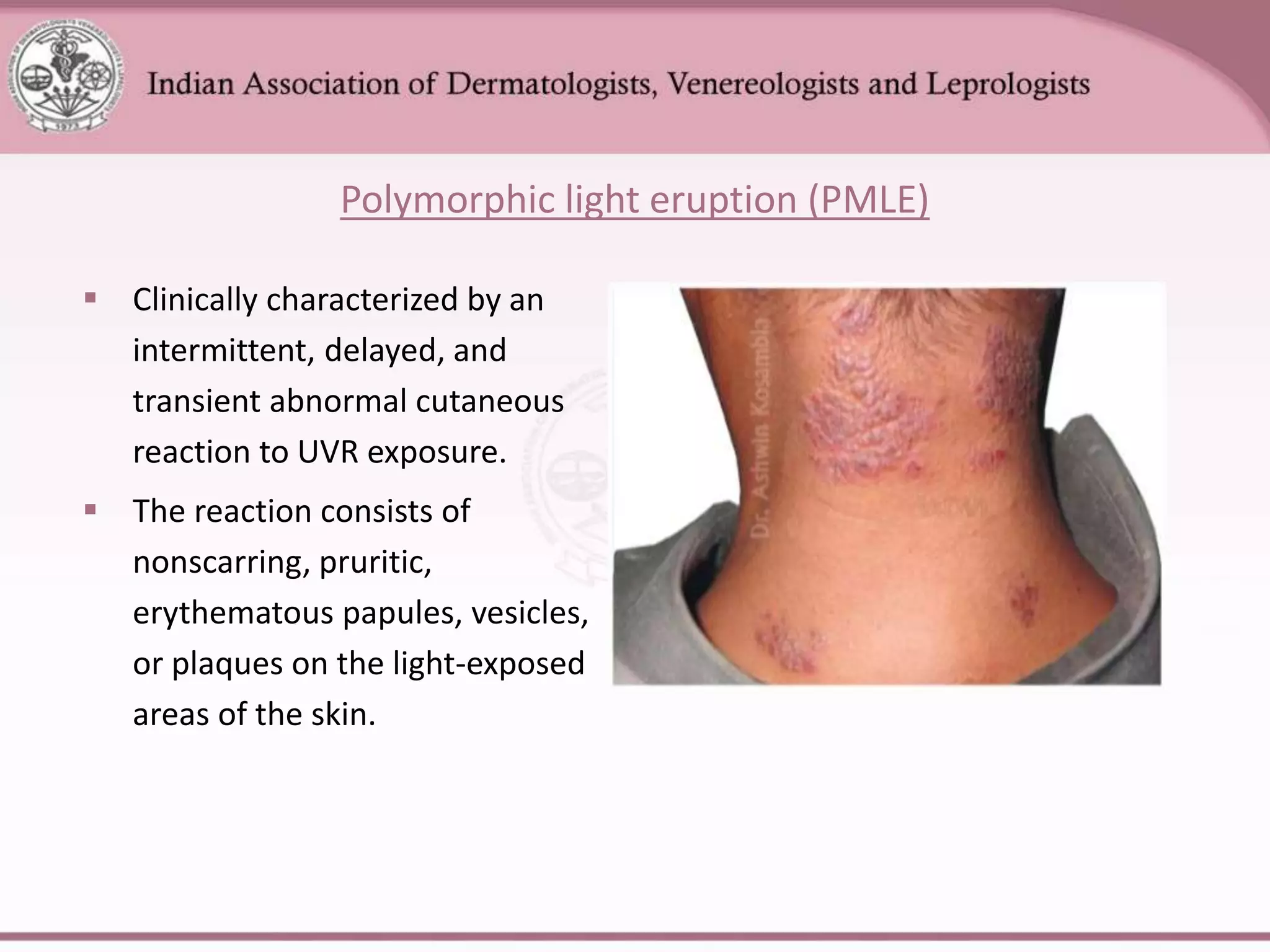
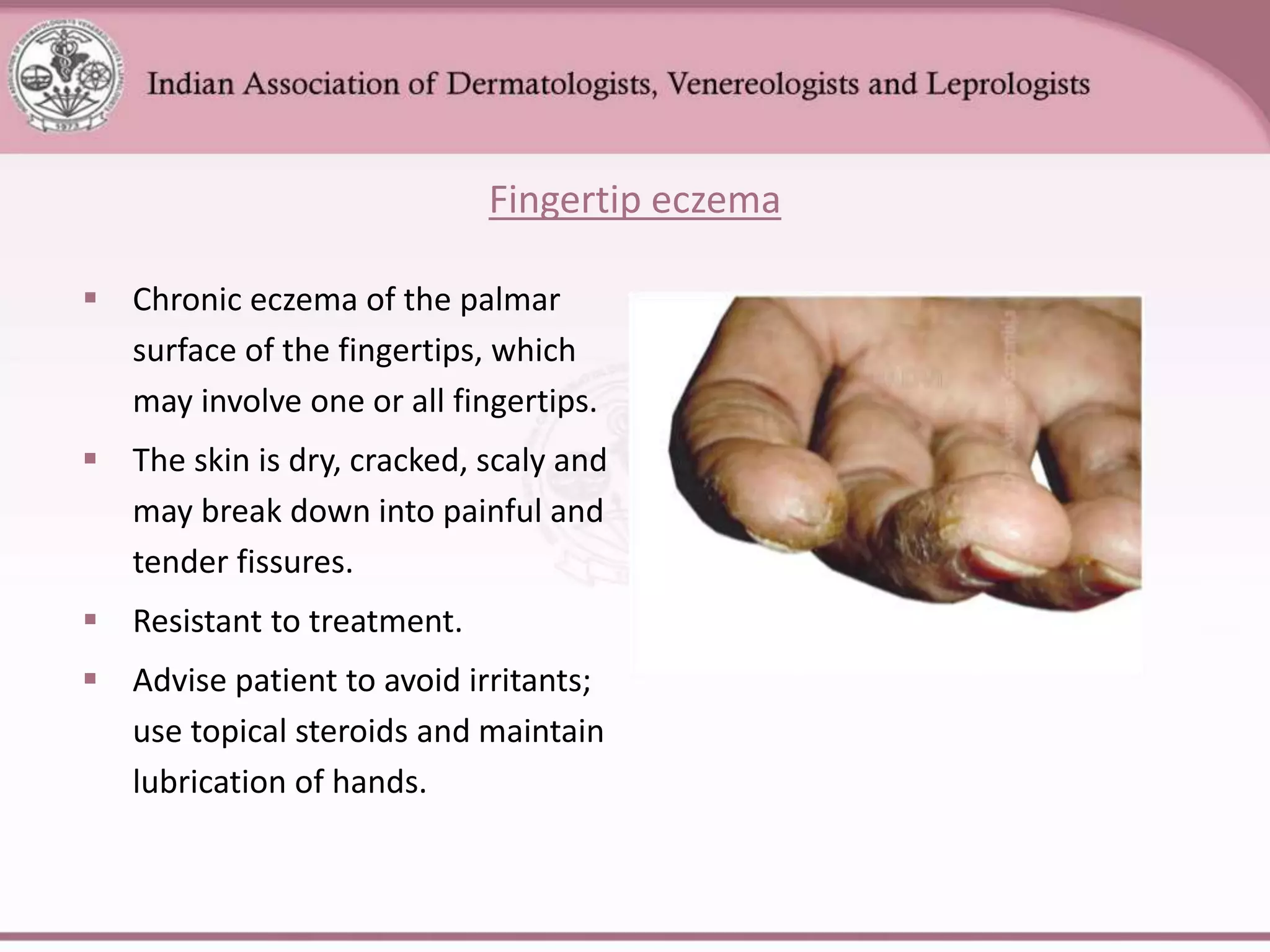
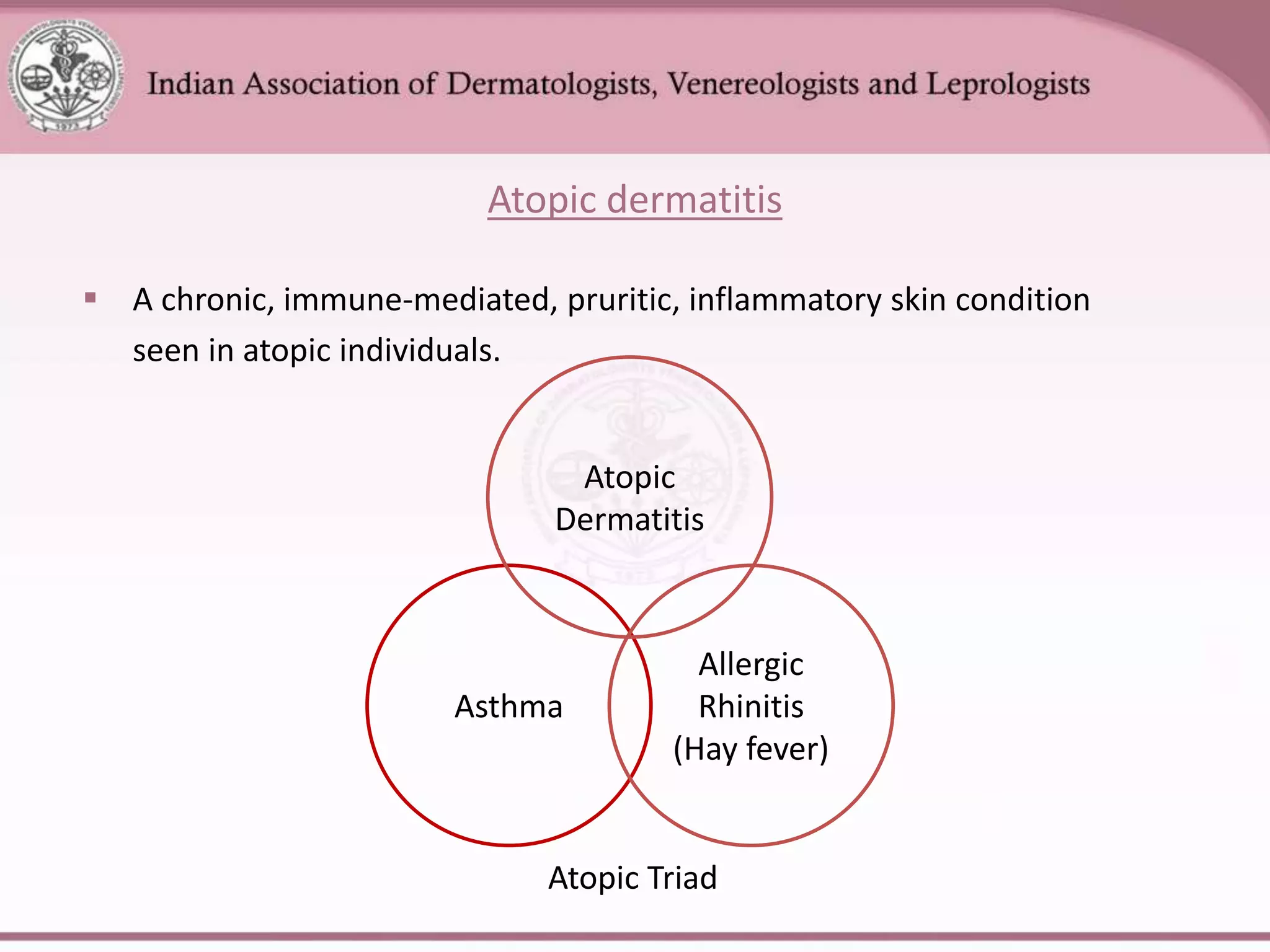
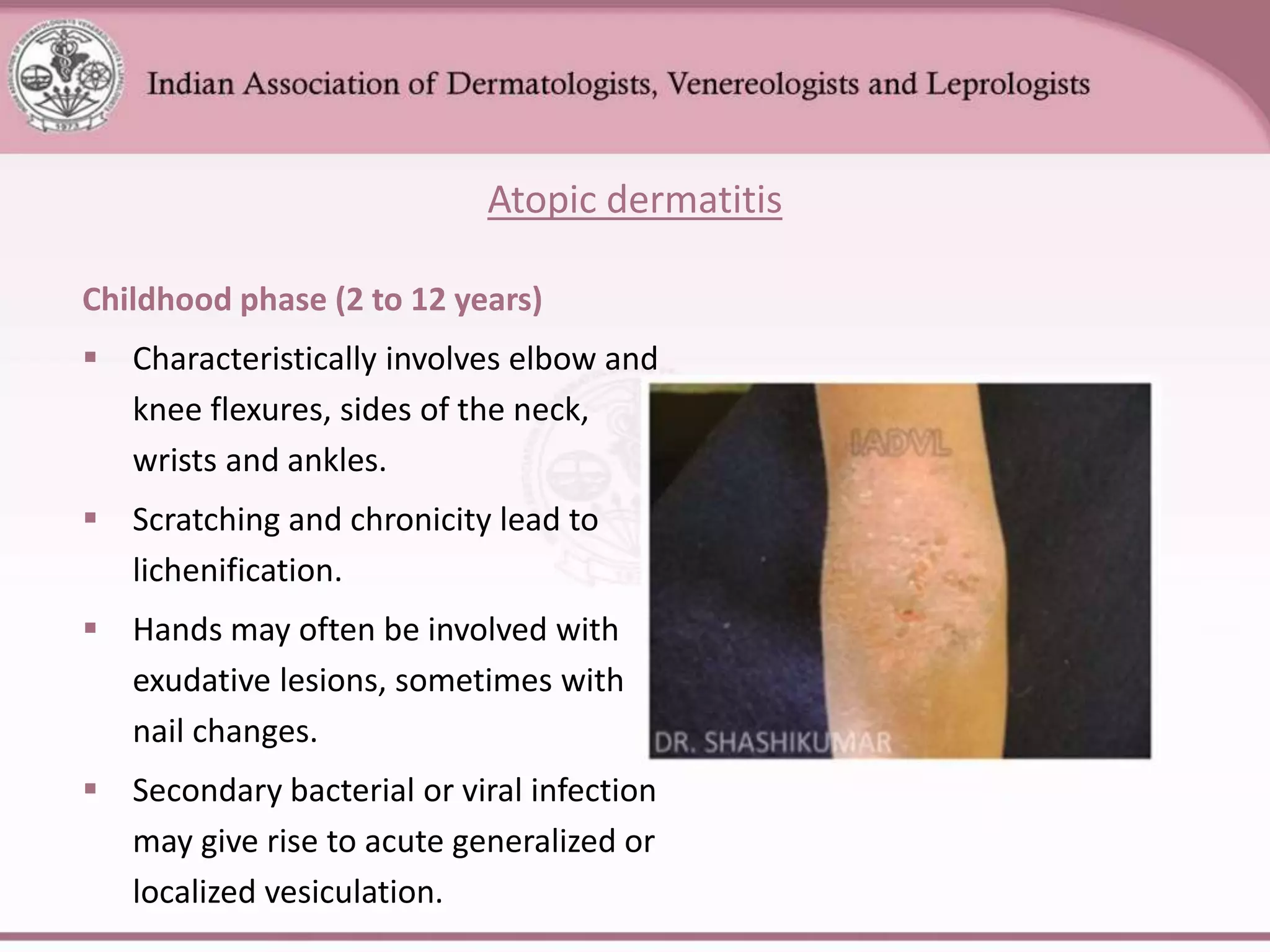
This document provides an overview of eczema (dermatitis), including its classification into exogenous and endogenous types. Exogenous eczemas have an identifiable external cause, like irritant contact dermatitis from exposure to chemicals or allergic contact dermatitis from skin allergens. Endogenous eczemas have an internal cause, such as atopic dermatitis which is associated with the atopic triad of asthma, allergic rhinitis, and eczema. The document describes the clinical stages of eczema and various types like hand eczema, photodermatitis, and pompholyx. Diagnostic methods like patch testing are also summarized.