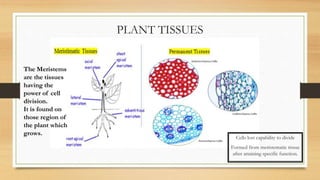
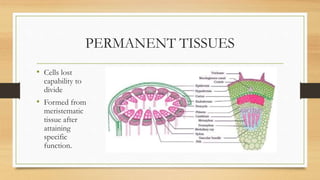
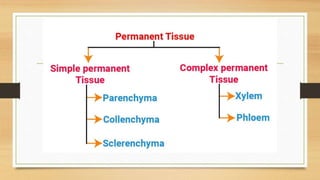
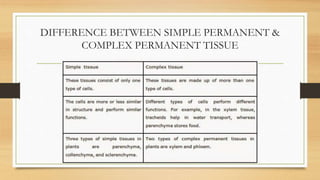
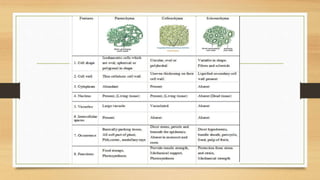
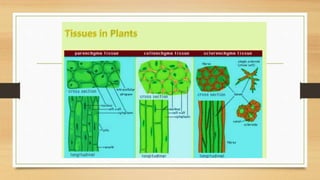
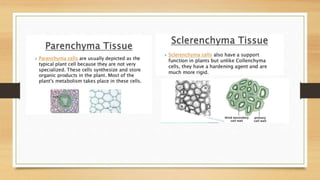
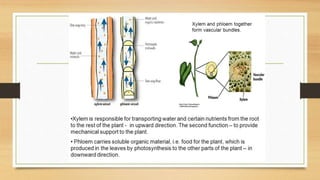
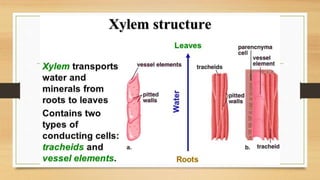
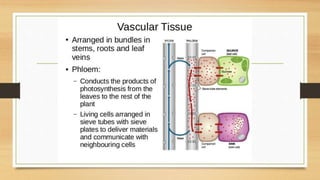
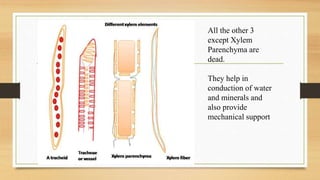
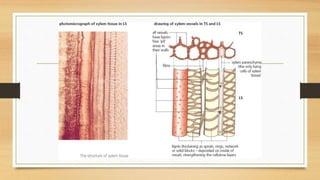
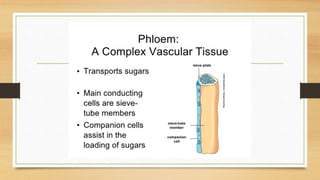
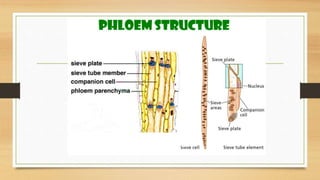
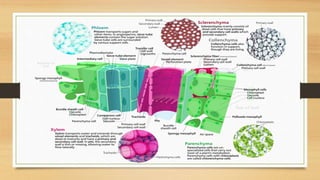
The document introduces the concept of tissues, defined as groups of similar cells, with histology as the study of tissues. It elaborates on the differences between plant and animal tissues, focusing on meristematic and permanent tissues in plants, including types of meristematic tissues and their functions. Additionally, it describes the characteristics of simple and complex permanent tissues, specifically xylem and phloem.