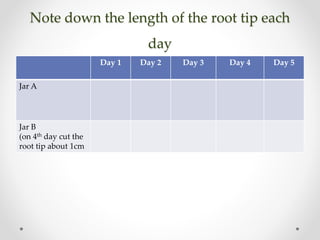
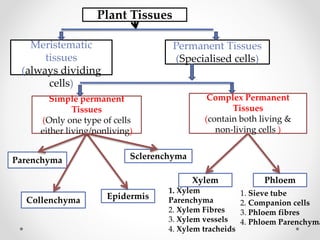
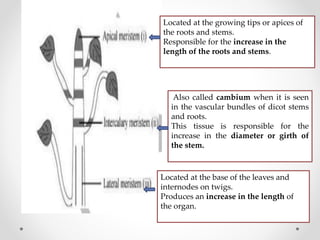
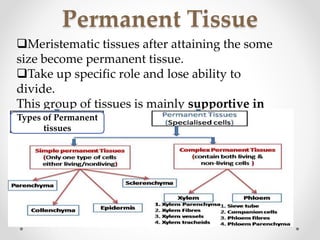
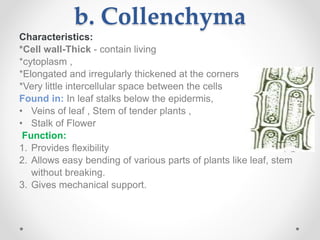
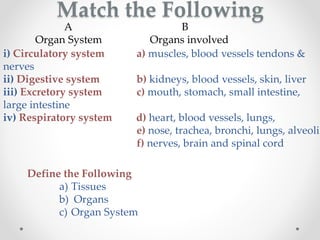
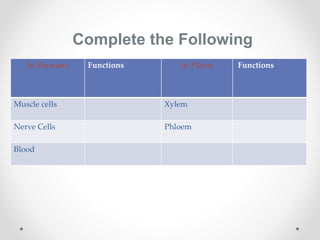
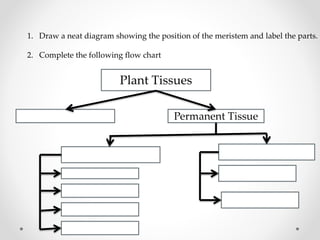
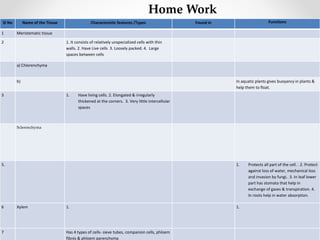
This document discusses plant tissues. It begins by explaining that multicellular organisms are made of tissues, organs, and organ systems. The key tissues discussed are meristematic tissues, which allow growth, and permanent tissues, which are specialized. Permanent tissues include simple tissues like parenchyma, collenchyma, and sclerenchyma, as well as complex vascular tissues like xylem and phloem, which transport water and nutrients. The document provides details on the characteristics, location, and functions of each type of tissue.