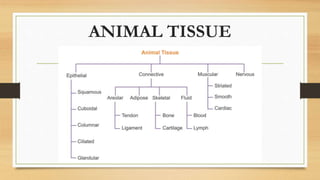
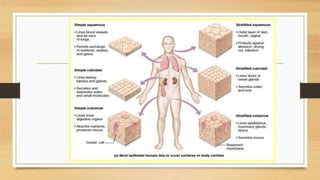
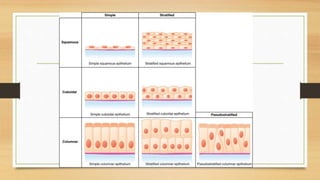
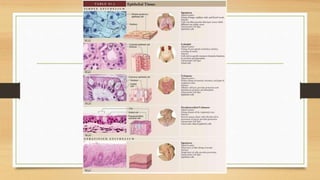
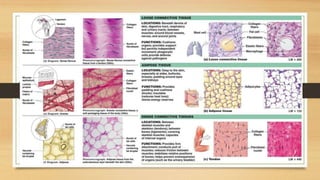
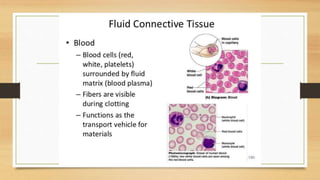
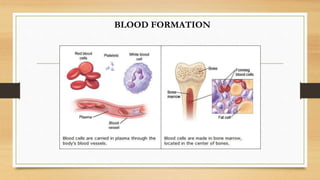
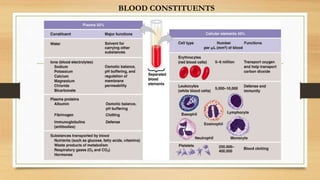
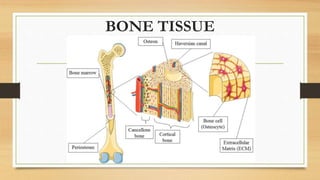
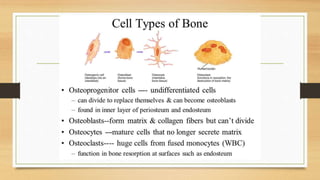
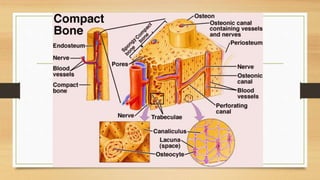
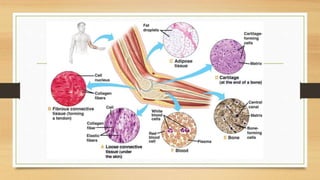
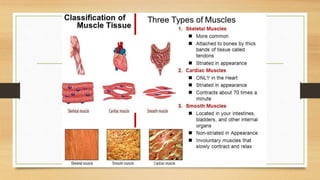
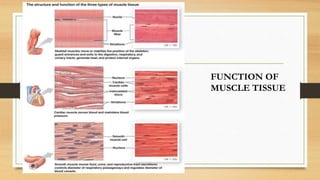
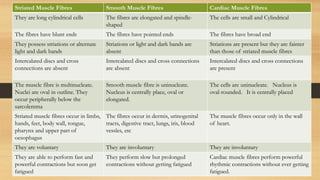
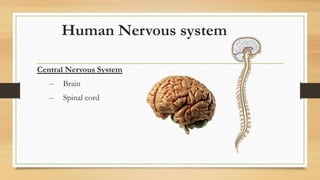
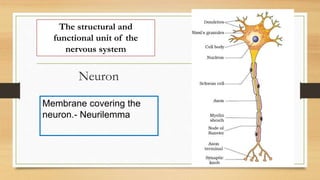
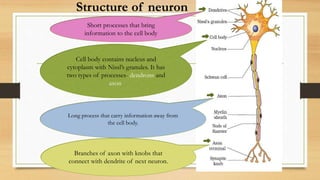
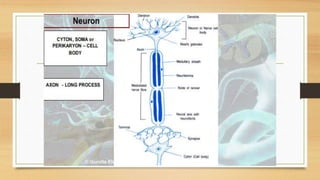
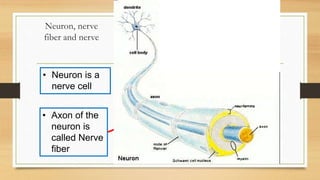
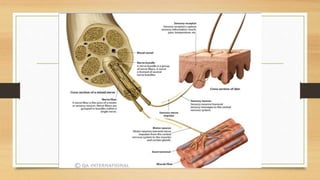
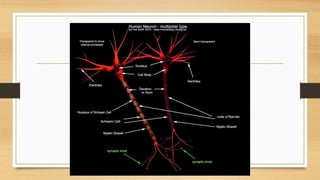
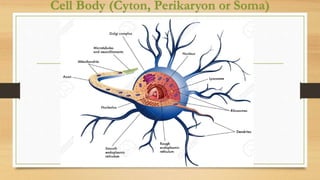
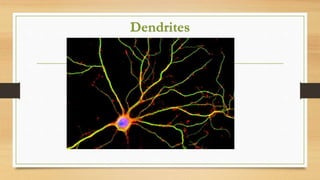
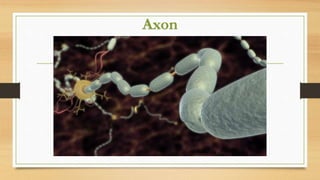
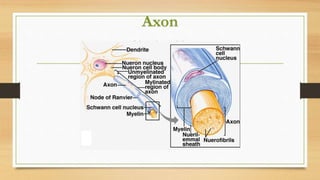
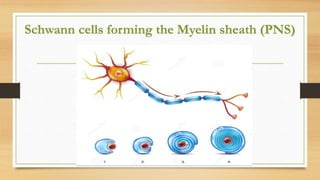
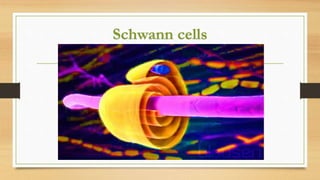
The document discusses various types of animal tissues, including epithelial, connective, muscular, and nervous tissues. It highlights the characteristics and functions of different muscle types (striated, smooth, cardiac) and the structure of neurons in the nervous system. Key features such as muscle fiber characteristics, neuron's structure, and the roles of different cells in both muscle and nervous tissues are detailed.