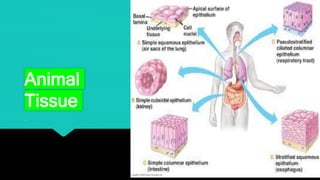
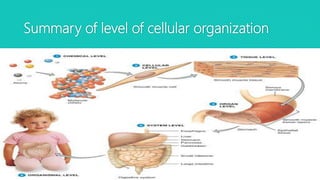
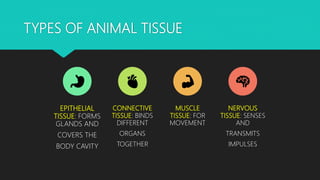
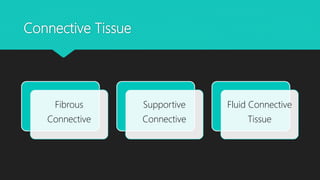
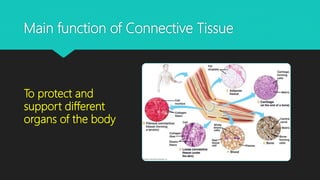
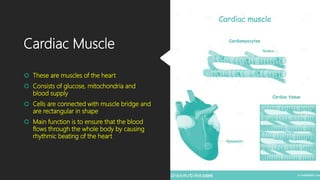
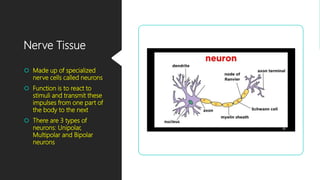
The document discusses the different types of tissues in animals. It begins by explaining that a zygote differentiates into various tissues after fertilization. There are four main types of tissues - epithelial, connective, muscle and nervous tissue. Epithelial tissue covers the body and lines organs, connective tissue binds and supports other tissues, muscle tissue enables movement, and nervous tissue senses the environment and transmits signals. Each tissue is then further defined by its constituent cell types and functions.









![References
Dhital, M., 2019. Slideshare: Animal Tissue Notes. [Online]
Available at: https://www.slideshare.net/ManojDhital2/animal-tissue-notes?qid=4a11fc37-e168-472c-b092-f10724c731ae&v=&b=&from_search=1
[Accessed 14 August 2020].
Majumder, B., 2014. Slideshare: Animal Tissues. [Online]
Available at: https://www.slideshare.net/BiswarupMajumder/animal-tissues-100417056?qid=4a11fc37-e168-472c-b092-f10724c731ae&v=&b=&from_search=19
[Accessed 16 August 2020].
Motsoko, E., 2018. Slideshare. [Online]
Available at: https://www.slideshare.net/MOYAHABOMOTSOKO/unit-4-animal-tissue-111742232?qid=4a11fc37-e168-472c-b092-f10724c731ae&v=&b=&from_search=7
[Accessed 16 August 2020].
Piston, V. J., 2013. Animal Tissue. [Online]
Available at: https://www.slideshare.net/vieljoypiston/animal-tissue-by-viel-joy-piston?qid=4a11fc37-e168-472c-b092-f10724c731ae&v=&b=&from_search=5
[Accessed 17 July 2020].
Rana, J., 2015. Slideshare: Animal Tissue PPT by Jasveer Rana. [Online]
Available at: https://www.slideshare.net/jasveerrana79/animal-tissue-ppt-by-jasveer-rana?qid=4a11fc37-e168-472c-b092-f10724c731ae&v=&b=&from_search=10
[Accessed 16 August 2020].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/animaltissue-200930143053/85/Animal-tissue-20-320.jpg)