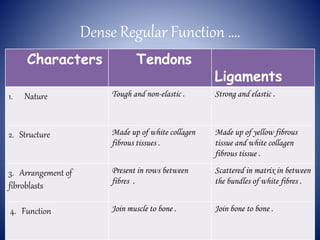
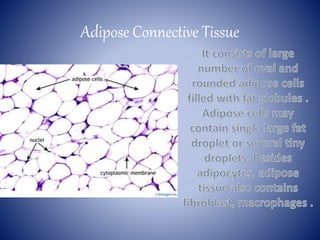
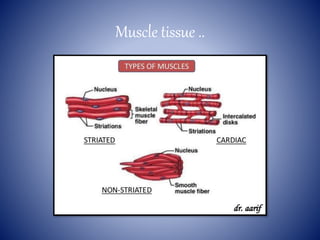
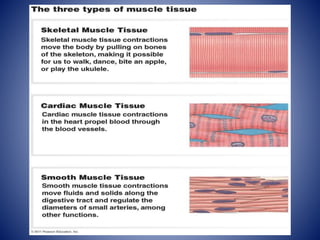
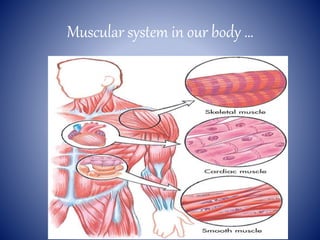
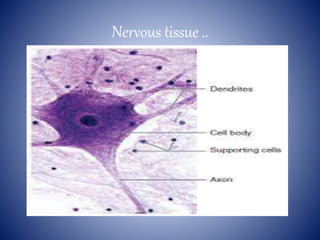
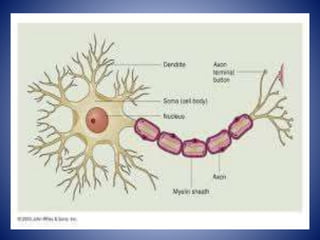
This document provides information on the four main types of animal tissues: epithelial, connective, muscular, and nervous tissues. It describes the origin, function, and examples of each tissue type. Epithelial tissues cover organs and form barriers, and come in several forms like squamous, cuboidal, and columnar. Connective tissues include areolar, dense, adipose, skeletal, and fluid tissues that provide structure, binding, storage and transport. Muscular tissues allow locomotion and movement. Nervous tissues control and coordinate functions through impulse conduction. The document contains detailed information on the classification, structure and functions of these fundamental tissue types.



![EPITHELIAL TISSUES ….
Word epithelial is composed of two words Epi –
upon , thelio – grows .[Means- A tissue which grows
upon another tissue is called EPITHELIAL] .
Nature :
1. It is the simplest tissue. It is the
protective tissue of animal ’s body.
2. It covers most organs and cavities within
the body.
3. It also form a barrier to keep different
body systems separate .
4. It always rest upon underlying connective
tissues.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bhavy-160109141032/85/tissue-4-320.jpg)
![EPEHTELIAL TISSUES continue ..
5. Epithelial cells are closely packed, so there is very little
inter-cellular space between the cells. Due to less of
intercellular space blood vessels, lymph vessels and
capallaries are unable to pierce this tissue, so blood
circulation is absent in epithelium. Hence cells depend for
their nutrients up on the underlying connective tissue.
6. At the junction of the [Epithelial tissue and connective
tissue] layer is present which is called of basement
membrane, which is formed of mucopolysaccharides and
collagen fibrils.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bhavy-160109141032/85/tissue-5-320.jpg)
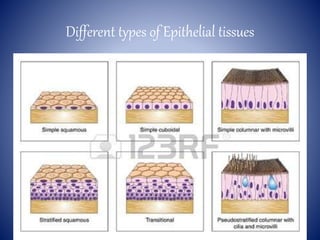
![Epithelial tissues …
STRUCTURE LOCATION FUNCTION
Simple Squamous :
Simple layer of flatened & polygonal
cells, large centrally located nucleus.
Alveoli, blood vessels heart
wall
Filtration, absorption and
secretion
Simple Cuboidal :
Single layer of cube-shaped cells,
centrally located nucleus .
Testes , Ovary, kidney tubules, salivary
duct and pancreatic ducts
Excretion, Secretion and
absorption
Simple Columnar :[non
ciliated]
Single layer of pillar shaped
cells.
Lining of stomach, small and large
intestine, digestive glands and gall
bladder .
Secretion and absorption
Simple Columnar :[ciliated
Simple layer of ciliated rectangular Oviduct, Vas deferens, few portions of Movement of gametes, and](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bhavy-160109141032/85/tissue-7-320.jpg)