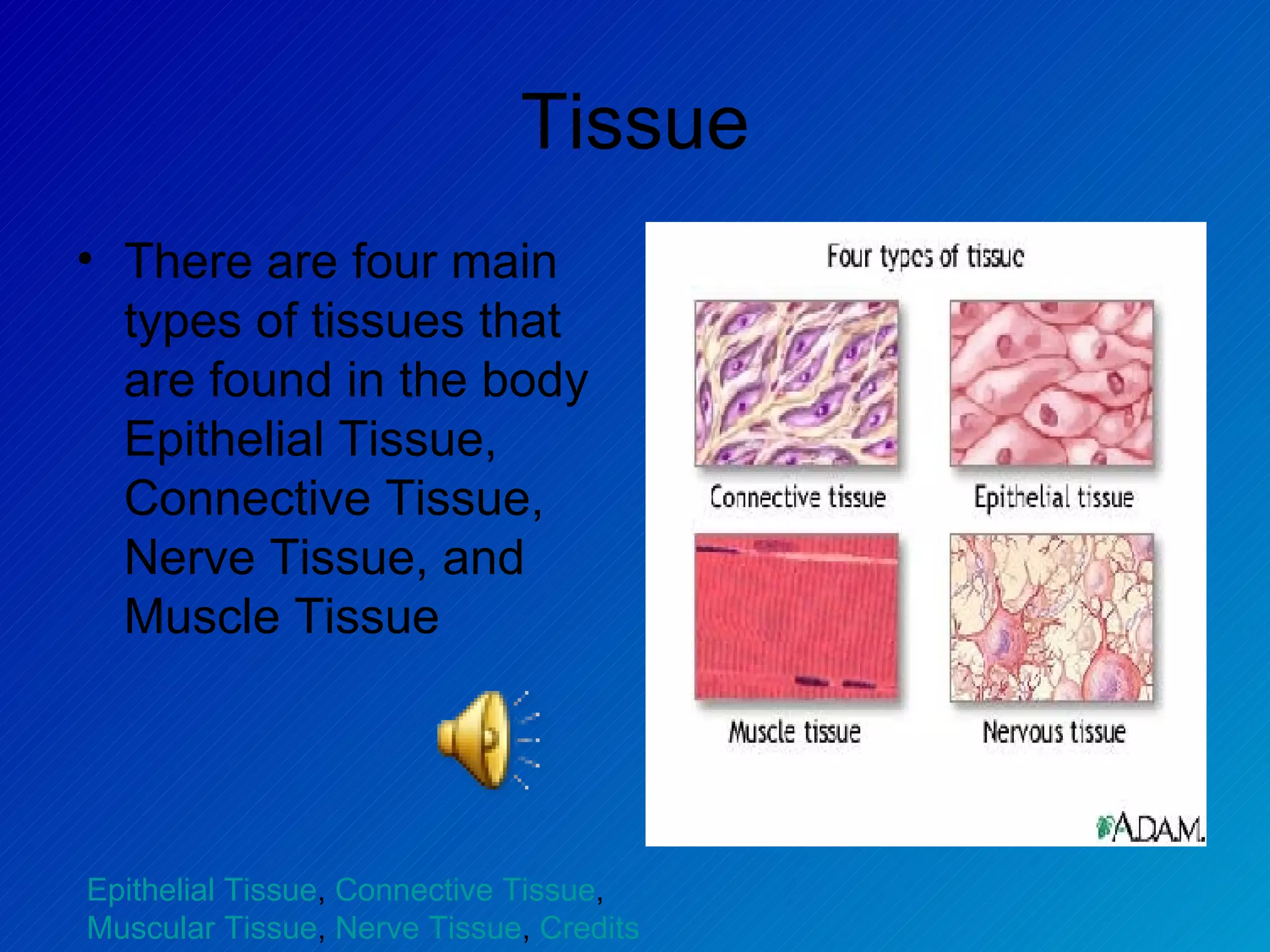
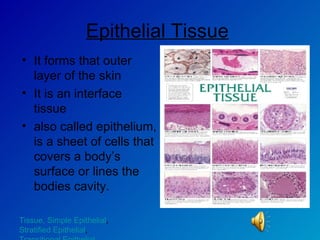
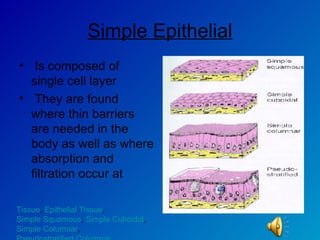
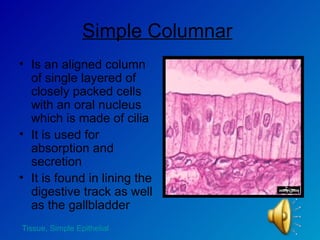
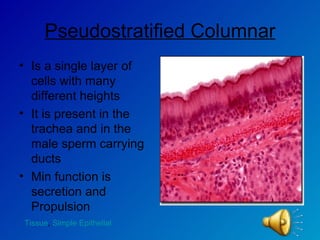
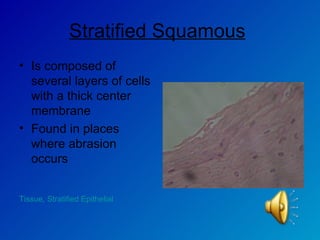
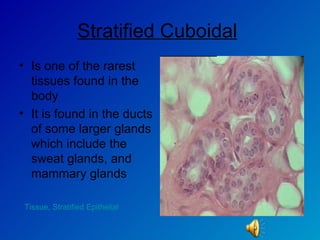
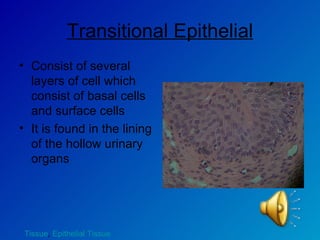
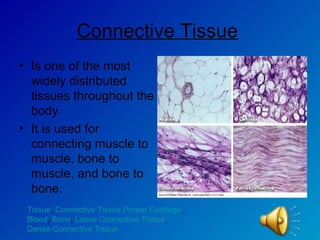
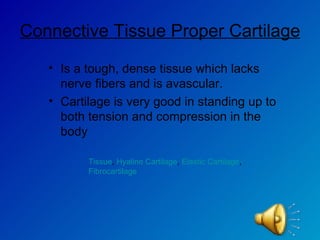
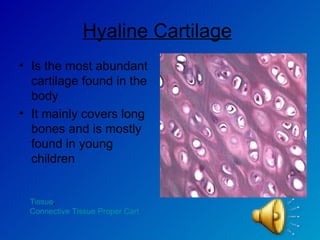
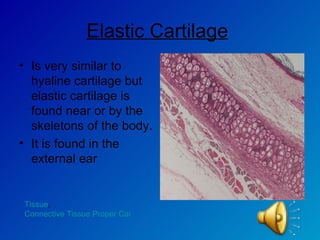
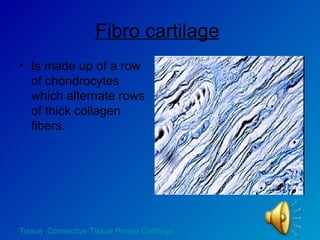
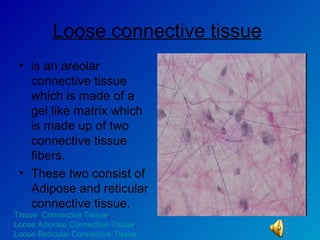
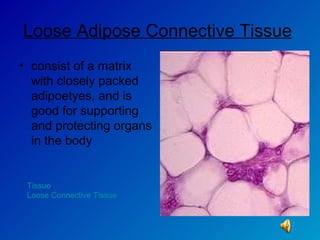
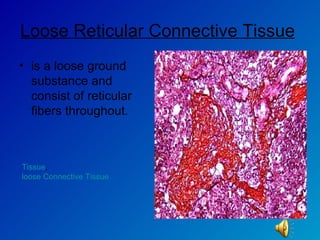
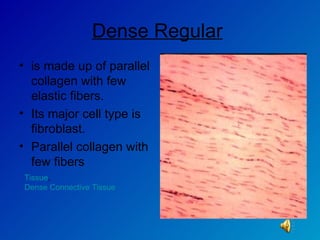
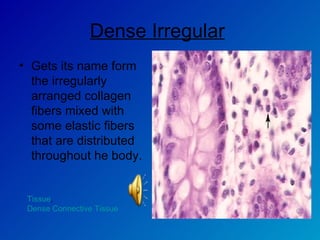
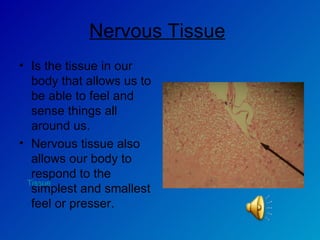
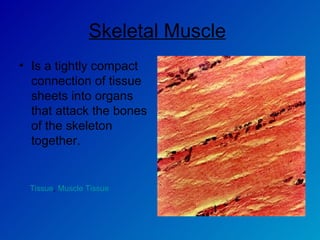
The document summarizes the four main types of tissues in the body: epithelial tissue, connective tissue, muscle tissue, and nervous tissue. It provides detailed information on the different subtypes of each tissue, including their structure, location in the body, and main functions. Simple epithelial tissue forms thin barriers and allows for absorption/filtration. Connective tissue connects and supports other tissues. Muscle tissue enables body movement. Nervous tissue allows for sensation and response.