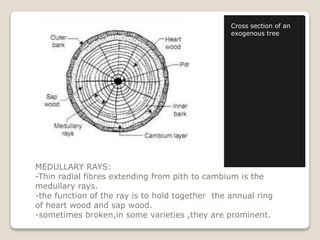
The document summarizes the structure of a tree from the macroscopic level. It discusses that a tree consists of a trunk, crown, and roots. It then describes the main macroscopic components of a tree's structure: the pith, heartwood, sapwood, cambium layer, inner bark, outer bark, and medullary rays. The pith is at the center and nourishes the young tree, while the heartwood and sapwood make up the woody tissue, with the heartwood being the inner, non-living portions and the sapwood being the outer, actively growing portions. The cambium layer separates the sapwood from the inner bark and is responsible for growth.