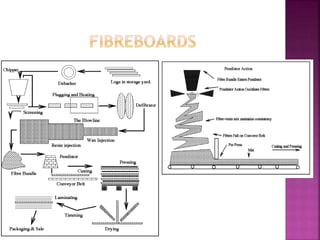
This document provides information on various types of industrial timber, including veneers, plywood, fibreboards, impregnated boards, compressed boards, block boards, and laminated boards. It describes the manufacturing processes and properties of each type of industrial timber. The key types discussed are used to make furniture, construction materials, and other wood products.