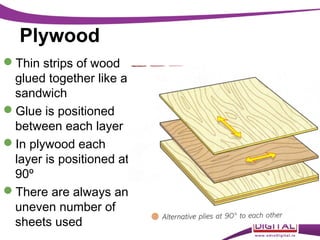
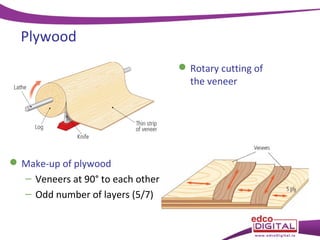
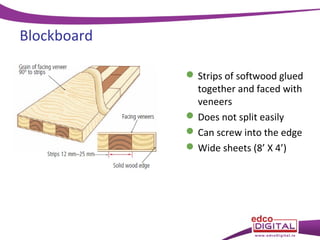
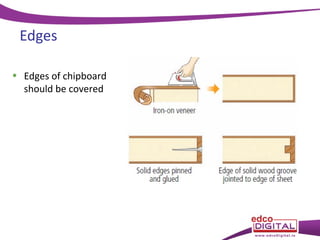
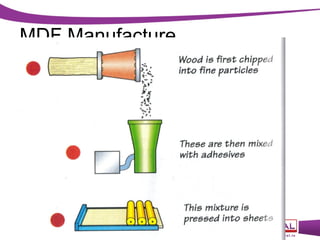
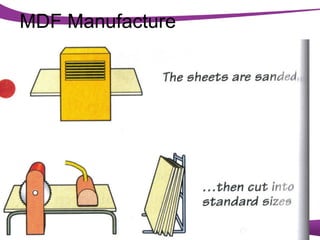
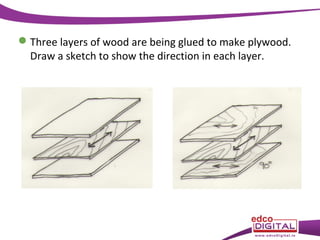
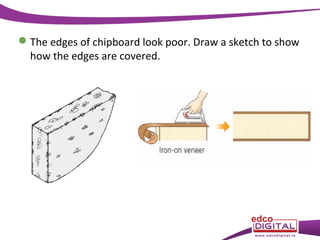
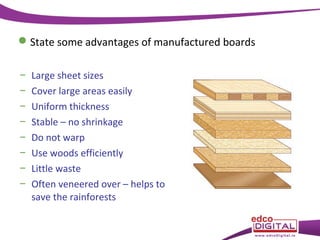
This document discusses various manufactured boards that are used as substitutes for solid wood. It describes how plywood is made by gluing thin wood veneers together in alternating 90 degree layers. Other manufactured boards mentioned include blockboard, pineboard/lamwood, oriented strand board (OSB), chipboard, medium density fibreboard (MDF), and hardboard. The document provides details on their manufacturing processes and advantages such as helping conserve forests, being economical alternatives that come in large uniform sizes and are stable.