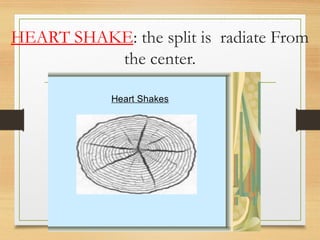
Timber is a form of wood categorized into endogenous and exogenous trees, with exogenous trees being more commonly used in construction. They are divided into softwood from conifers and hardwood from deciduous trees, each with distinct characteristics. Seasoning timber is essential to remove moisture and prevent decay, and it is utilized in various applications including construction, furniture, and agricultural tools.