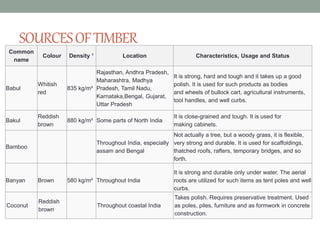
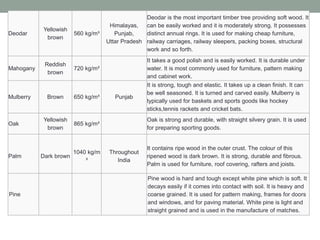
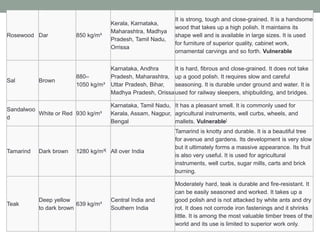
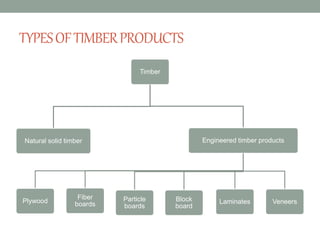
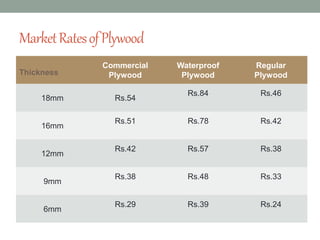
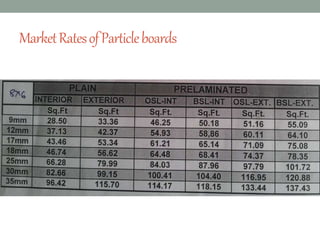
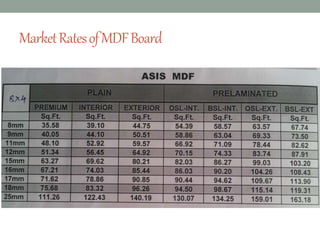
The document provides an extensive overview of various types of timber used in India, detailing their characteristics, uses, and market rates for different timber products such as softwood, plywood, laminates, and fiberboards. Each timber type includes attributes such as color, density, and specific applications, while also highlighting the manufacturing processes and classifications of engineered wood products. The content keys in on timber's utility in furniture and construction, emphasizing factors like durability, maintenance, and environmental impact.