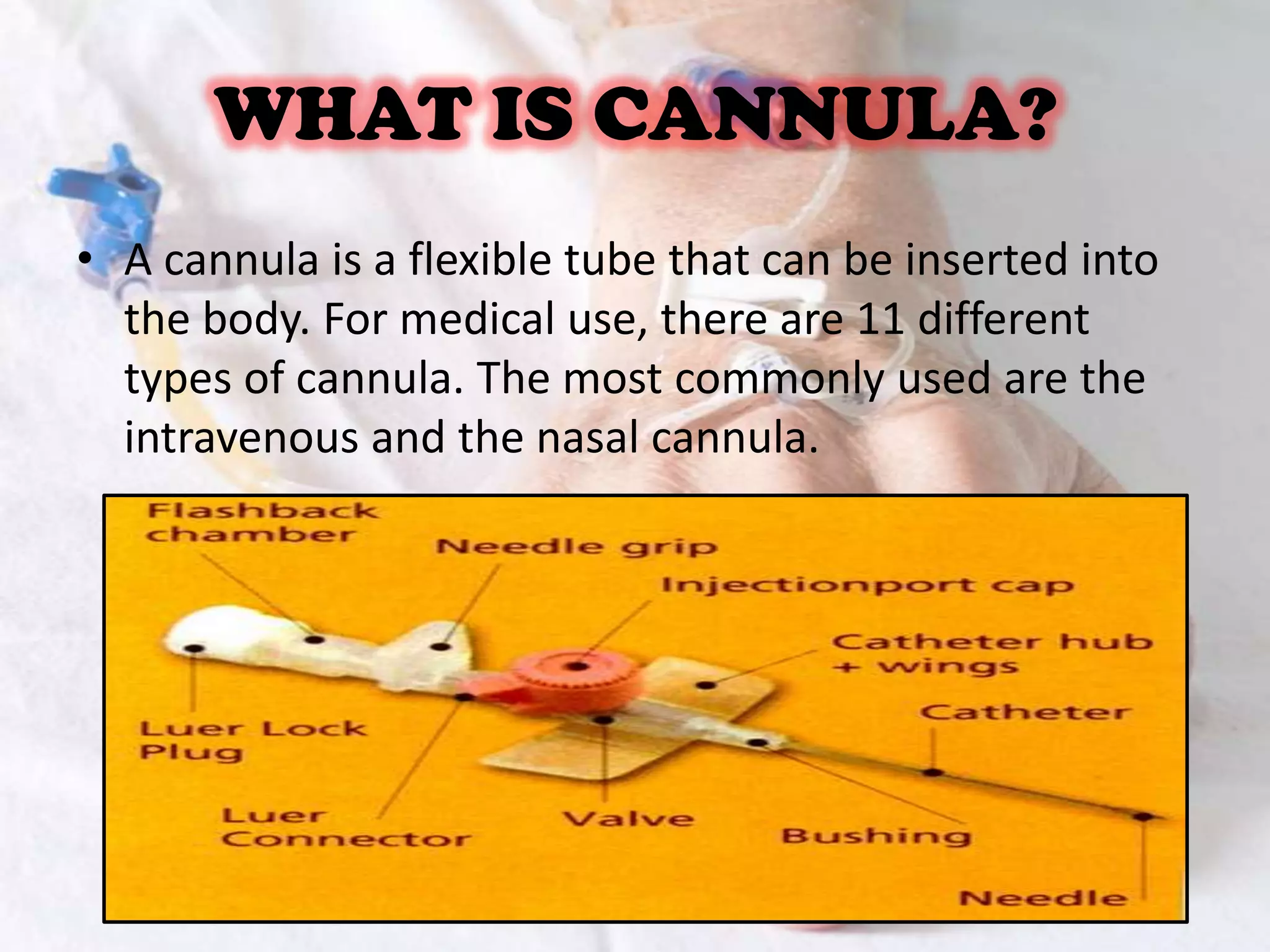
A cannula is a flexible tube inserted into the body for medical use. The most common types are intravenous (IV) and nasal cannulas. IV cannulation involves inserting a cannula into a vein to administer fluids, medications, blood products, or collect blood samples. The proper procedure is to introduce yourself, explain the process, select a vein, clean the skin, insert the cannula bevel up at a 30 degree angle, secure it, and remove the needle. Potential complications include infiltration, extravasation, thrombosis, phlebitis, and infection. IV fluids help maintain blood pressure, hydration, and electrolyte balance and common types are saline solutions and dextrose solutions.