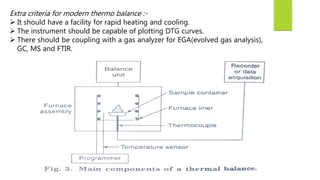
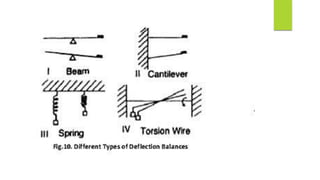
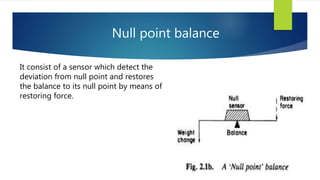
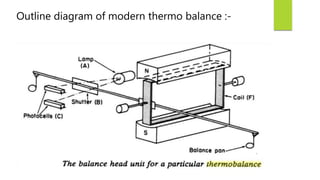
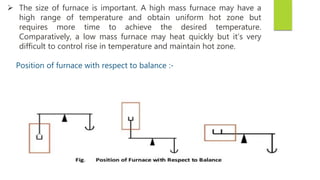
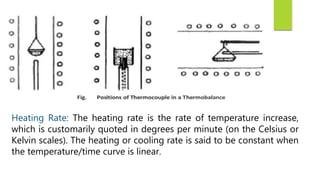
This document discusses Thermo gravimetric analysis (TGA), a technique where the weight of a substance is recorded as it is heated or cooled at a controlled rate. TGA is used to detect changes in mass that occur due to thermal events like desorption, absorption, and chemical reactions. Results are displayed as Thermo gravimetric (TG) curves that plot mass change versus temperature or time. The curves reveal temperatures where mass loss occurs due to decomposition or evaporation, as well as temperatures where the material is stable. TGA can be used to identify materials based on their characteristic temperature ranges of decomposition. Modern TGA instruments precisely measure weight changes, can rapidly heat and cool samples, and are often coupled to additional analytical techniques.