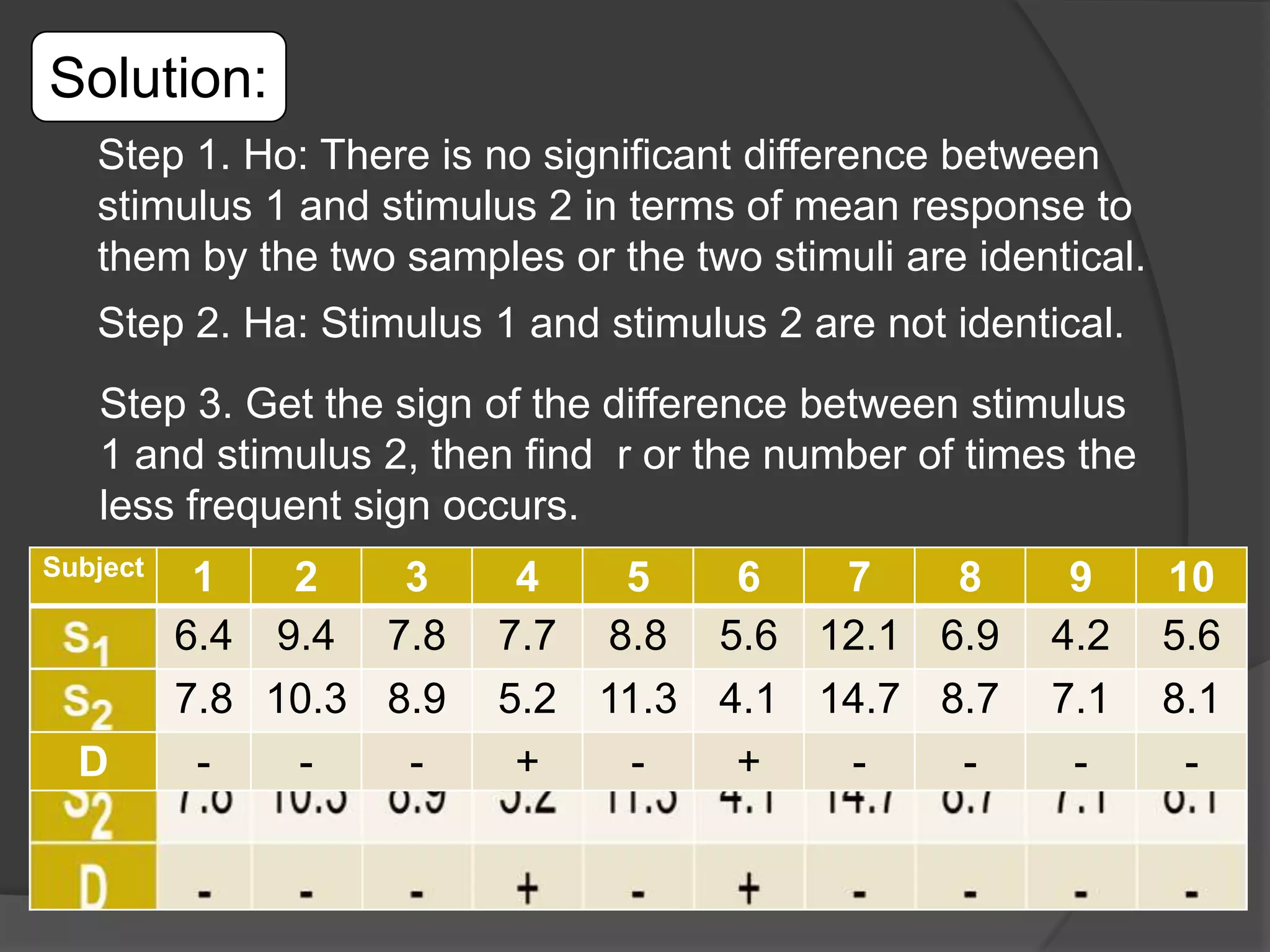
The sign test is used to compare two populations (A and B) by examining pairs of observations from each population. The number of times population A exceeds population B (X) is the test statistic. Under the null hypothesis, the two populations are identical and the probability of A exceeding B is 0.5.
To perform the sign test: (1) assign "+" if A>B, "-" if A<B, discard if equal; (2) count remaining pairs (n) and times the less frequent sign occurs (r); (3) compare r to critical values - if r is below the critical value, reject the null hypothesis that the two populations are identical.
The example tests if there is a