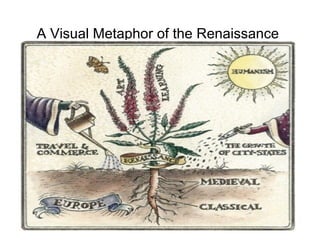
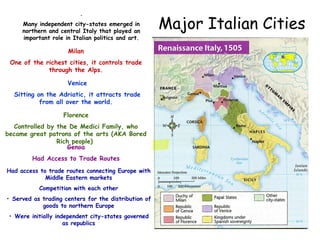
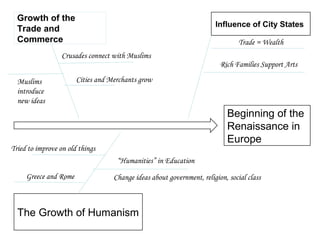
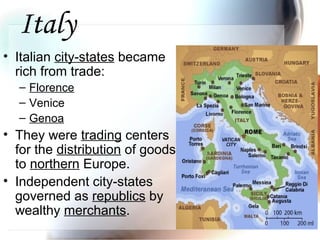
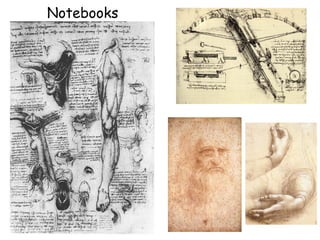
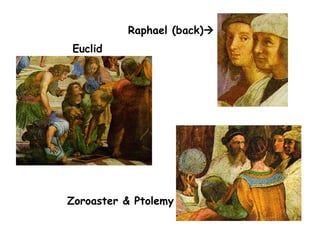
This document provides an overview of the Renaissance period in Europe, beginning in Italy in the 14th century. It discusses factors that contributed to the Renaissance such as increased trade, wealth in Italian city-states, and influence from classical Greek and Roman culture. Major artistic figures of the Renaissance are described like Leonardo da Vinci, Michelangelo, and Raphael. Their famous works and new techniques in art are summarized. Writers of the time including Dante, Petrarch, Erasmus, and Sir Thomas More are also mentioned.