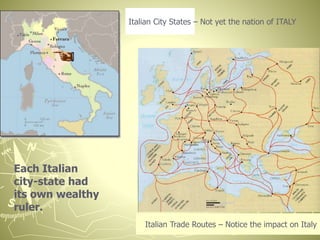
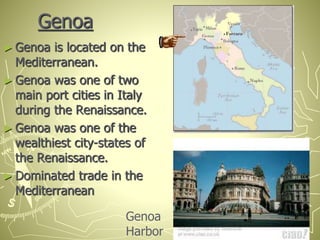
The Renaissance began in Italy in the late middle ages and spread across Europe. It was characterized by a revival of learning based on classical sources. Three important factors in the rise of the Renaissance were the growing wealth and power of Italian city-states like Florence, Venice, and Milan due to trade, which enabled cultural development; the rediscovery of ancient Greek and Roman texts, thanks to scholars like Petrarch; and new artistic techniques and perspectives developed by artists like Leonardo da Vinci, Michelangelo, and Raphael that mimicked nature. The movement enhanced science, philosophy, art, and literature.

















































![What was the Protestant
Reformation?
► Prior to the Reformation all Christians were Roman
Catholic
► The [REFORM]ation was an attempt to REFORM the
Catholic Church
► People like Martin Luther wanted to get rid of the
corruption and restore the people’s faith in the church
► In the end the reformers, like Luther, established their
own religions
► The Reformation caused a split in Christianity with the
formation of these new Protestant religions](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/therenaissanceandreformation-160905185958/85/The-renaissance-and-the-Reformation-53-320.jpg)