The document summarizes key aspects and events of the Renaissance period in Europe, including:
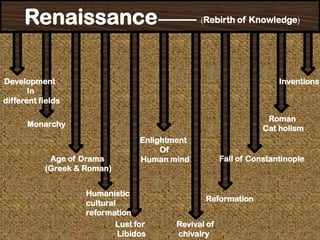
- The Renaissance began as a revival of interest in ancient Greek and Roman culture and emphasized human achievements over religious doctrine.
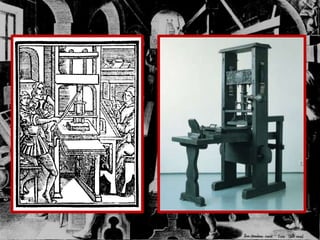
- Important developments included the fall of Constantinople spreading learning, the printing press allowing widespread knowledge sharing, and advances in science, medicine, and technology.
- The Protestant Reformation challenged the authority of the Catholic Church and led to new religious movements like Lutheranism.
- Renaissance art, literature, architecture, and other cultural works embraced realism and humanity rather than religious themes. Major artists, writers, and thinkers advanced new styles and ideas.