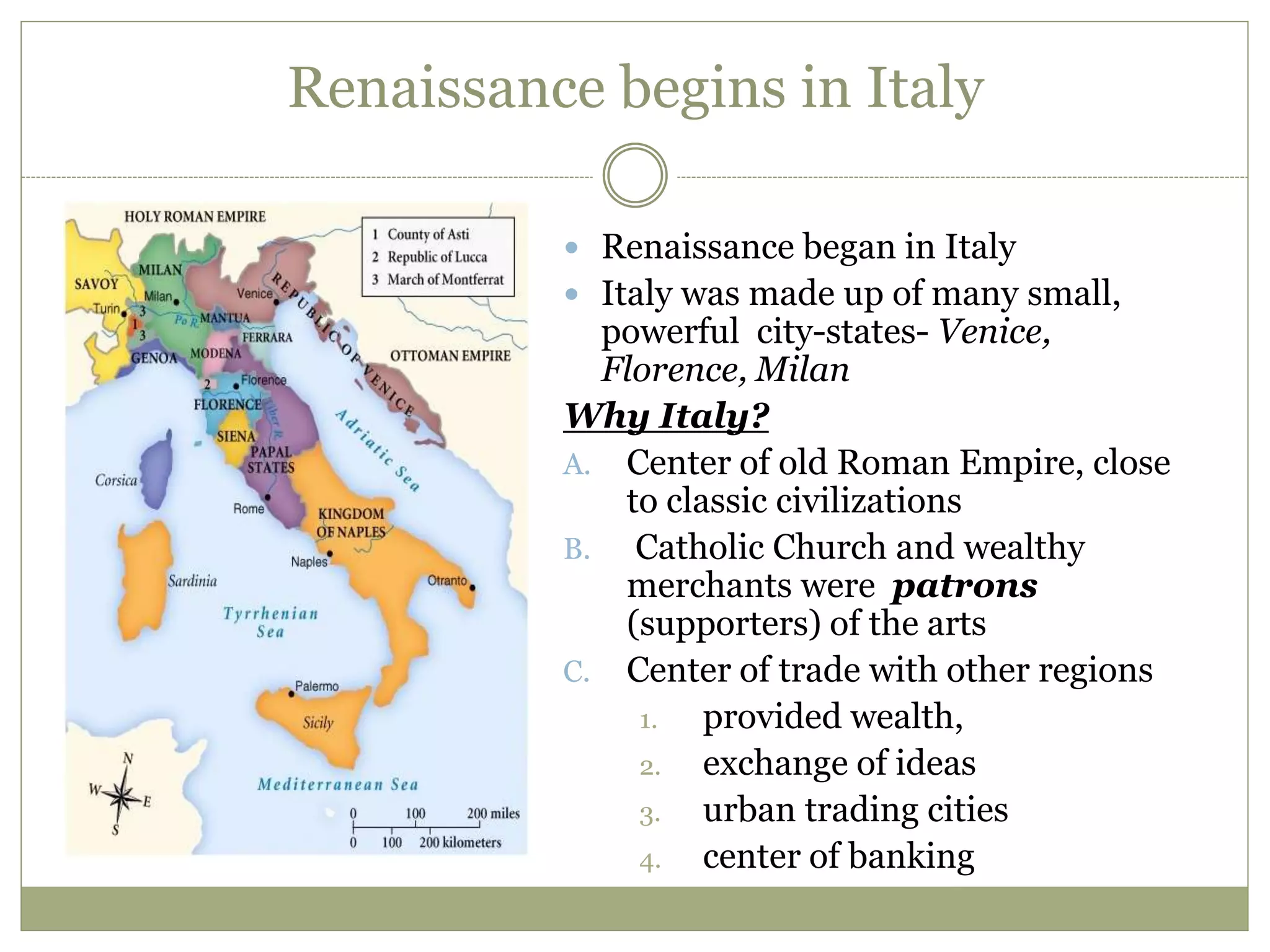
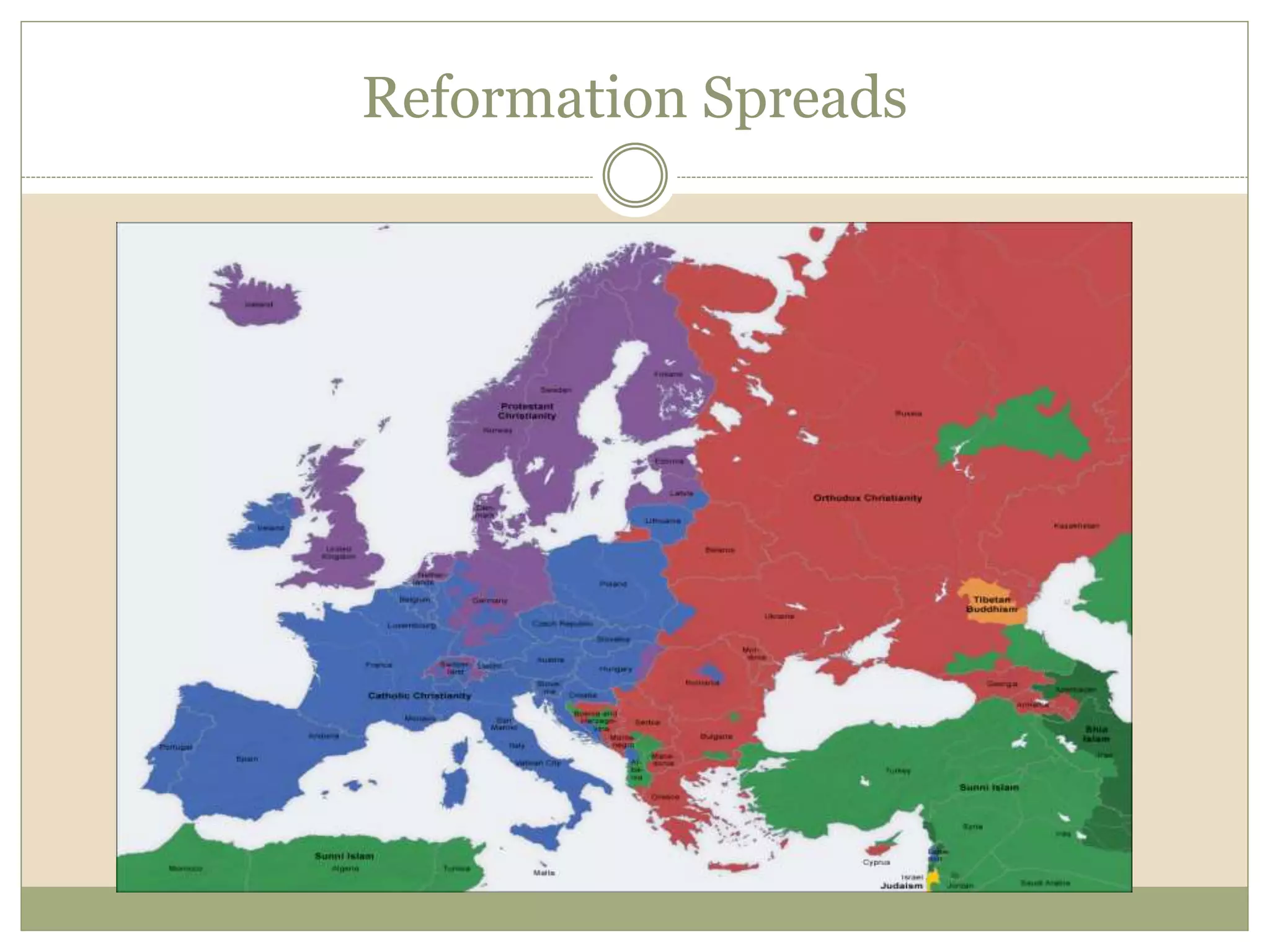
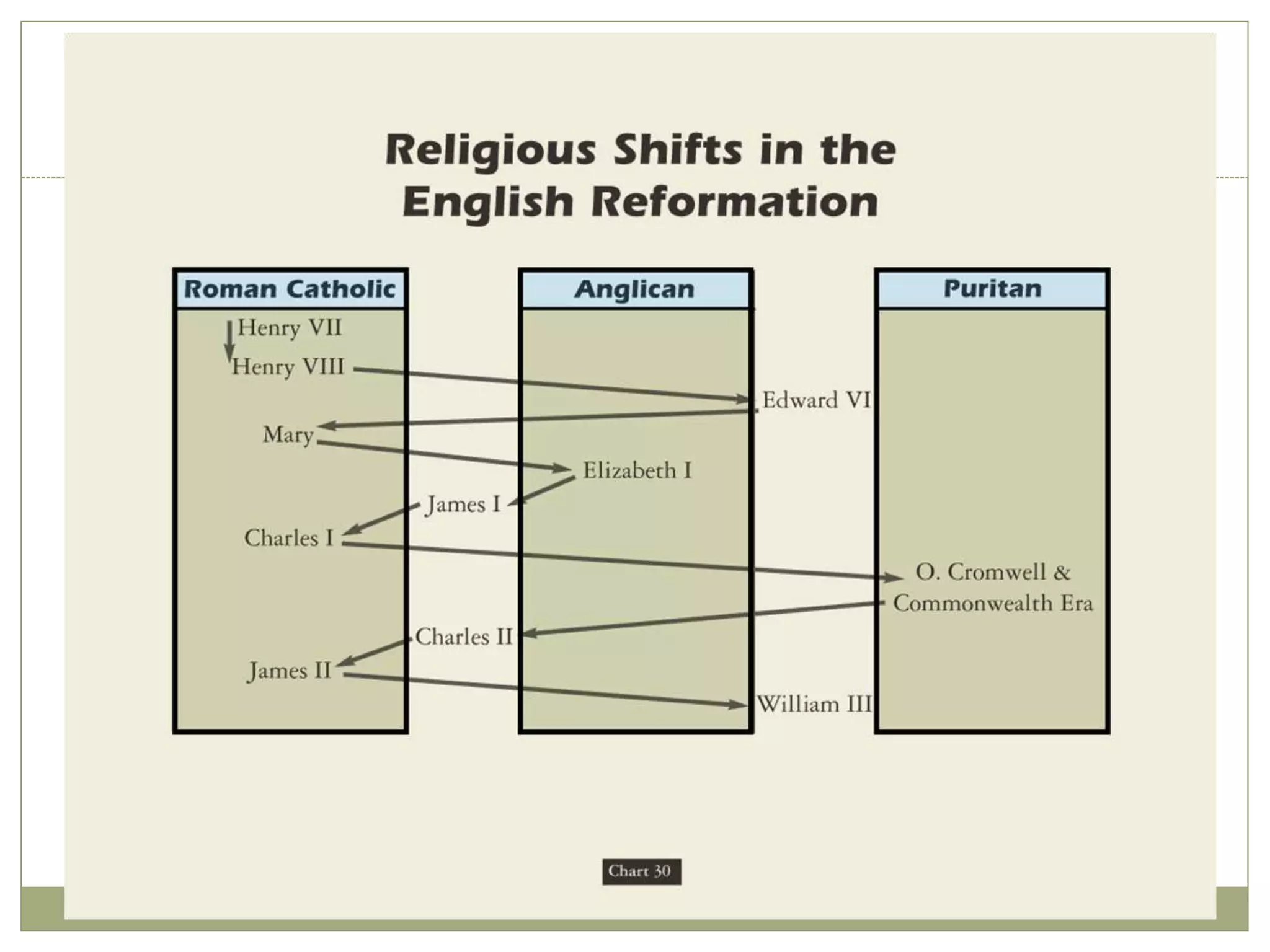
The Renaissance began in 14th century Italy as a period of cultural and intellectual revival following the Middle Ages. It spread across Europe over subsequent centuries as new ideas in politics, society, religion, and the arts emerged. The Protestant Reformation began as a religious challenge to the Catholic Church in the 16th century, led by Martin Luther. Luther's teachings and the spread of new Protestant faiths like Calvinism divided Europe along religious lines and weakened the power and influence of the Catholic Church.