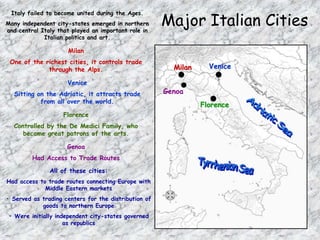
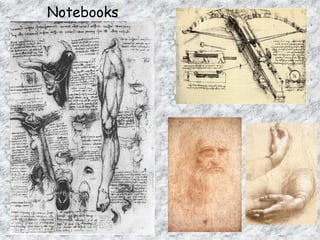
The Renaissance began in Italy in the late Middle Ages as a period of cultural and intellectual renewal. Major Italian city-states like Florence, Venice, and Genoa grew wealthy through trade and became centers of art and learning. The Crusades helped stimulate economic growth and exposed Europeans to new ideas from the Middle East. Humanism emerged, emphasizing secular and classical ideas, and was supported by wealthy patrons who commissioned works from artists like Michelangelo, Raphael, and Leonardo da Vinci. The printing press helped spread Renaissance ideas throughout Europe.