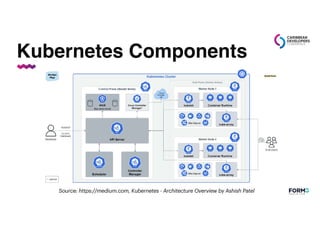
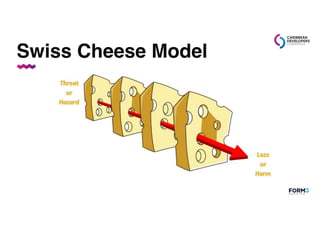
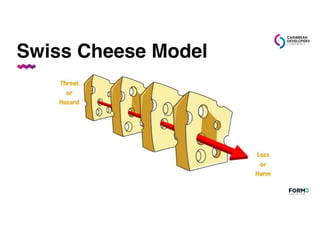
This document is a presentation by Patrycja Wegrzynowicz on Kubernetes security, including an overview of its architecture and the OWASP Kubernetes Top 10 vulnerabilities. It offers demonstrations of hacking scenarios to illustrate the risks associated with misconfigurations, inadequate logging, and insecure workloads. The session emphasizes the importance of continuous learning in maintaining security within Kubernetes environments.