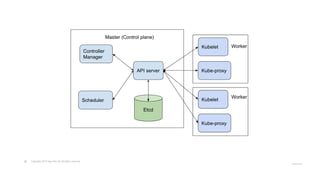
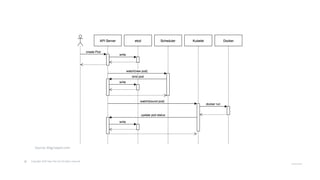
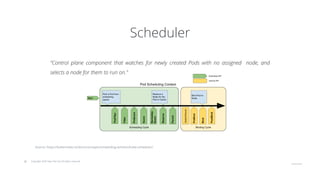
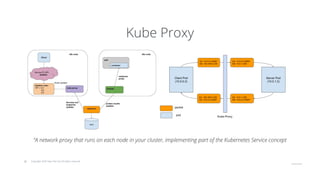
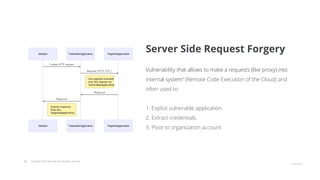
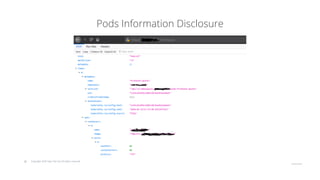
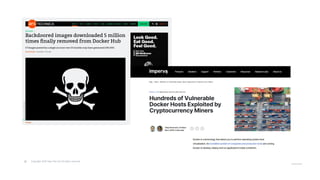
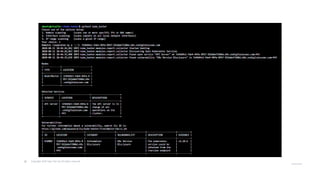
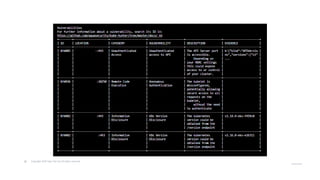
The document outlines strategies for securing Kubernetes clusters, detailing key components and tools for managing security vulnerabilities. It introduces the 'Kubernetes Goat' as a training environment for practicing security measures against various attack scenarios. Additionally, it provides best practices for defending clusters and highlights tools like Kube Hunter, Kube Bench, and Calico for enhancing Kubernetes security.