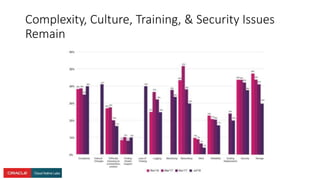
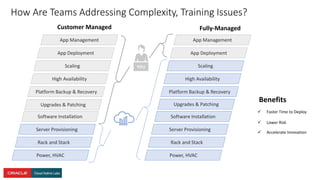
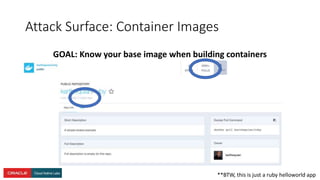
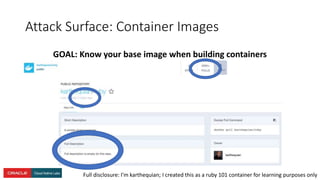
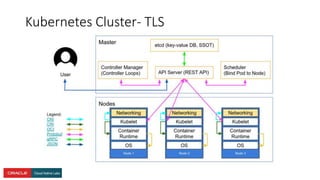
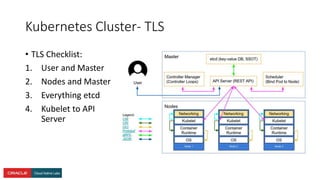
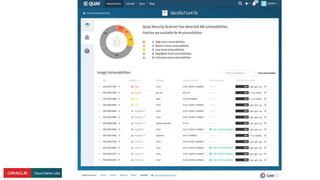
The document presents a comprehensive overview of Kubernetes security challenges and best practices, addressing complexities in container management, deployment, and operations in cloud-native environments. It emphasizes the importance of reducing the attack surface through various techniques, including securing cluster components, managing access controls, and utilizing Kubernetes' built-in security features. Additionally, it highlights open-source tools available for enhancing security, such as kube-bench and clair, while encouraging periodic audits and adherence to best practices.