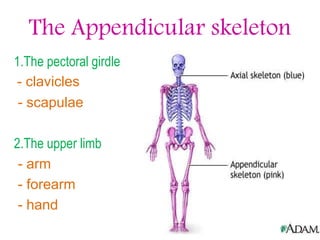
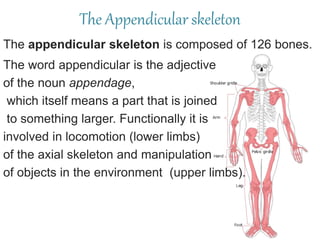
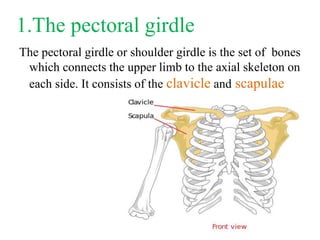
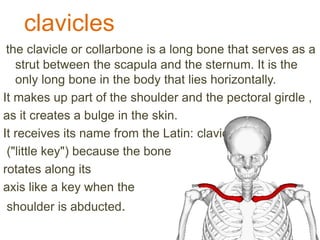
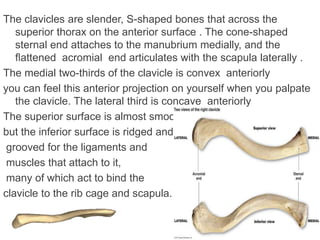
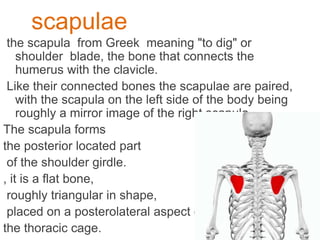
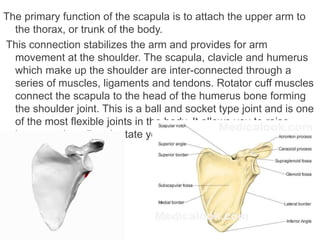
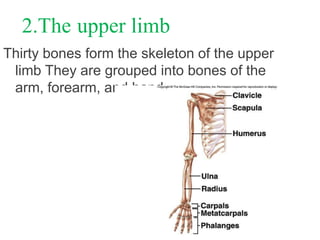
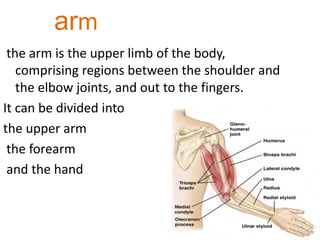
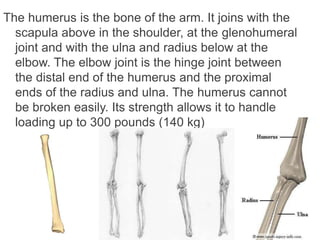
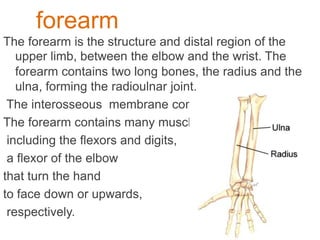
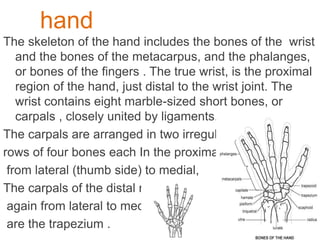
The appendicular skeleton is composed of 126 bones and includes the pectoral girdle, upper limbs, and lower limbs. The pectoral girdle connects the upper limbs to the axial skeleton and includes the clavicles and scapulae. The upper limbs contain 30 bones grouped into the arm, forearm, and hand. The arm includes the humerus bone. The forearm lies between the elbow and wrist and contains the radius and ulna bones. The hand includes the wrist bones and bones of the fingers.