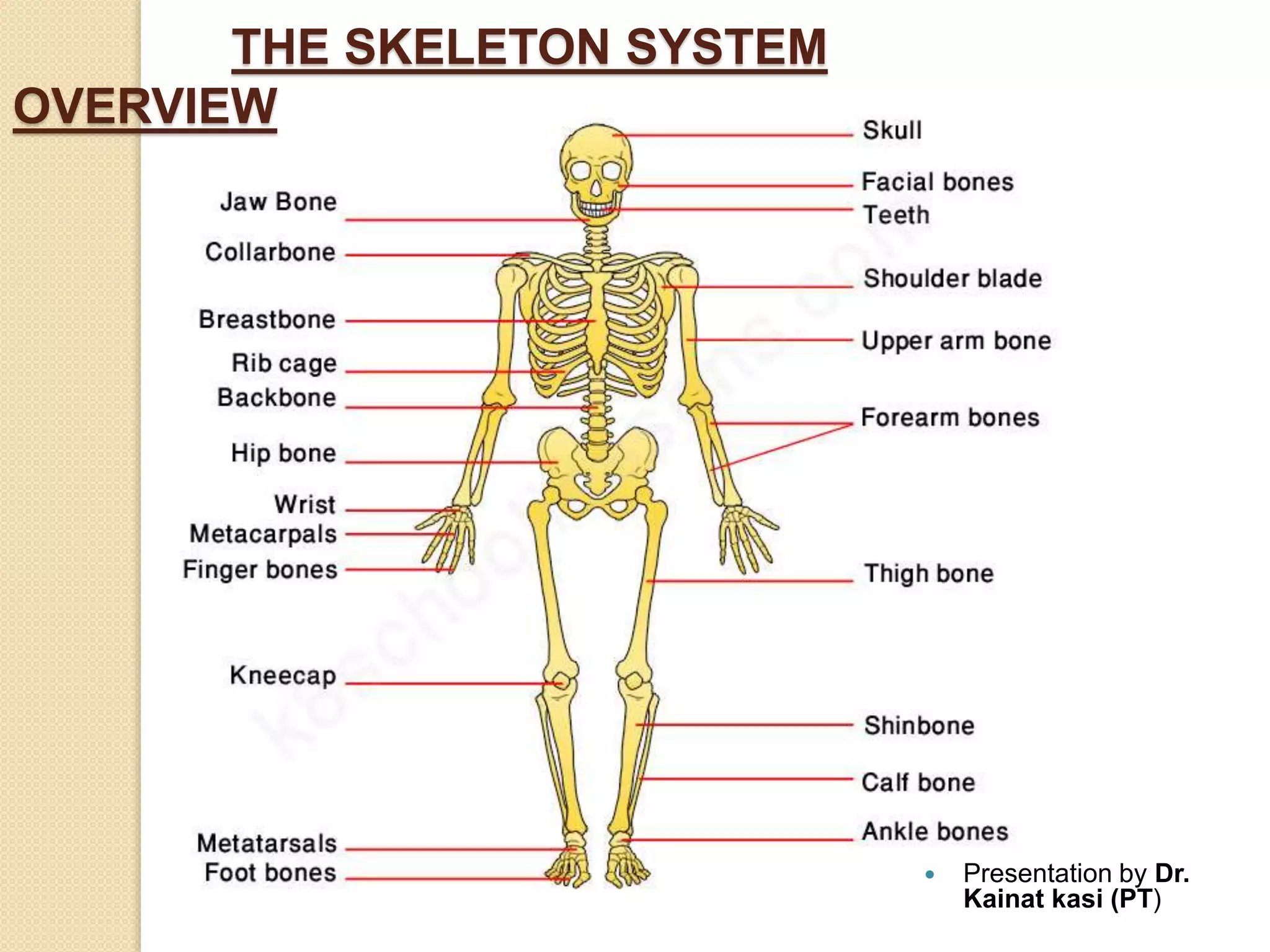
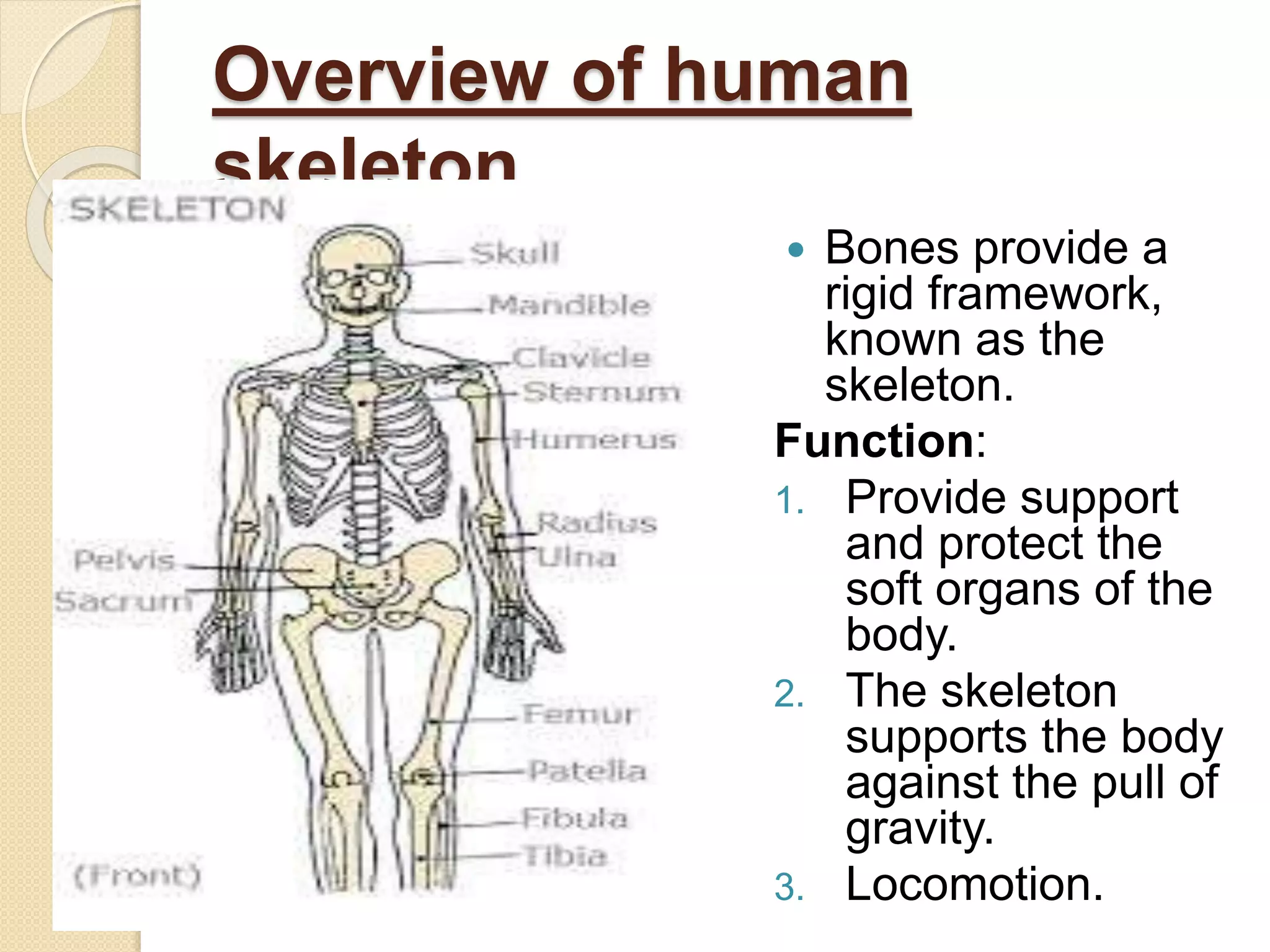
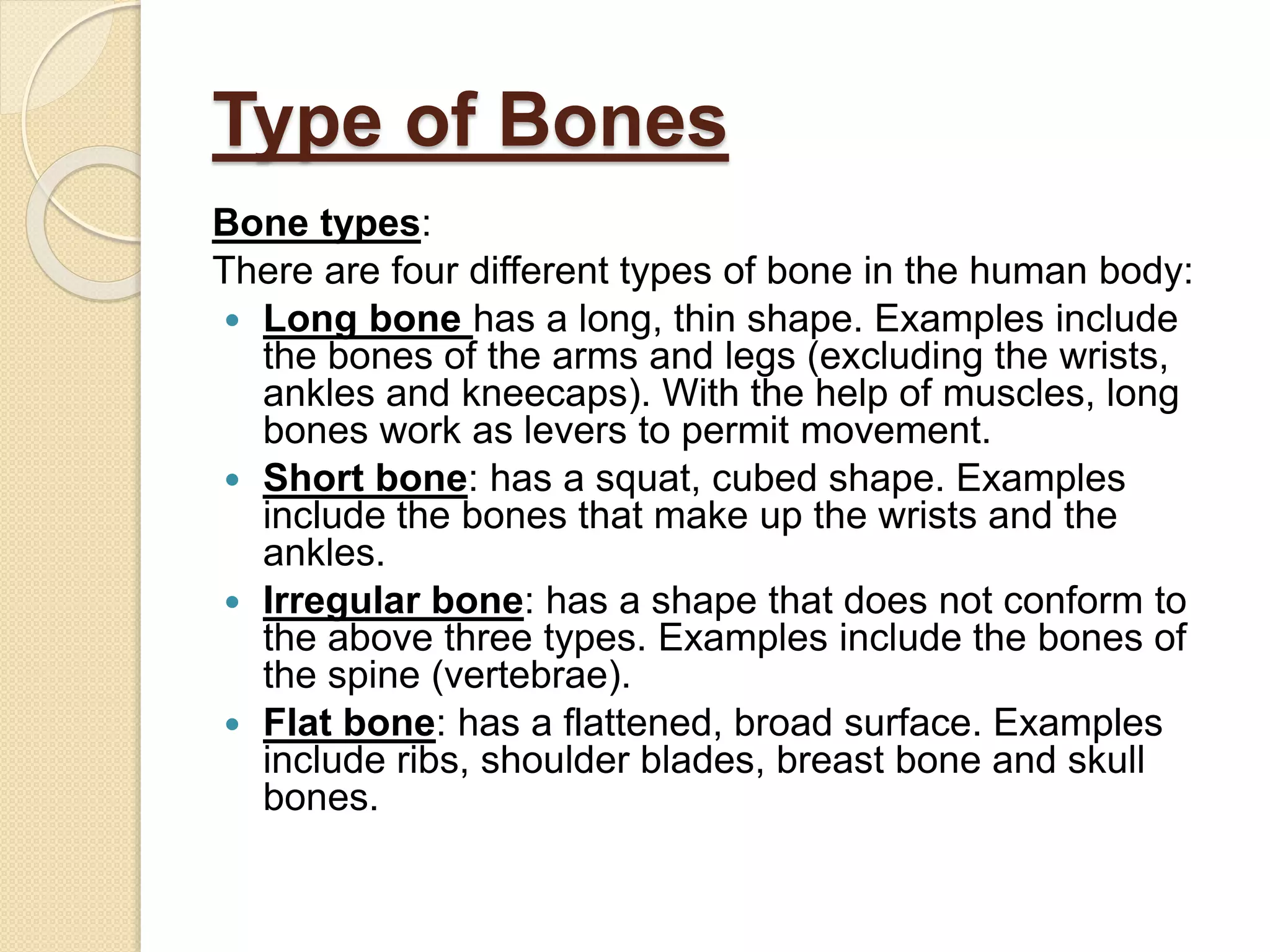
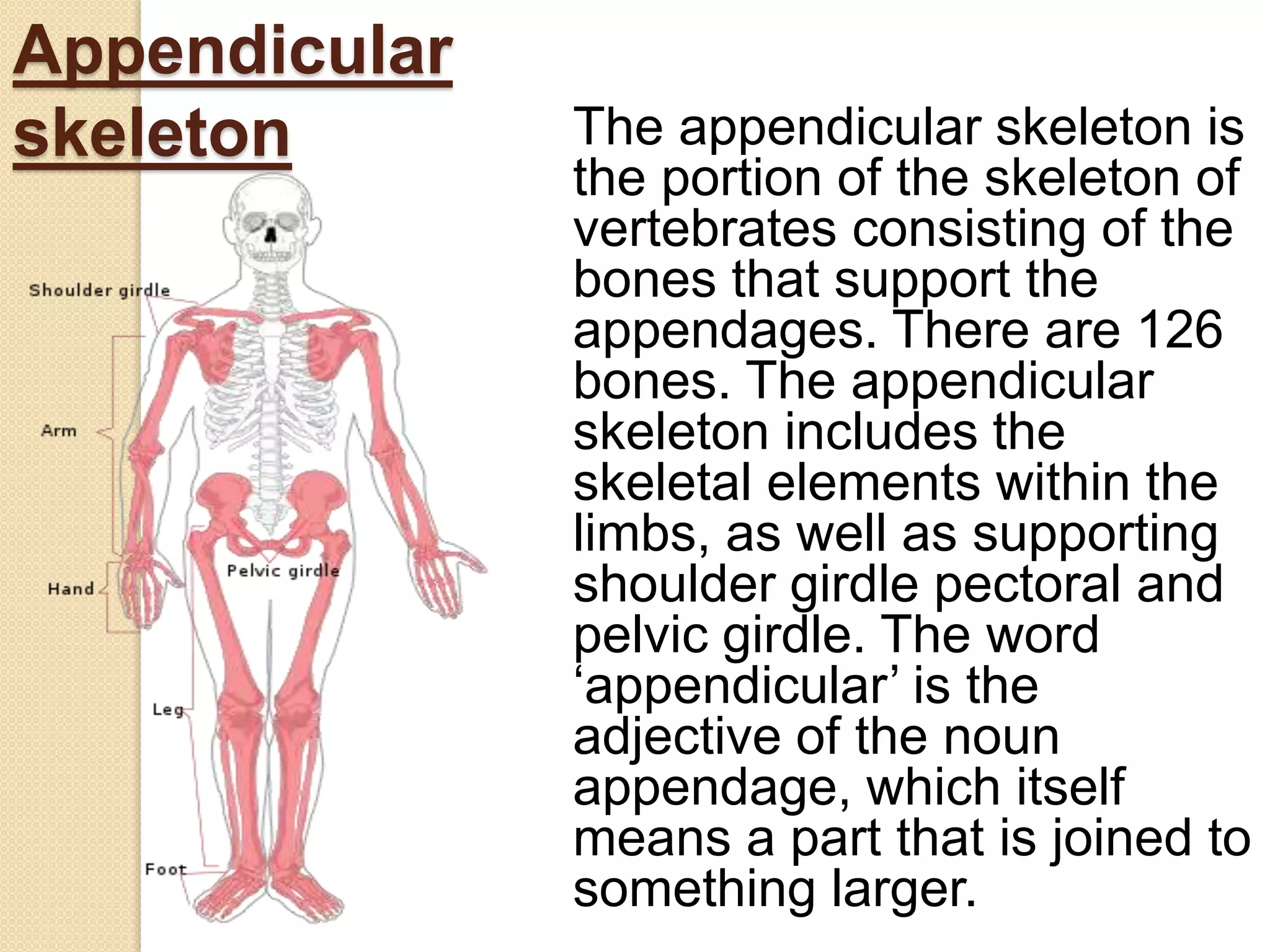
The human skeleton consists of 206 bones that provide structure, protect organs, allow movement, and store minerals. It is divided into the axial skeleton comprising the skull, vertebral column, ribs, and sternum, and the appendicular skeleton consisting of the shoulders, arms, hands, pelvis, legs, and feet. The four types of bones - long, short, irregular, and flat - have different shapes that enable their various functions in support, protection, and movement.




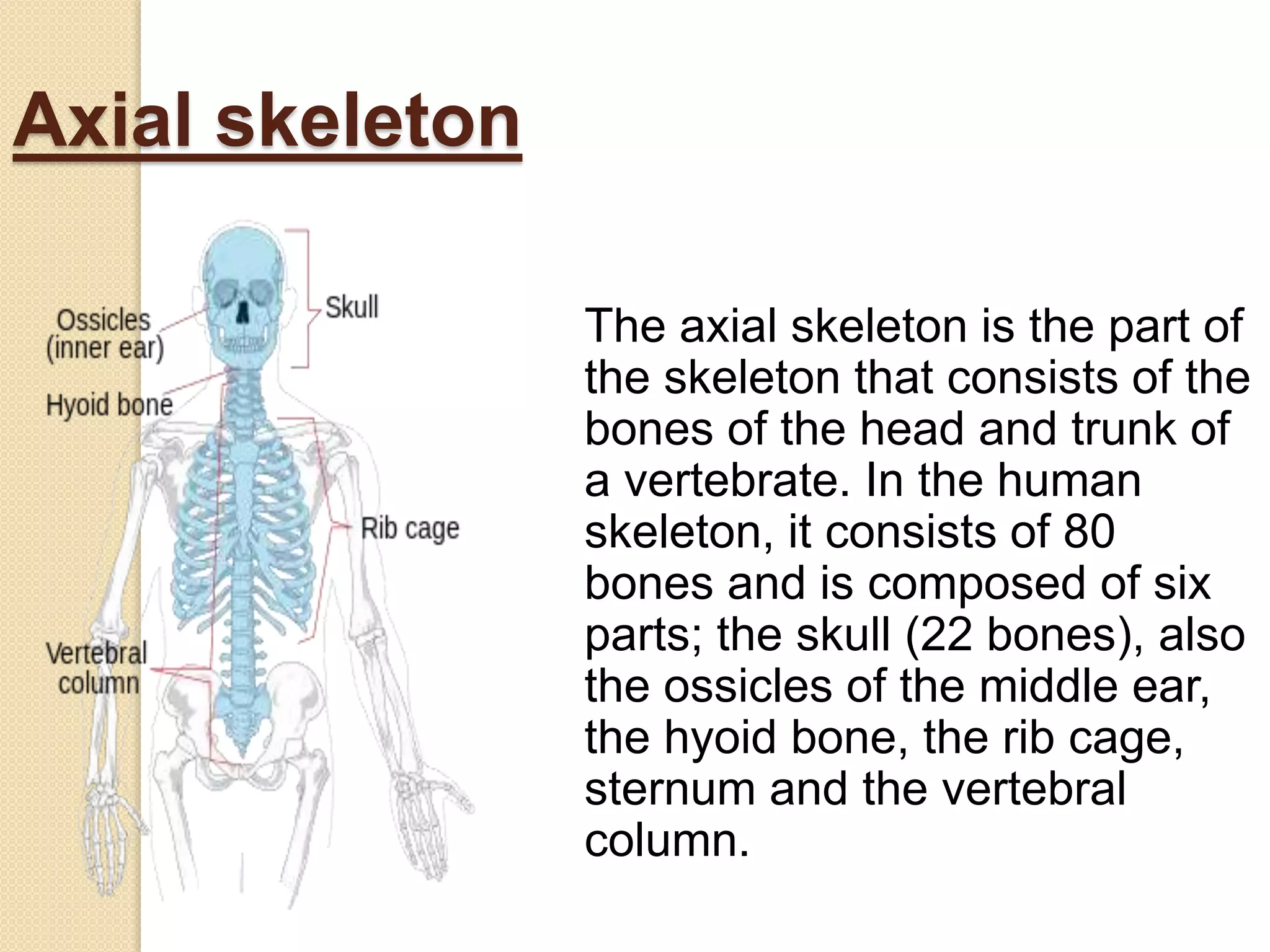
![Axial skeleton
Axial skeleton consists of:
1. Skull
i. Neurocranium [Occipital, parietal,
frontal, temporal, sphenoid, ethmoid]
ii. Face [Nasal, maxilla, lacrimal,
zygomatic , palatine, inferior nasal
conchae, vomer , mandible, hyoid]
iii. Ear [Ossicles, malleus, incus, stapes]
2.Thorax [Sternum ,rib cage ]
3.Vertebral column [cervical 7, thoracic
12, lumbar 5, sacrum 5, coccyx 4]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/theskeletonsystemoverview-210224212227/75/The-skeleton-system-overview-10-2048.jpg)