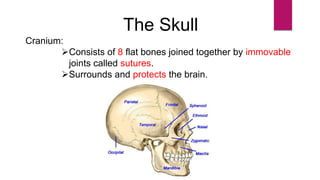
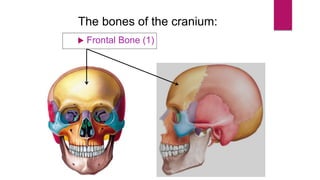
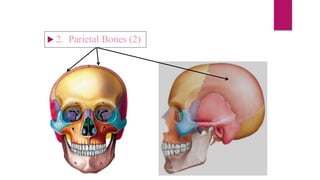
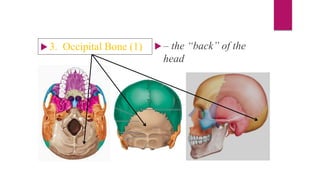
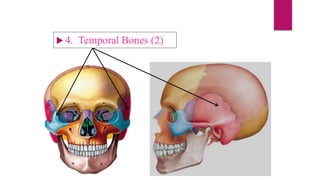
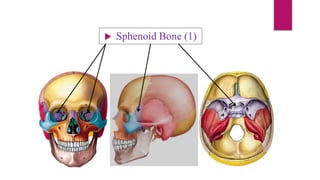
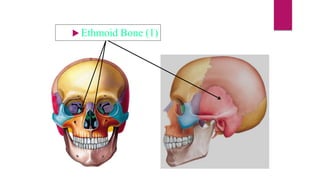
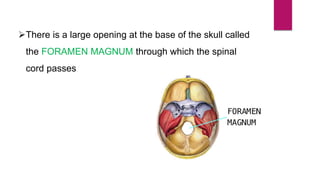
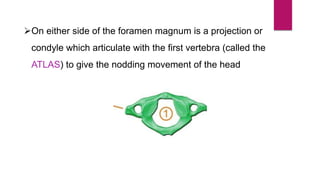
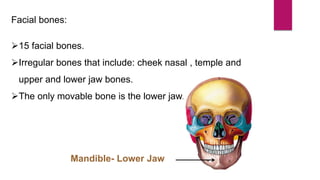
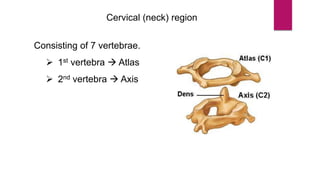
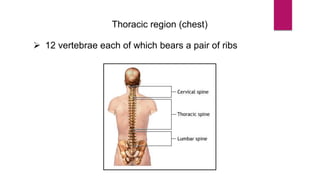
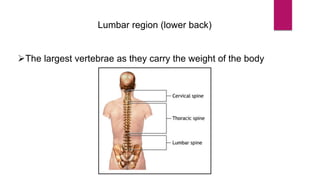
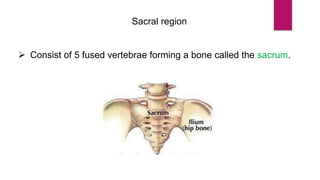
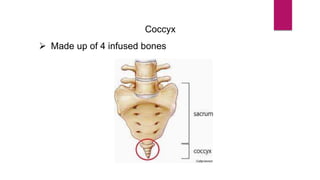
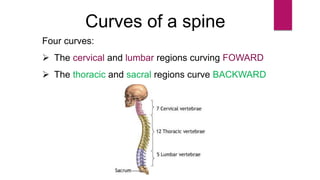
The human skeleton consists of the axial skeleton and appendicular skeleton. The axial skeleton includes the skull, vertebral column, ribs, and sternum. The skull is made up of 22 bones that form the cranium and facial bones. The vertebral column is divided into 5 regions - cervical, thoracic, lumbar, sacral, and coccyx. It provides structure and protection for the spinal cord. The appendicular skeleton includes the pectoral and pelvic girdles and their limb bones.