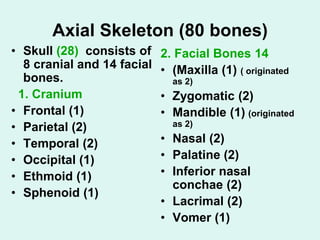
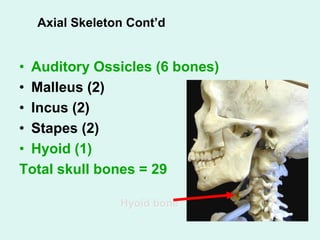
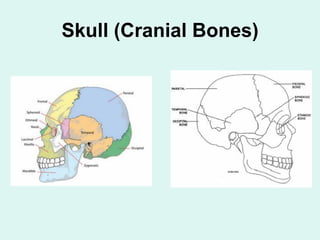
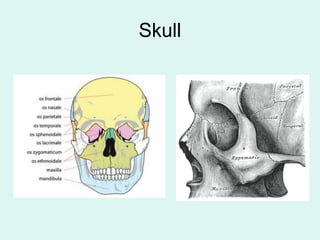
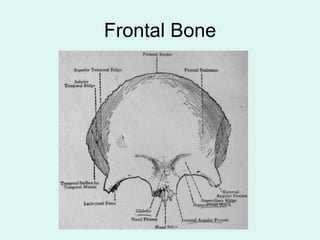
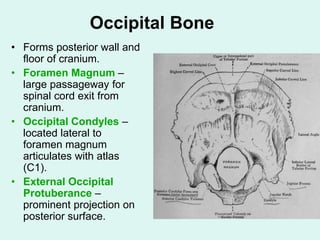
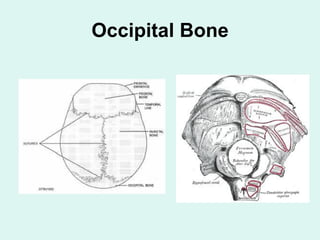
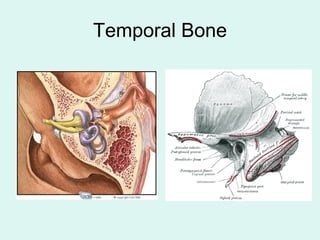
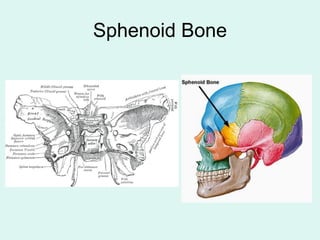
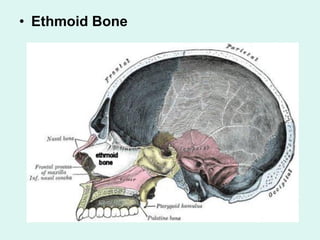
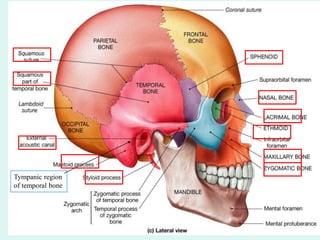
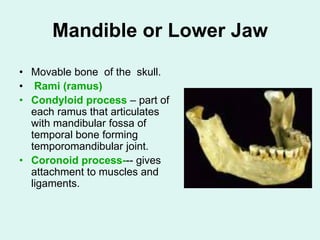
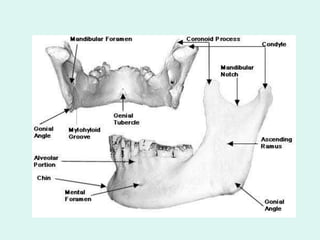
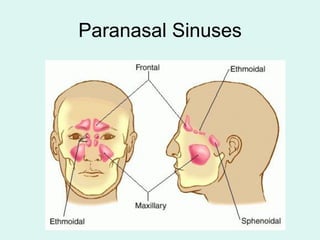
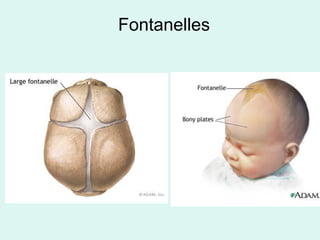
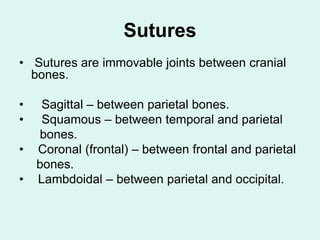
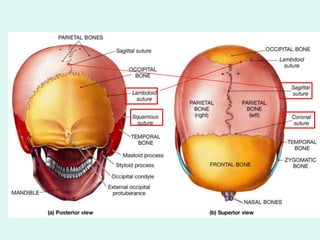
The document summarizes the division of the skeletal system into the axial and appendicular skeleton. The axial skeleton consists of 80 bones including the skull, vertebral column, ribs, and sternum. It forms the vertical axis of the body. The appendicular skeleton has 126 bones and includes the limbs and their attachments via girdles. The skull is made up of 28 cranial bones including the frontal, parietal, temporal, occipital, ethmoid, and sphenoid bones, as well as 14 facial bones such as the maxilla, zygomatic, and mandible.