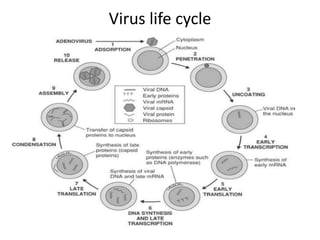
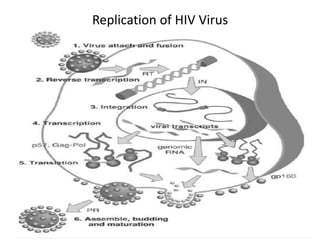
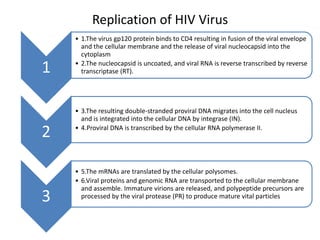
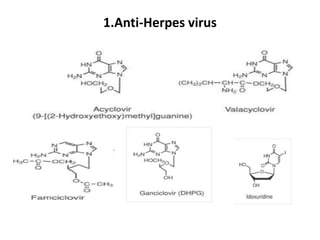
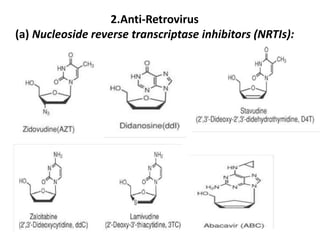
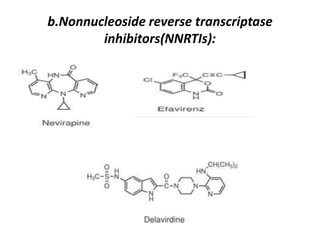
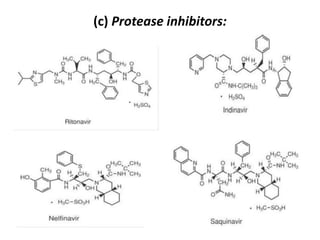
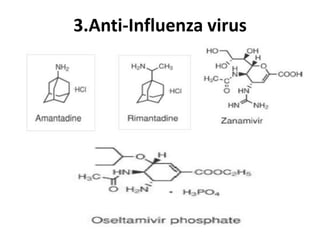
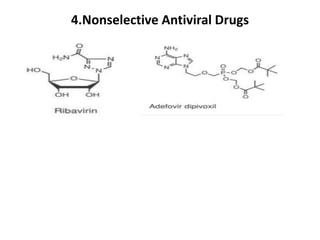
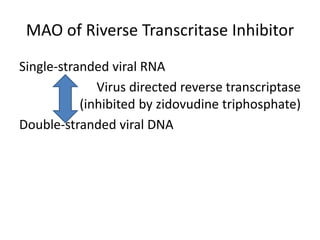
The document outlines the HIV virus replication cycle, describing key steps such as the binding of the virus GP120 protein to CD4 and subsequent reverse transcription of viral RNA. It also categorizes various antiviral agents targeting herpes, retroviruses, and influenza, detailing their mechanisms of action. Additionally, it highlights the role of protease inhibitors in HIV maturation and the effects of other antiviral drugs like amantadine and ribavirin.