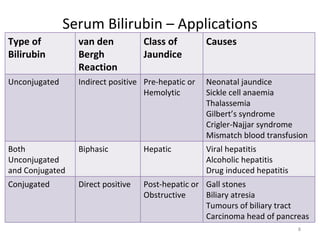
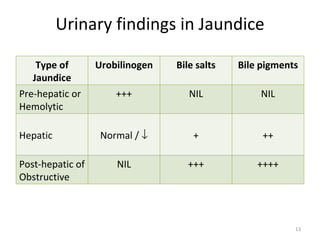
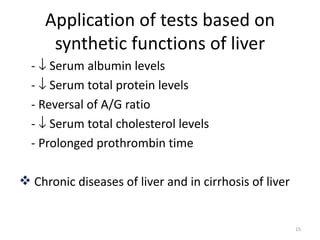
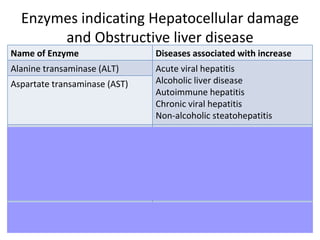
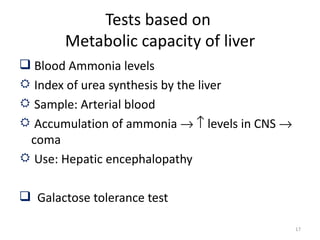
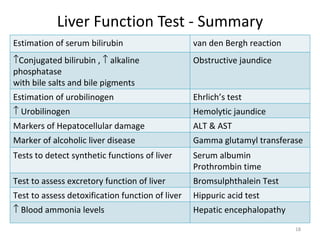
The patient, a 45-year-old female, presented with right upper quadrant pain, decreased appetite, vomiting, and pruritis. On examination, she was obese and the right hypochondriac region was tender. The probable diagnosis is obstructive jaundice. Biochemical investigations to confirm include elevated conjugated bilirubin and alkaline phosphatase on liver function tests, and bile salts and bile pigments in the urine.