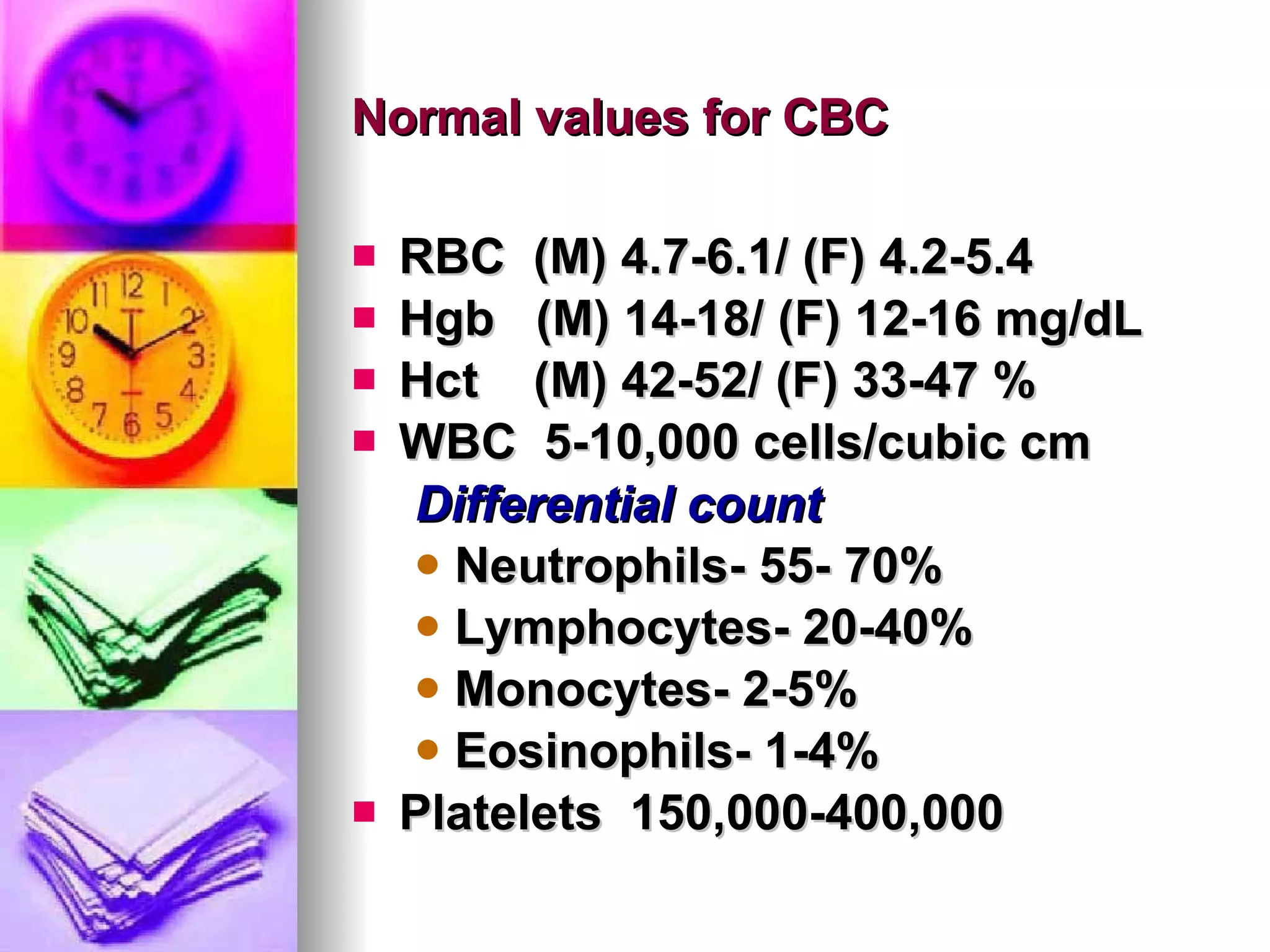
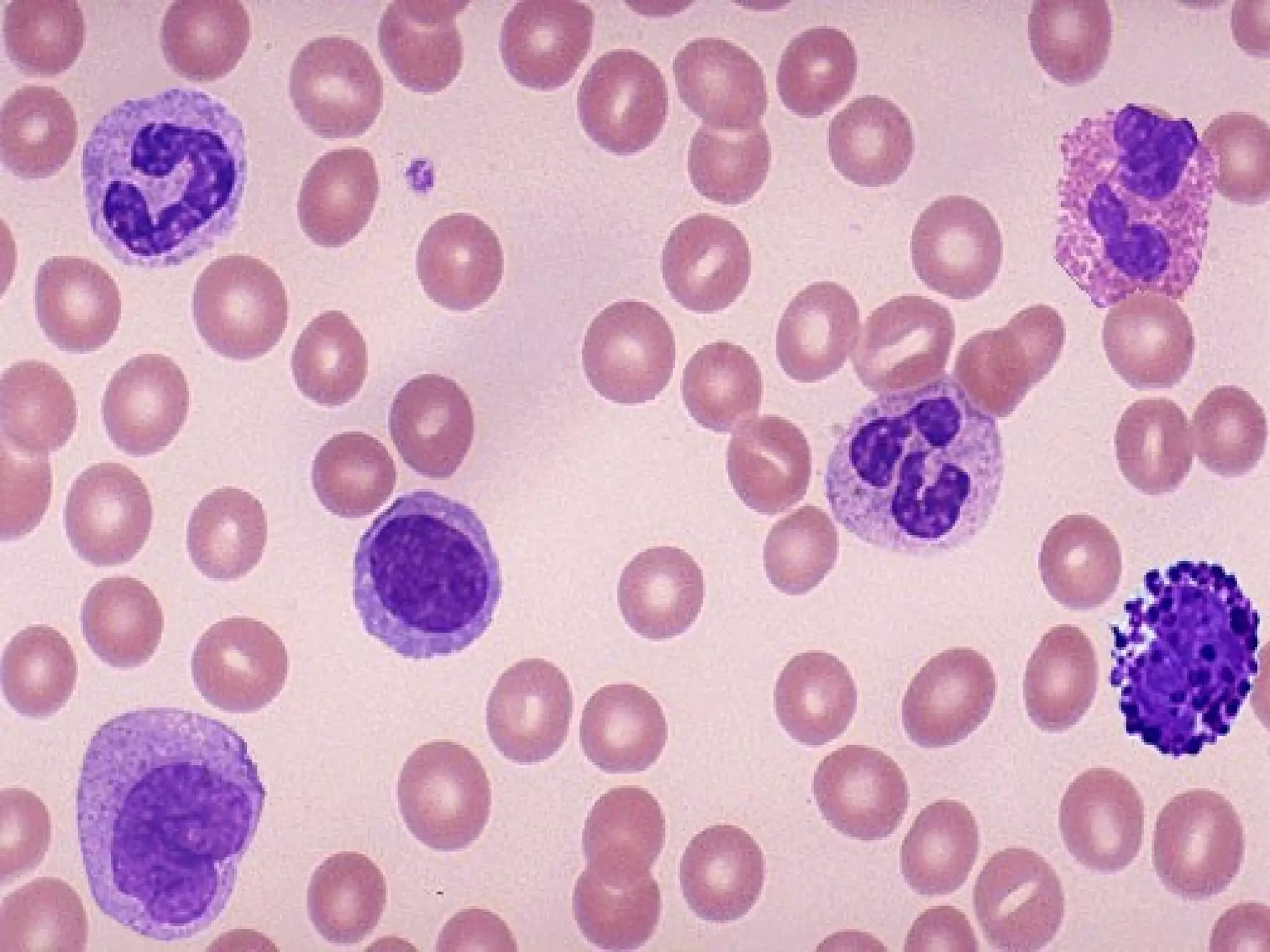
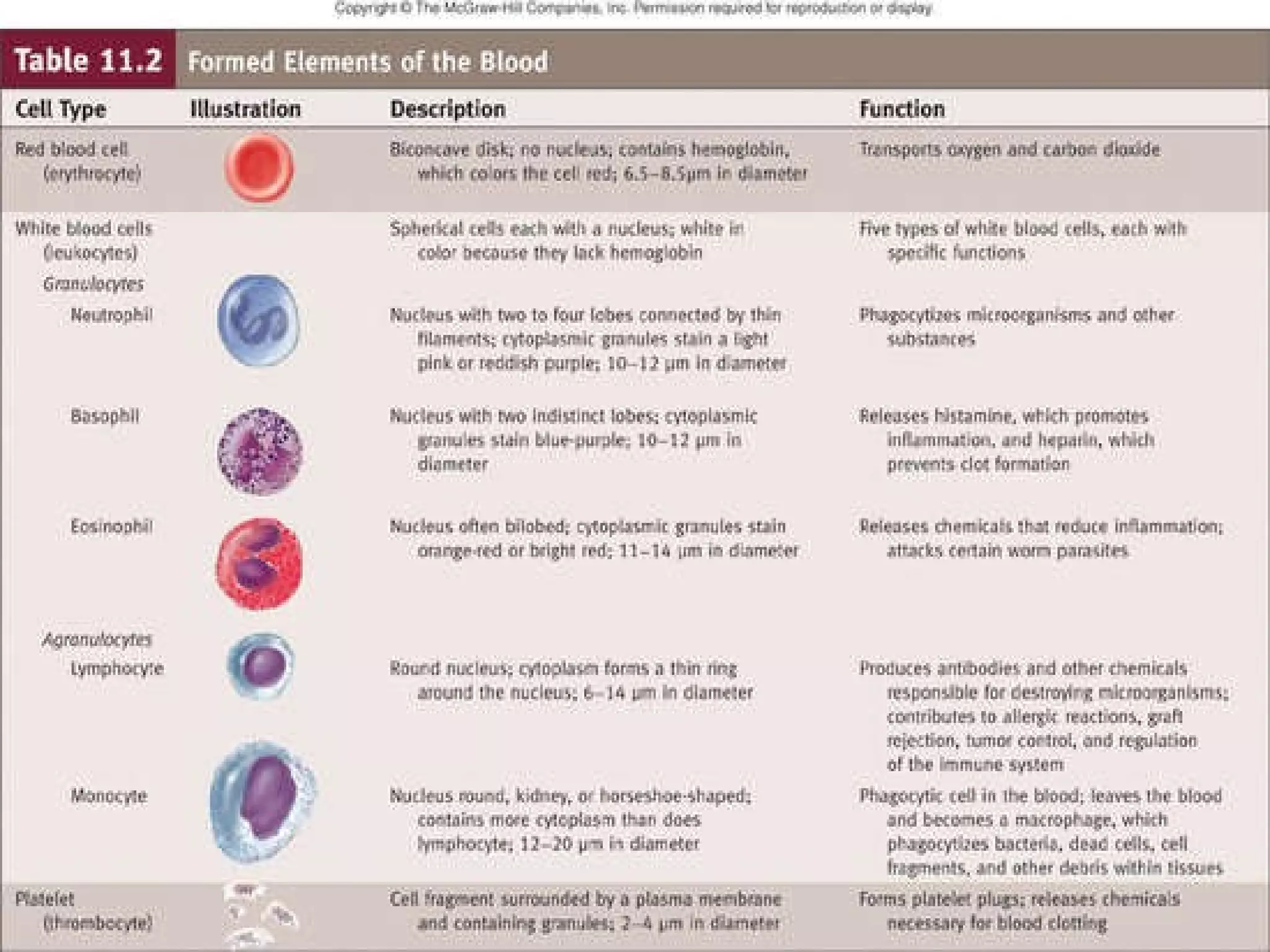
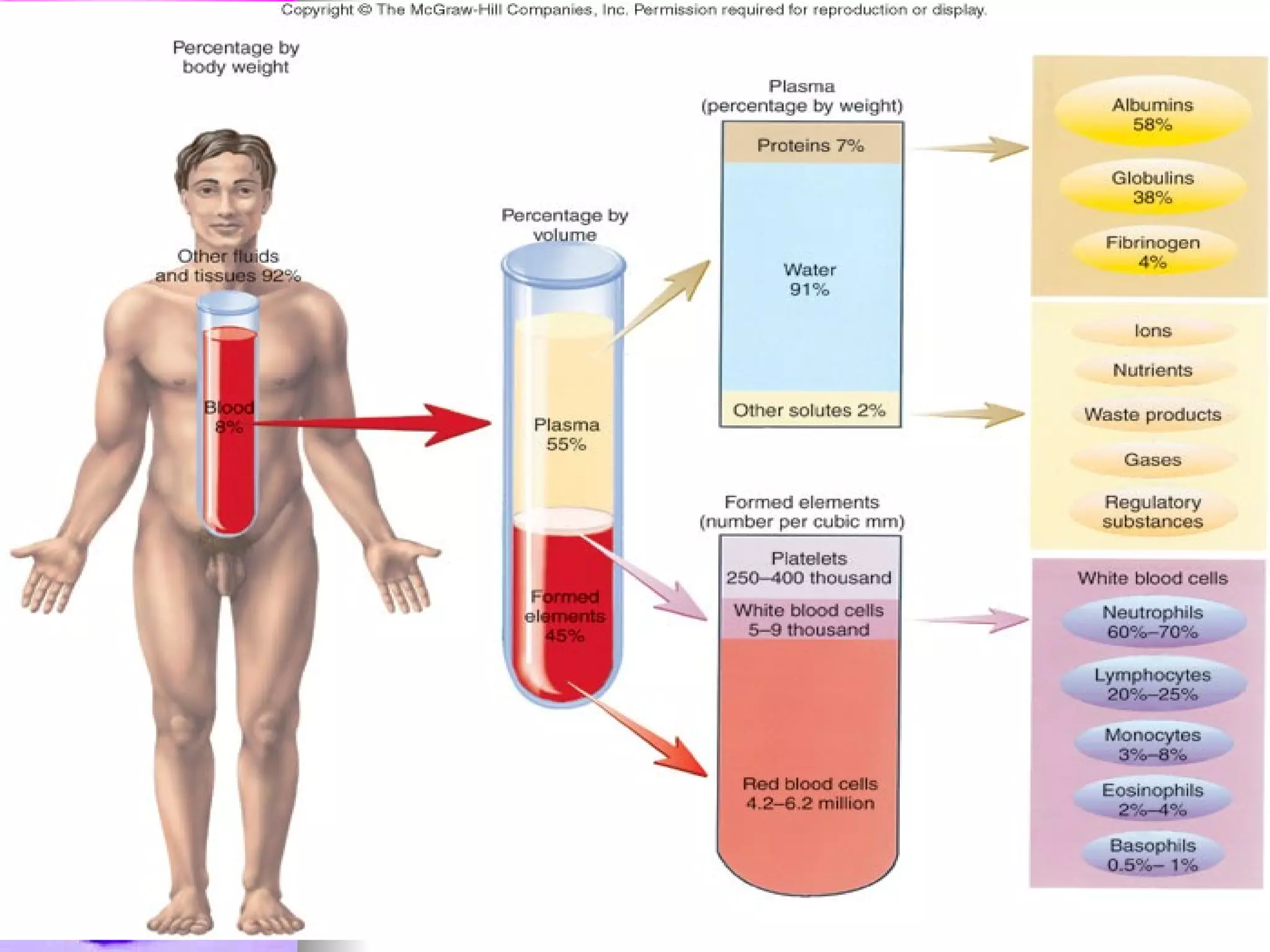
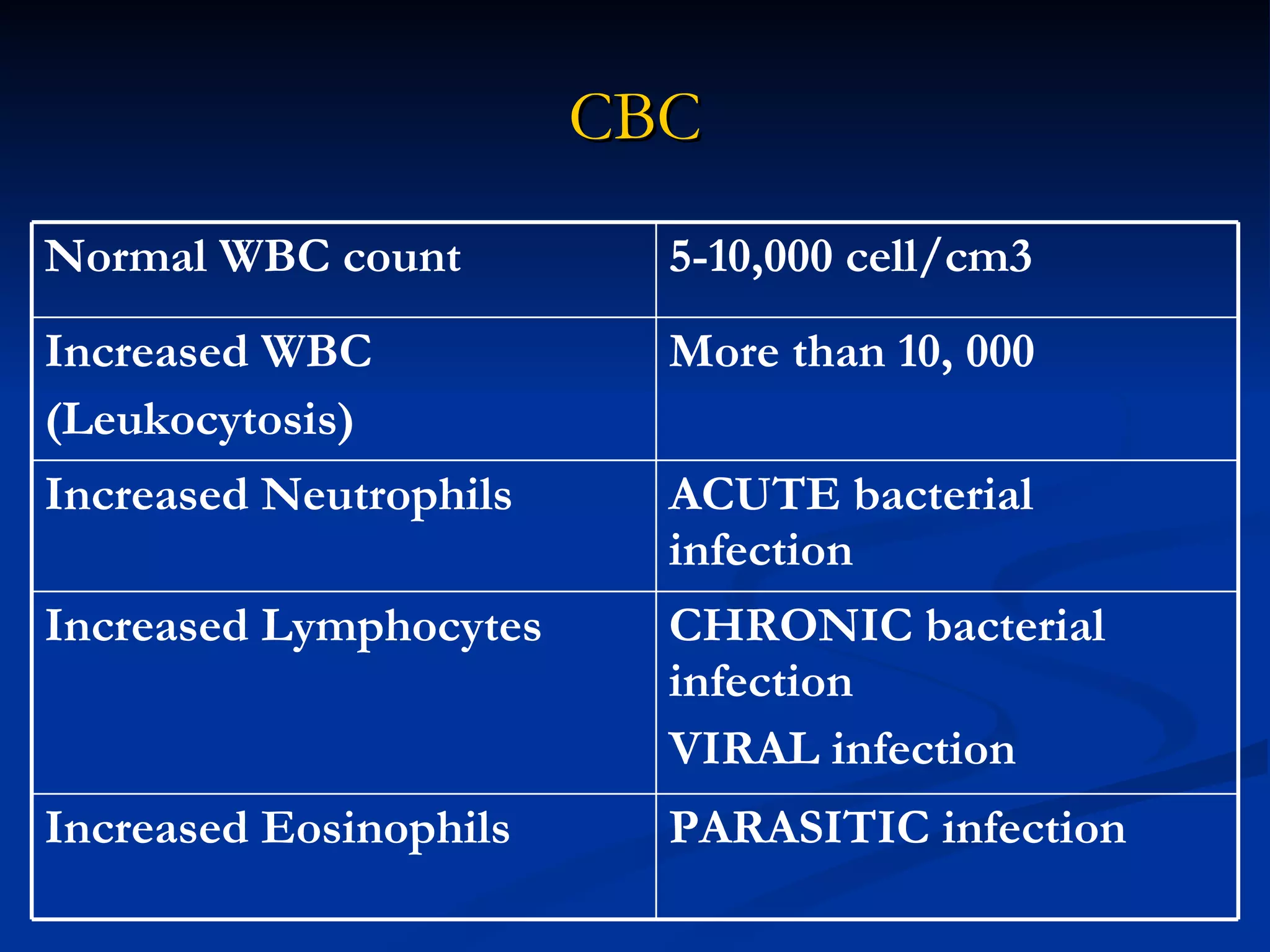
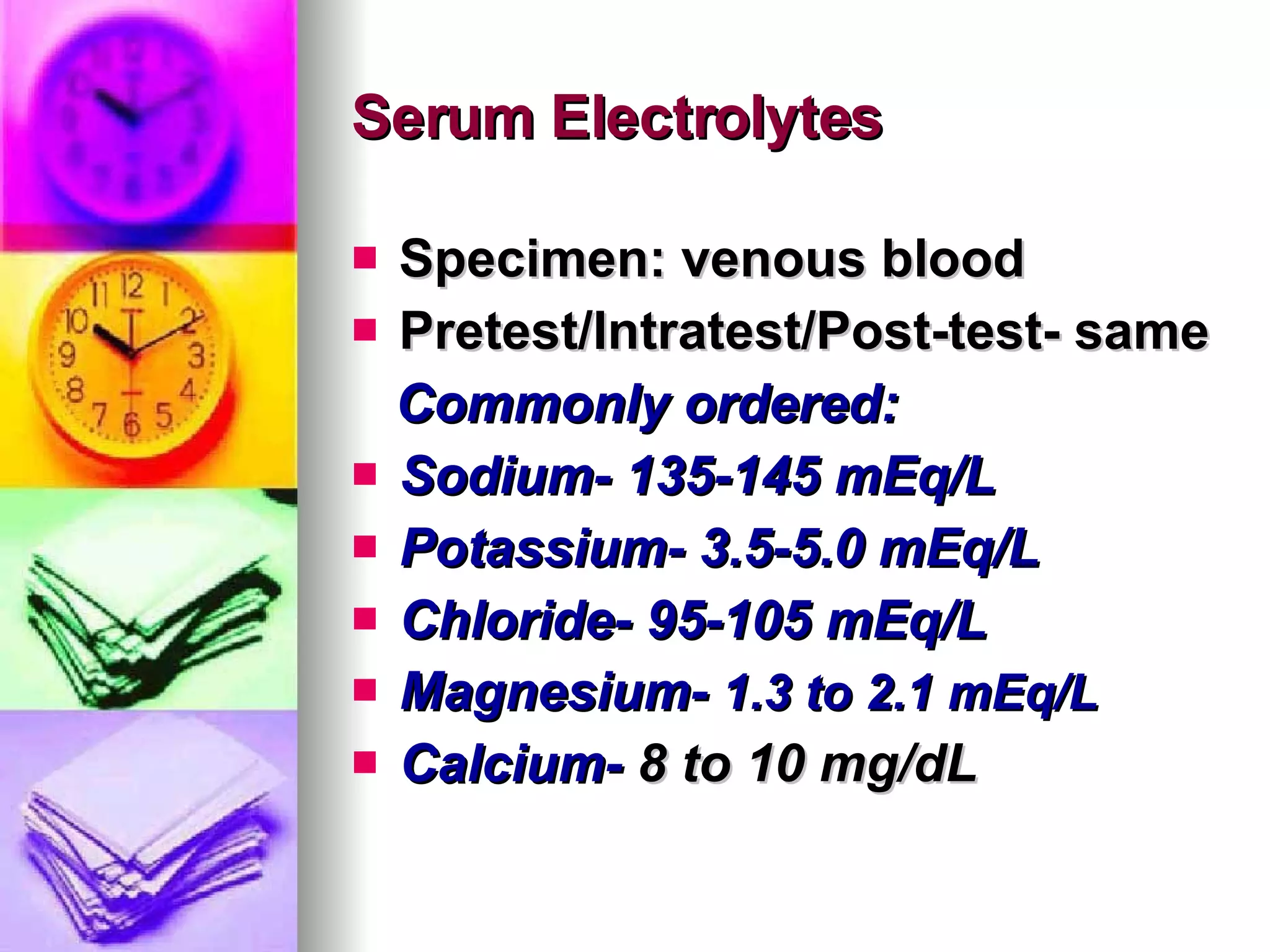
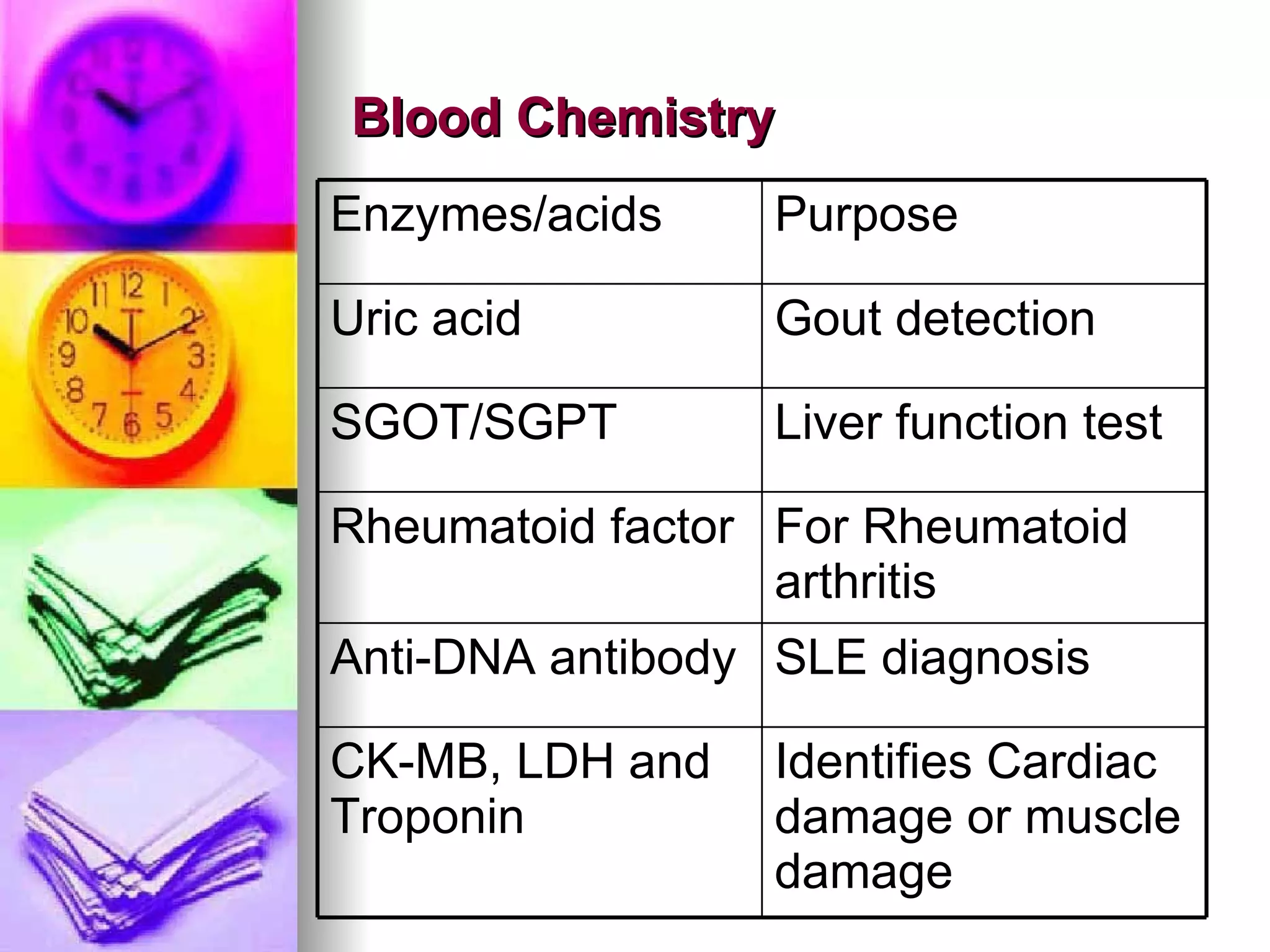
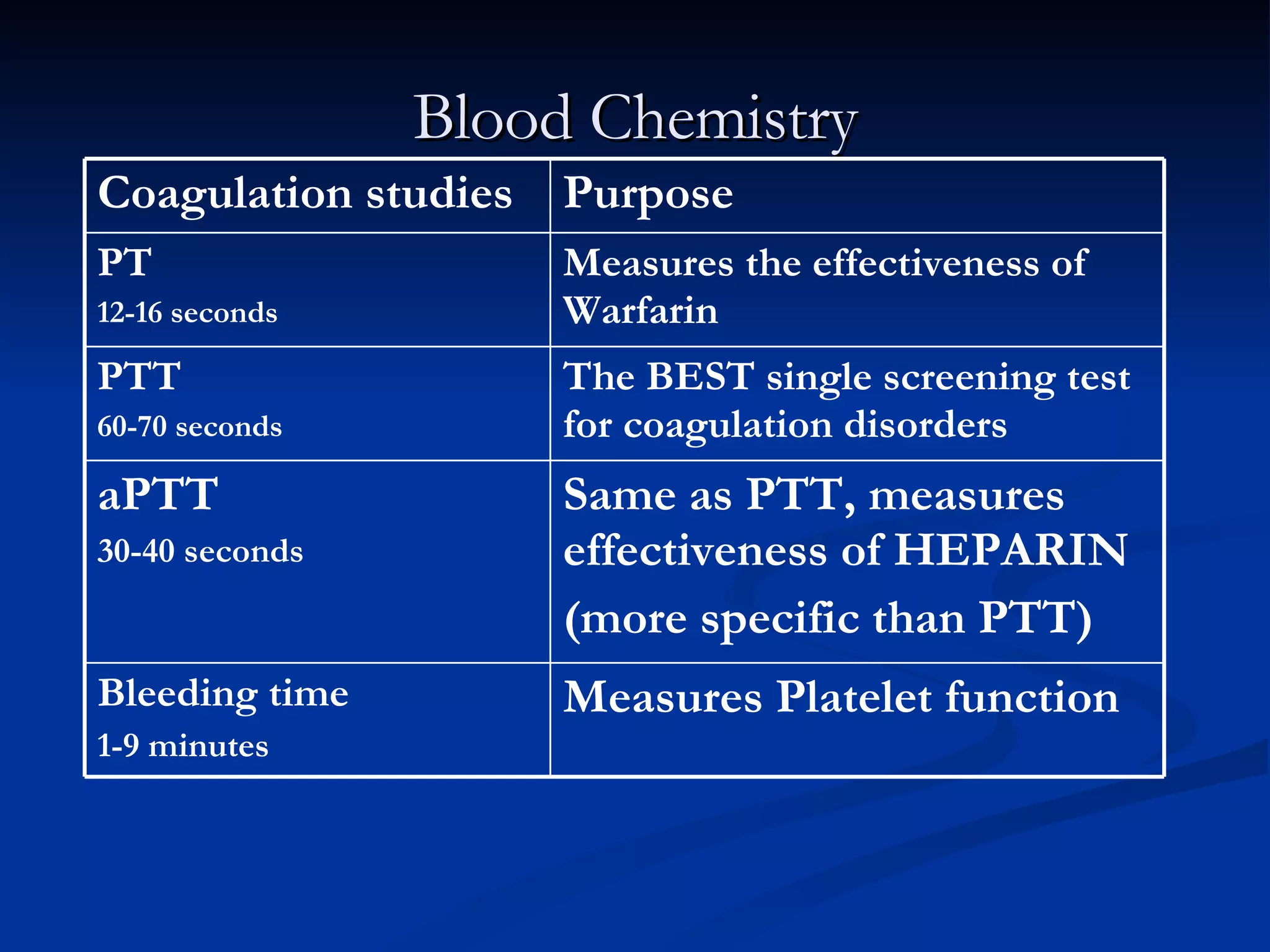
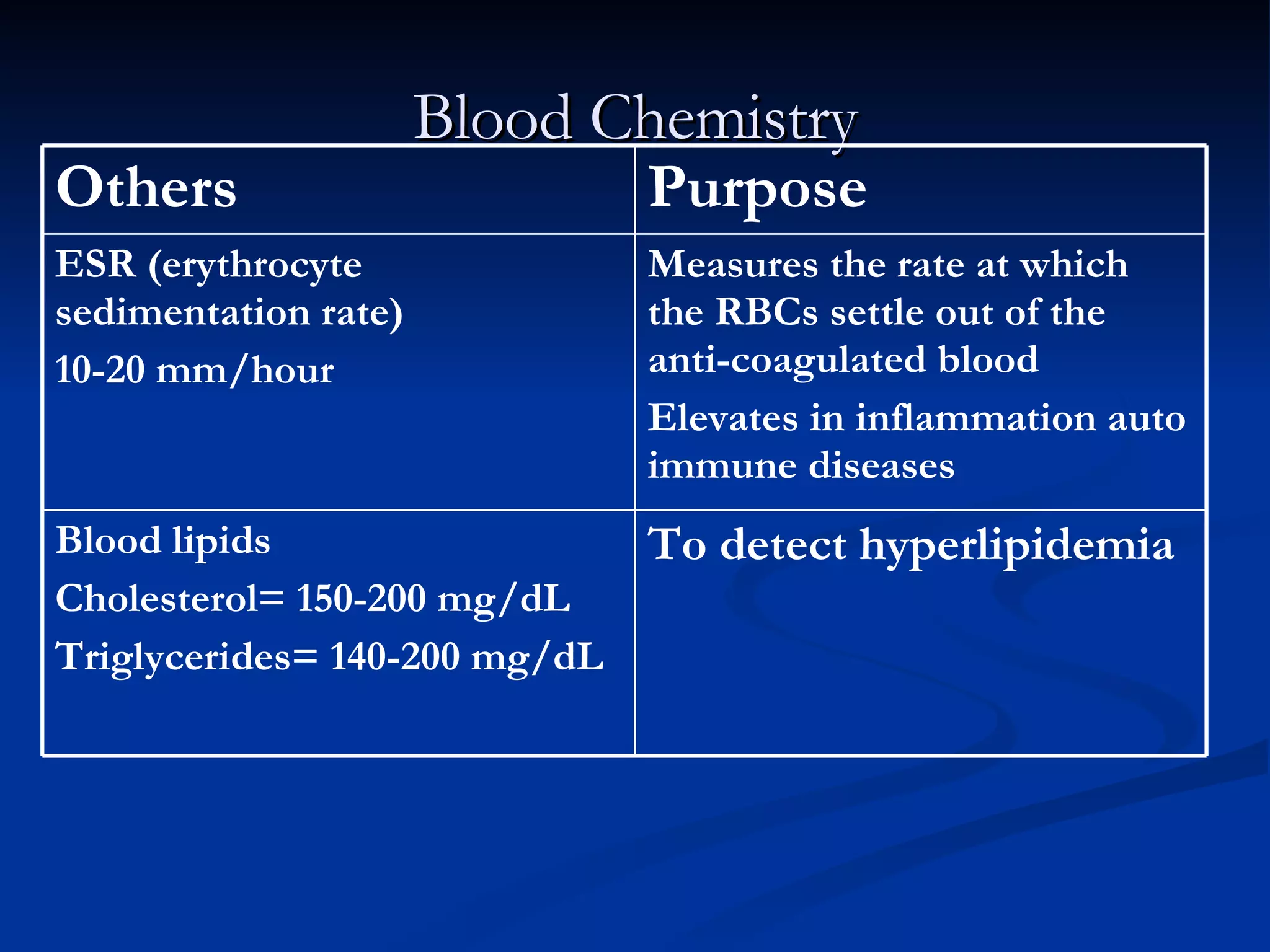
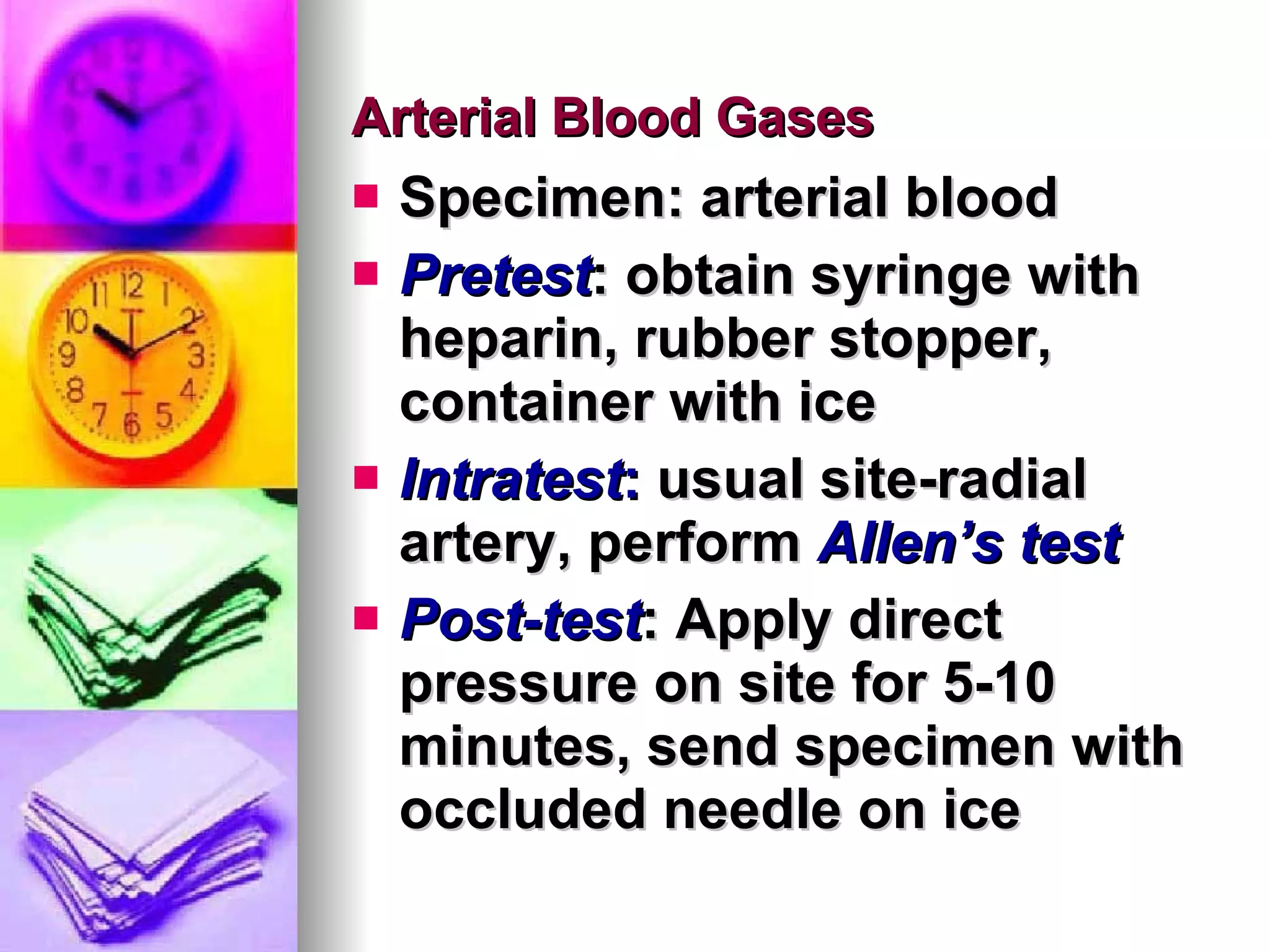
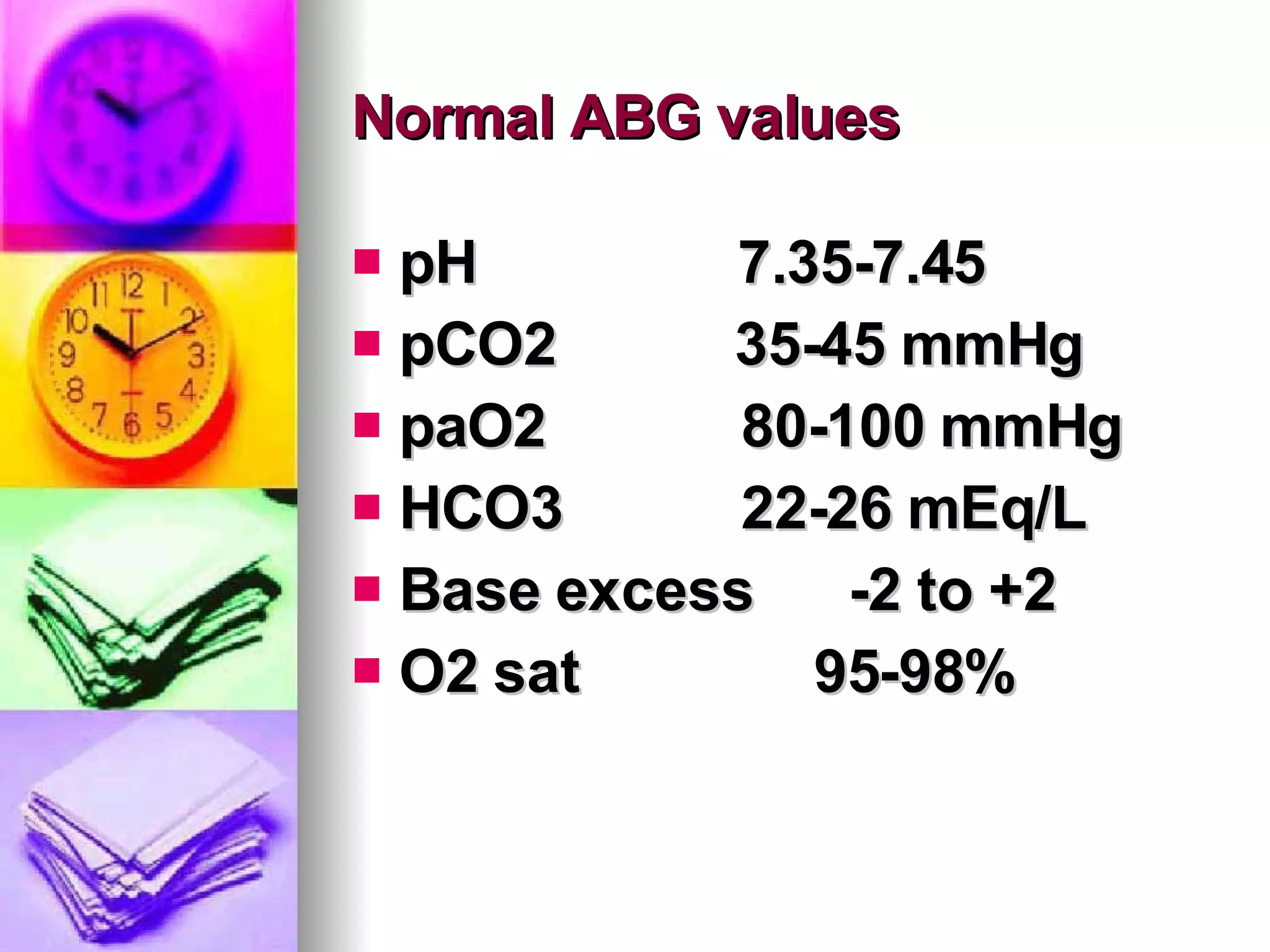
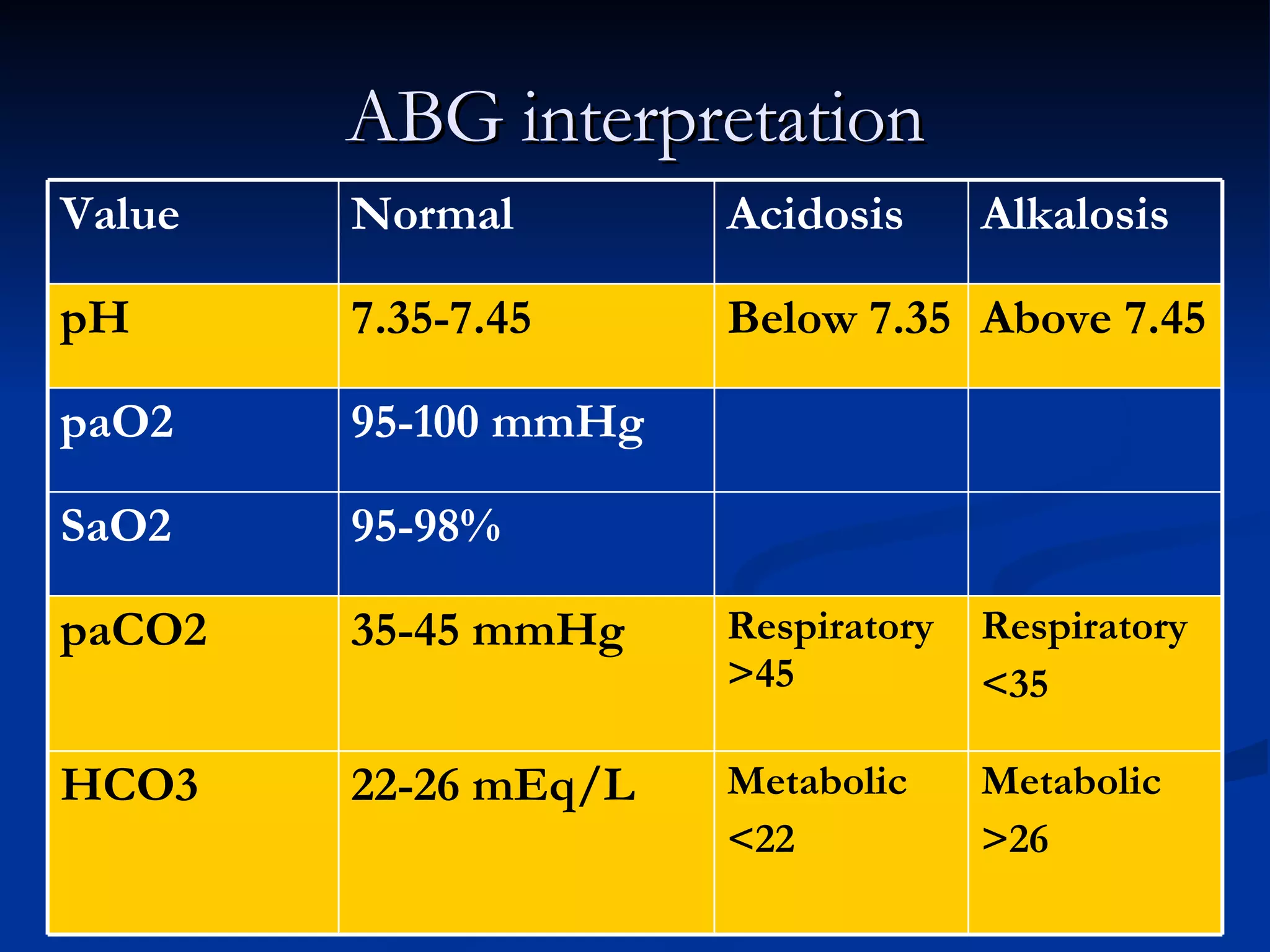
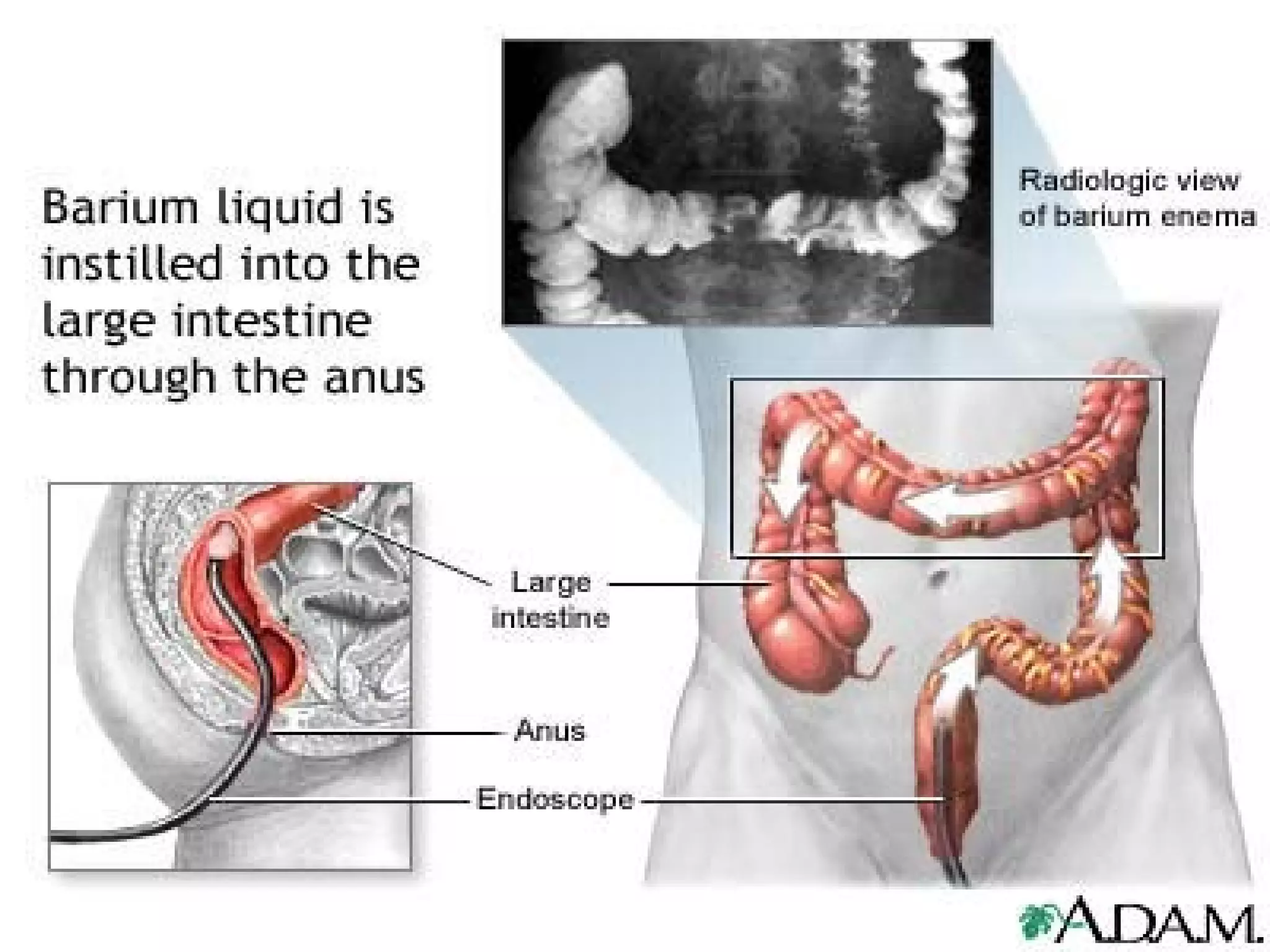
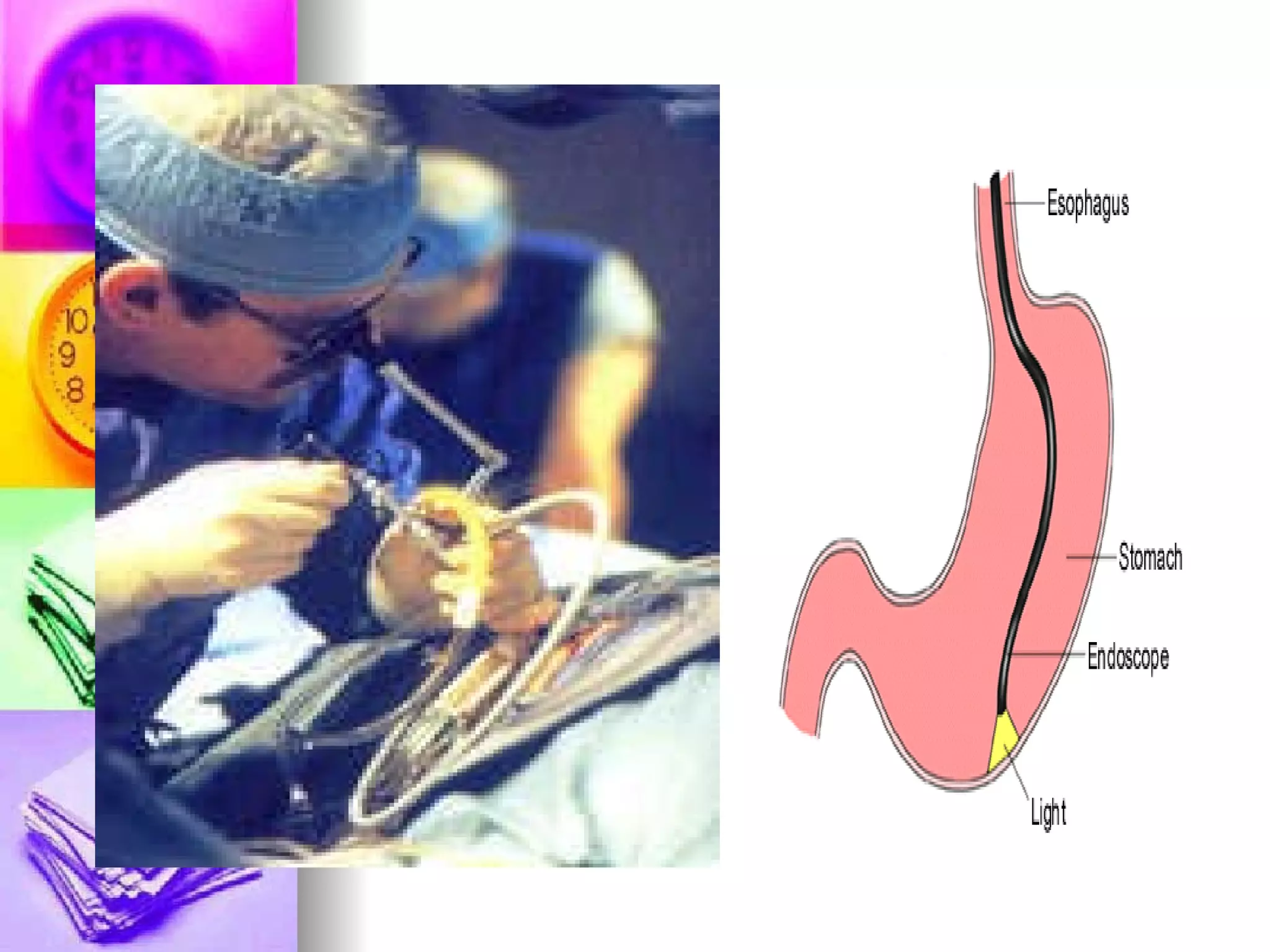
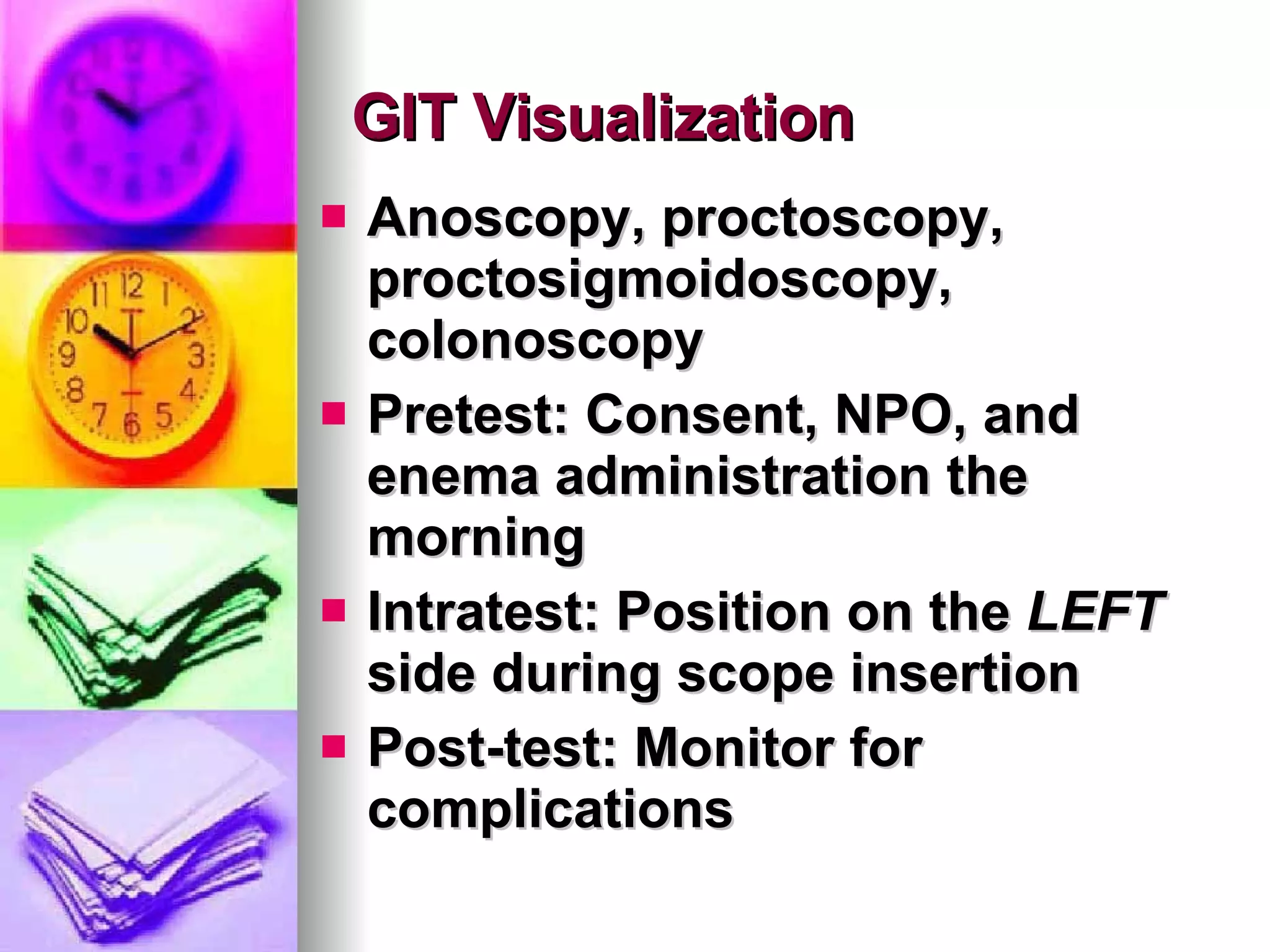
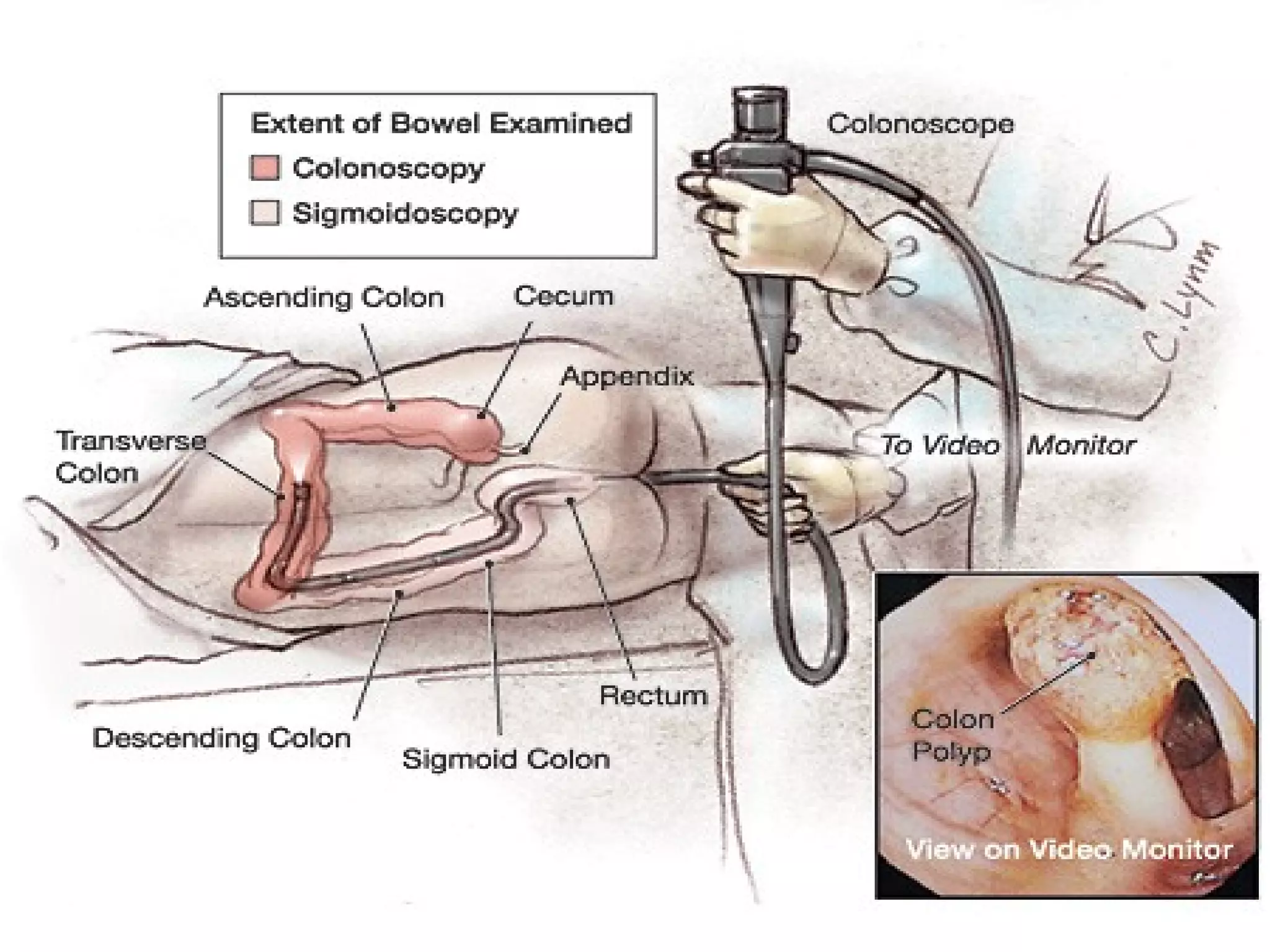
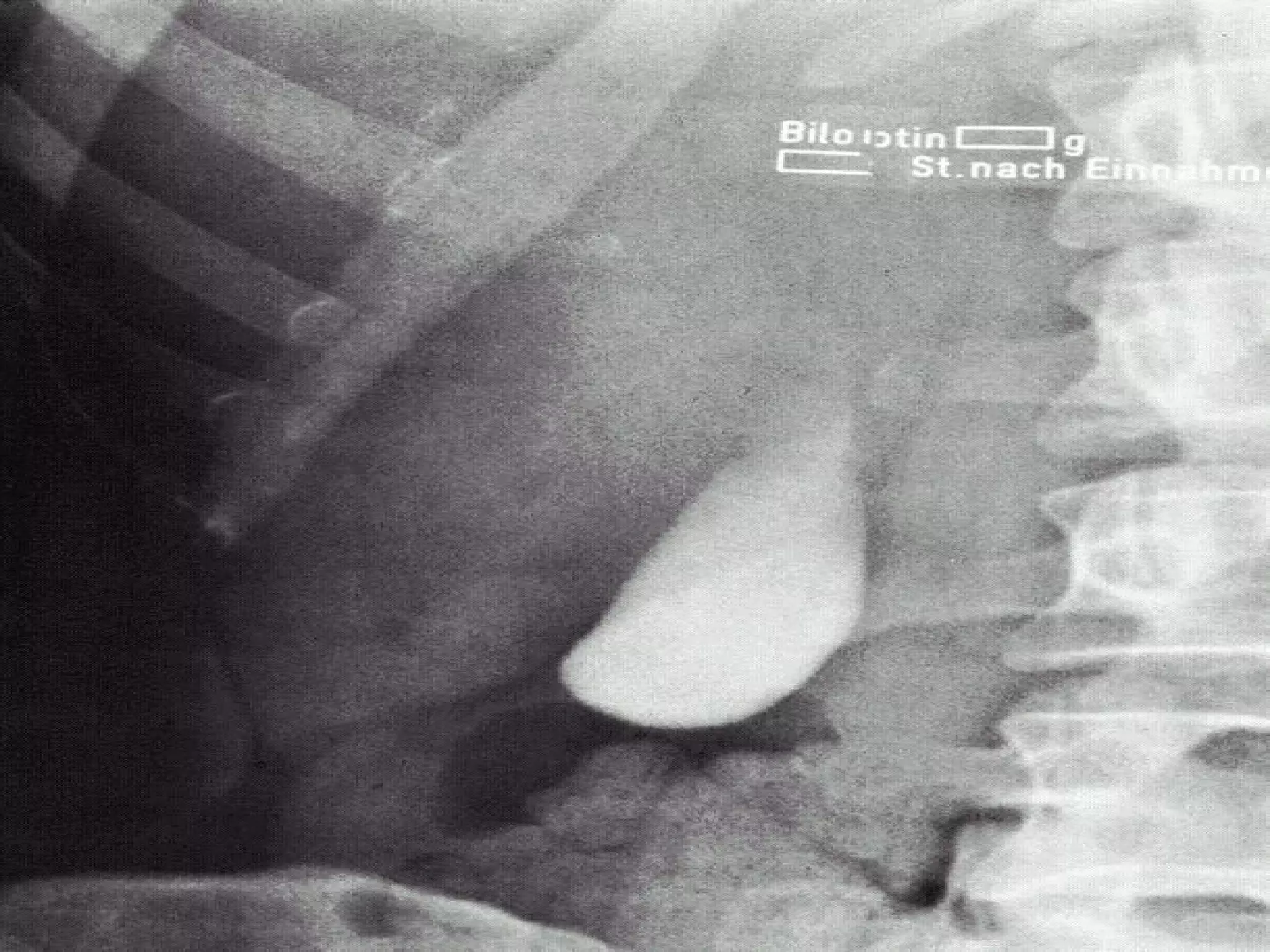
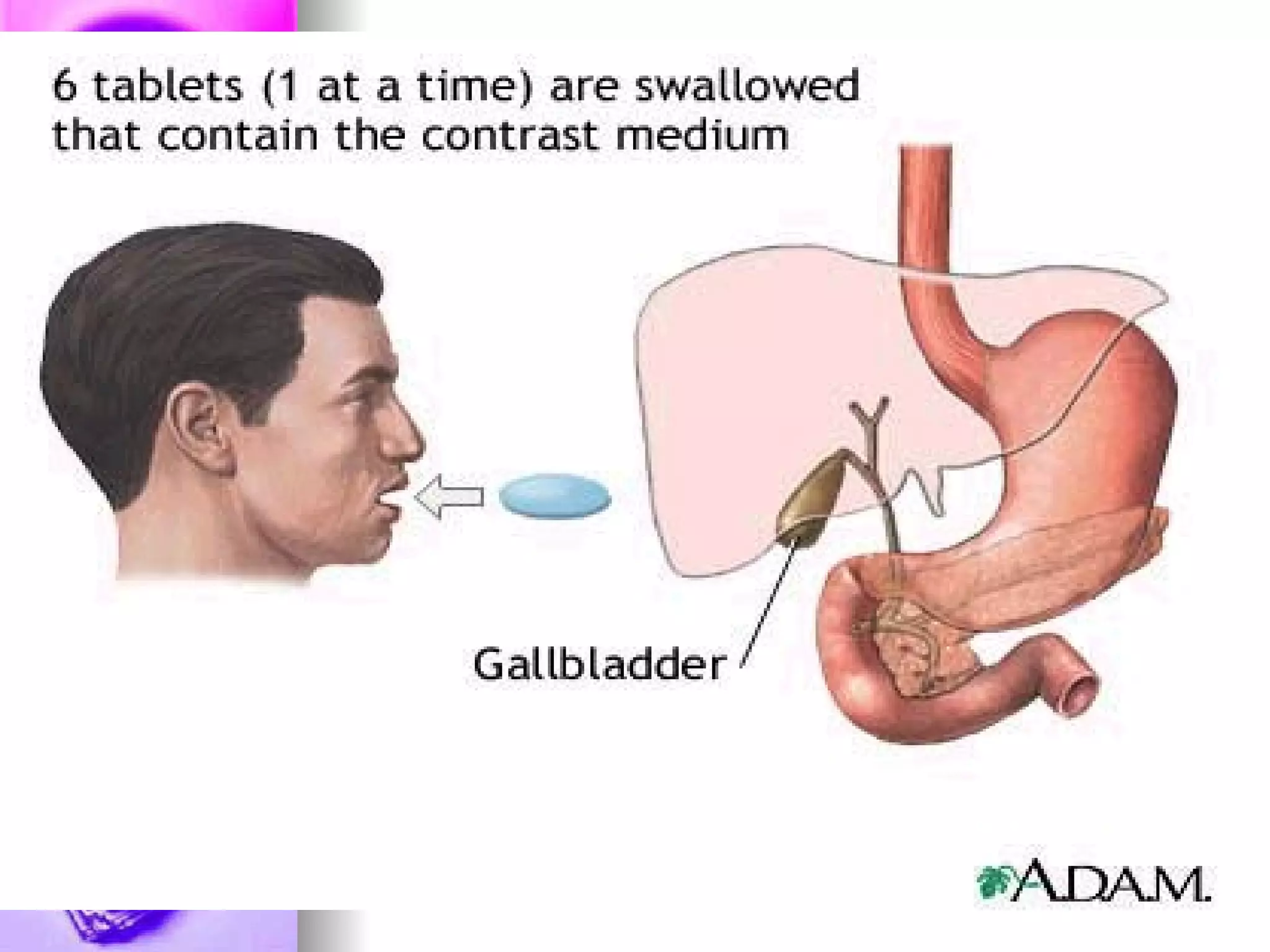
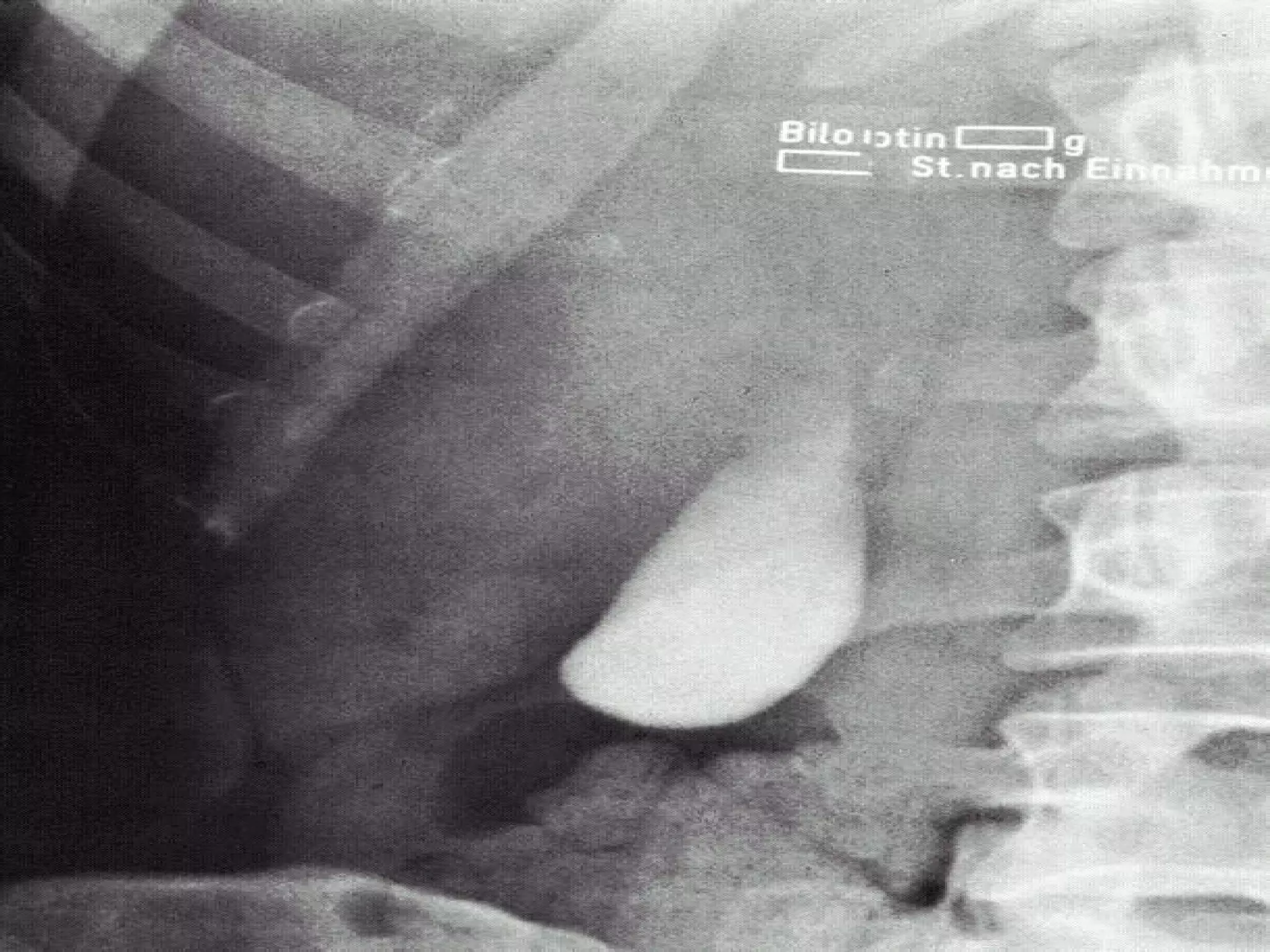
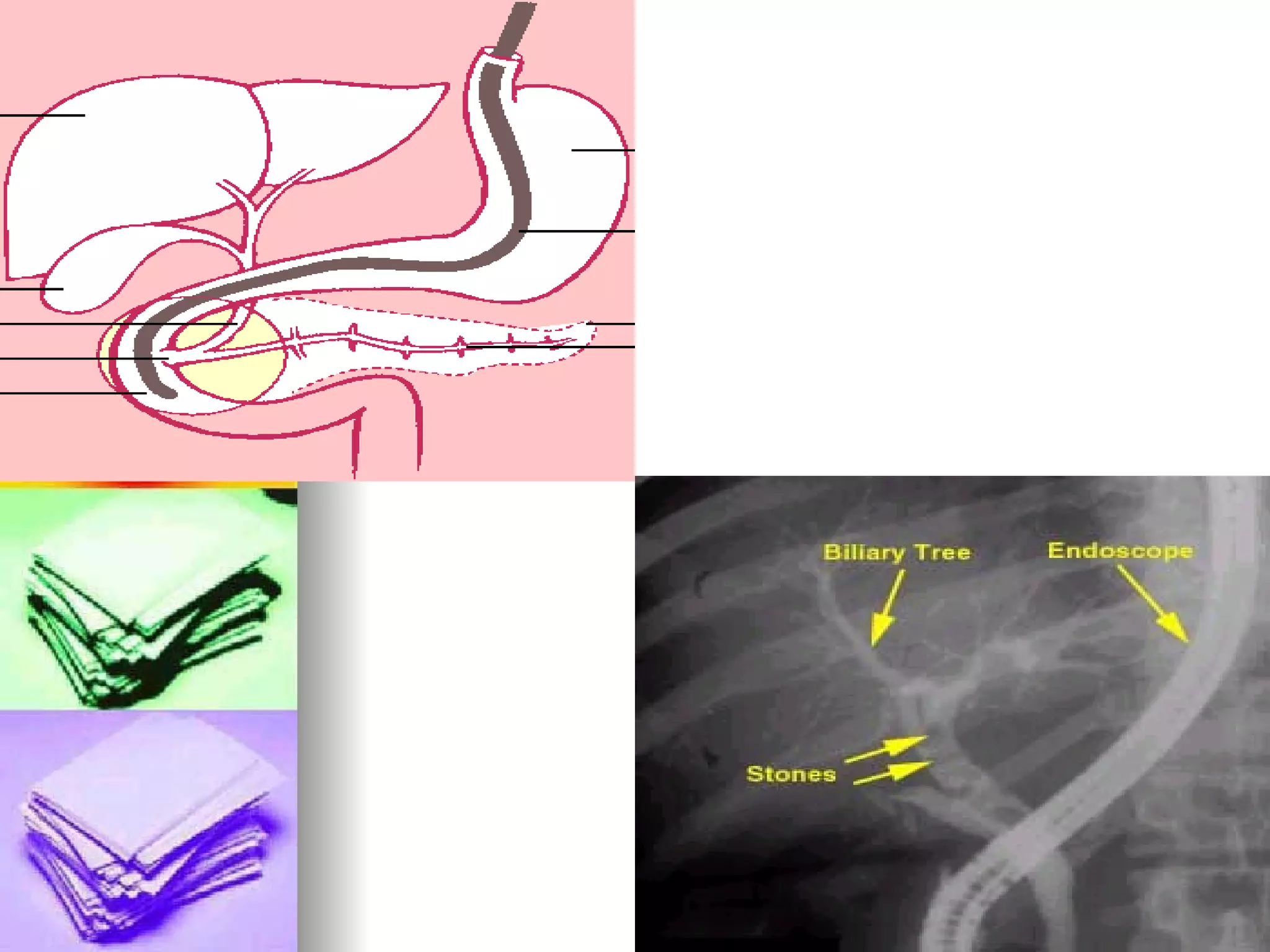
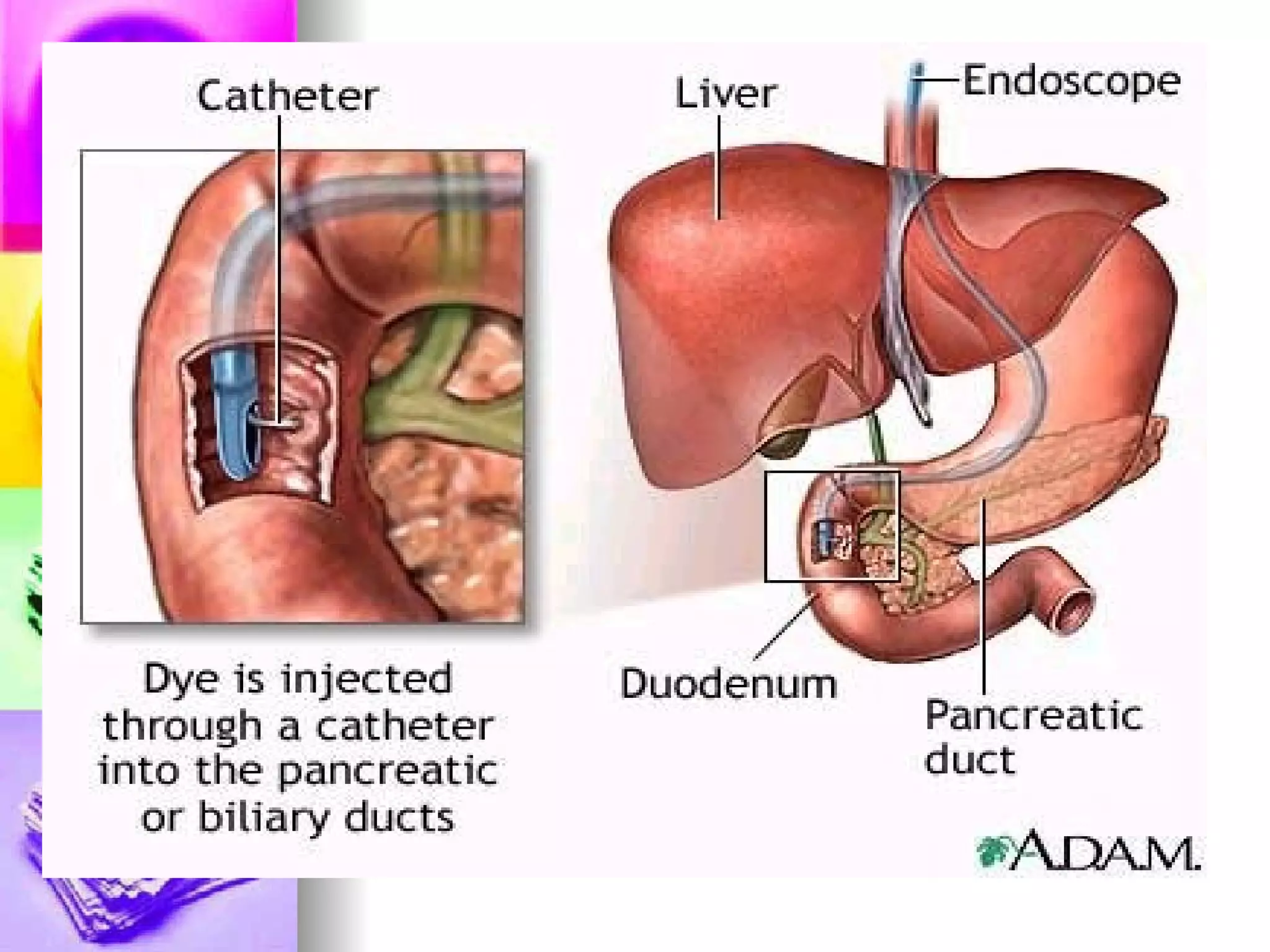
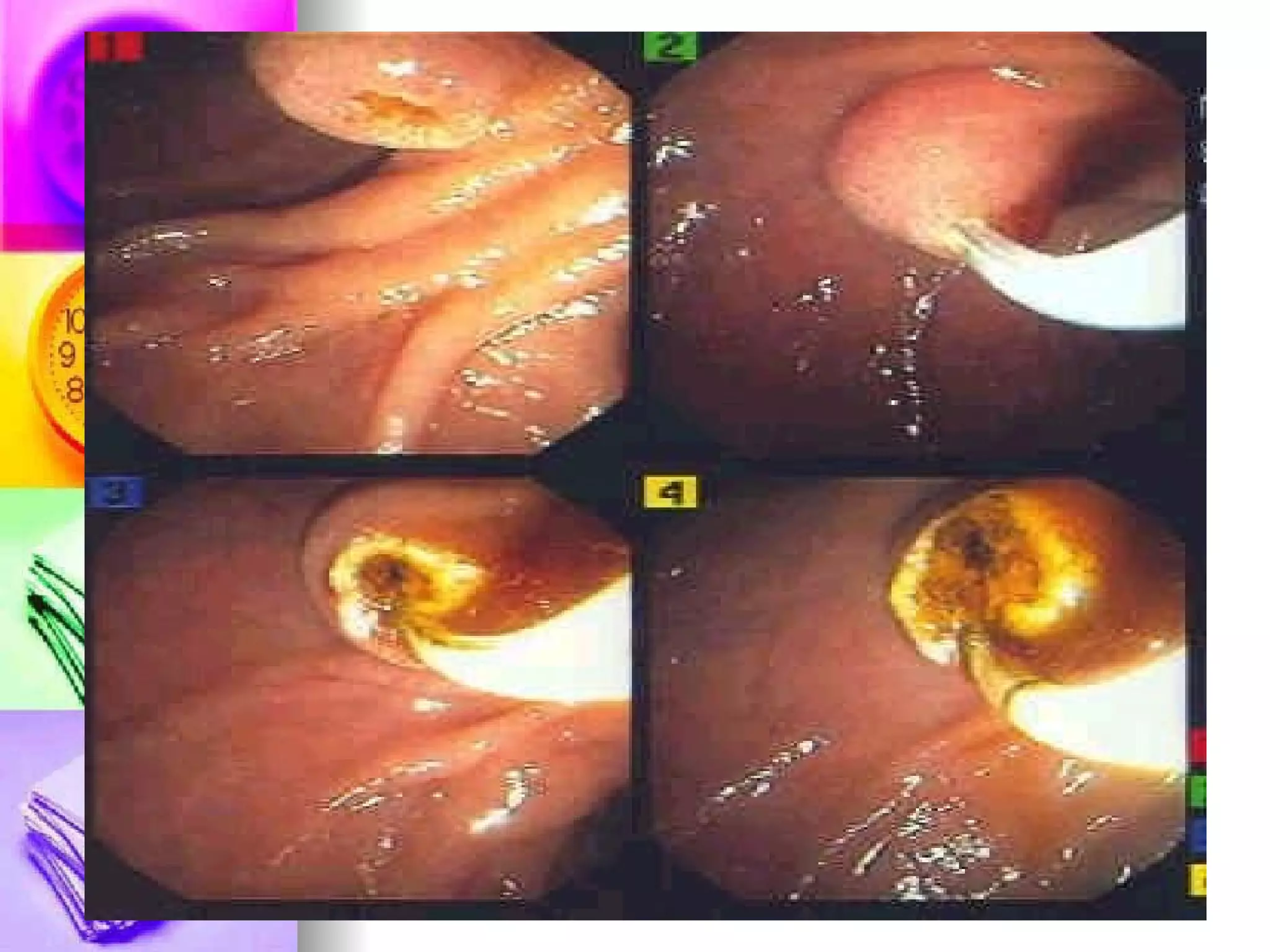
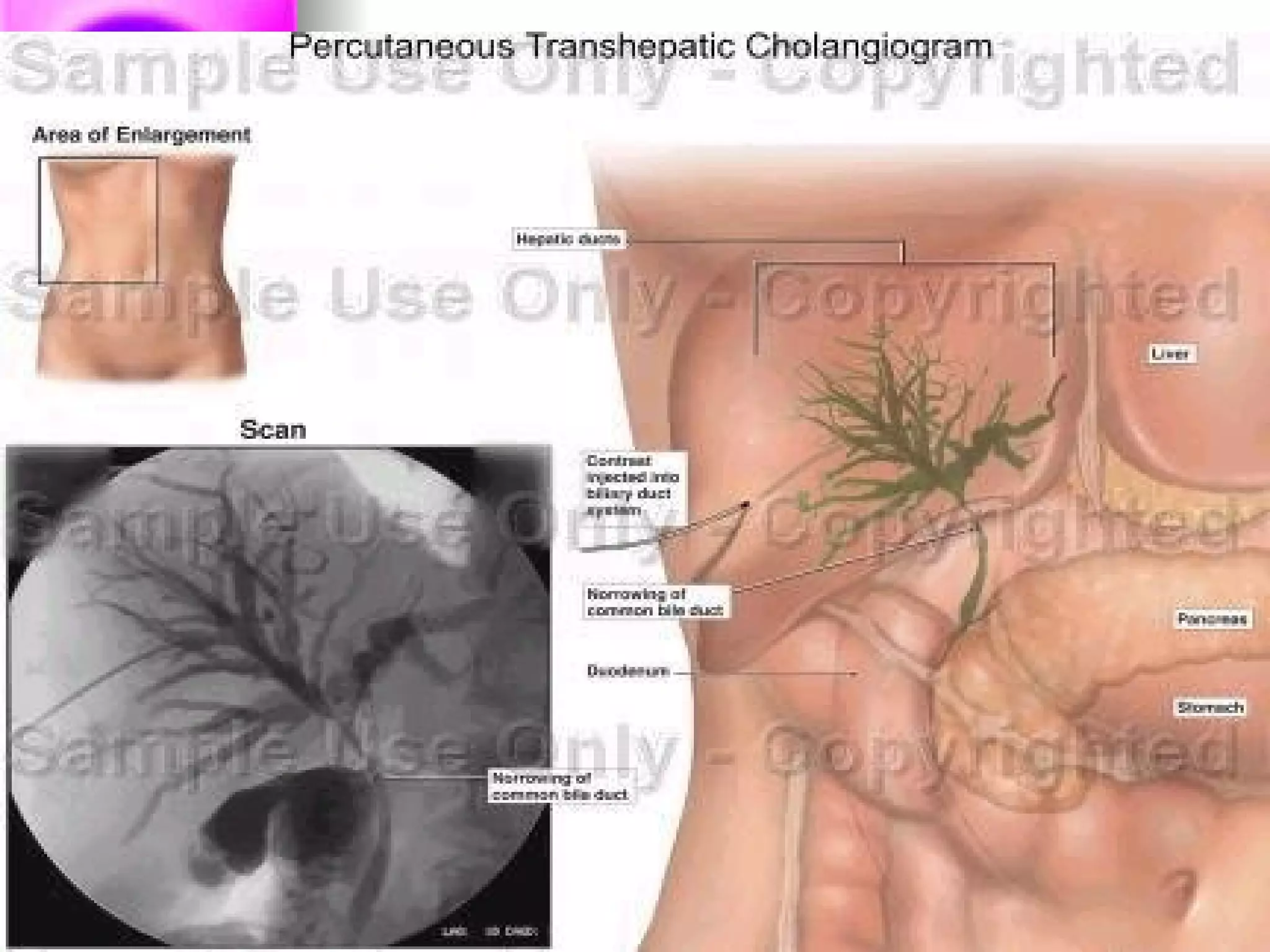
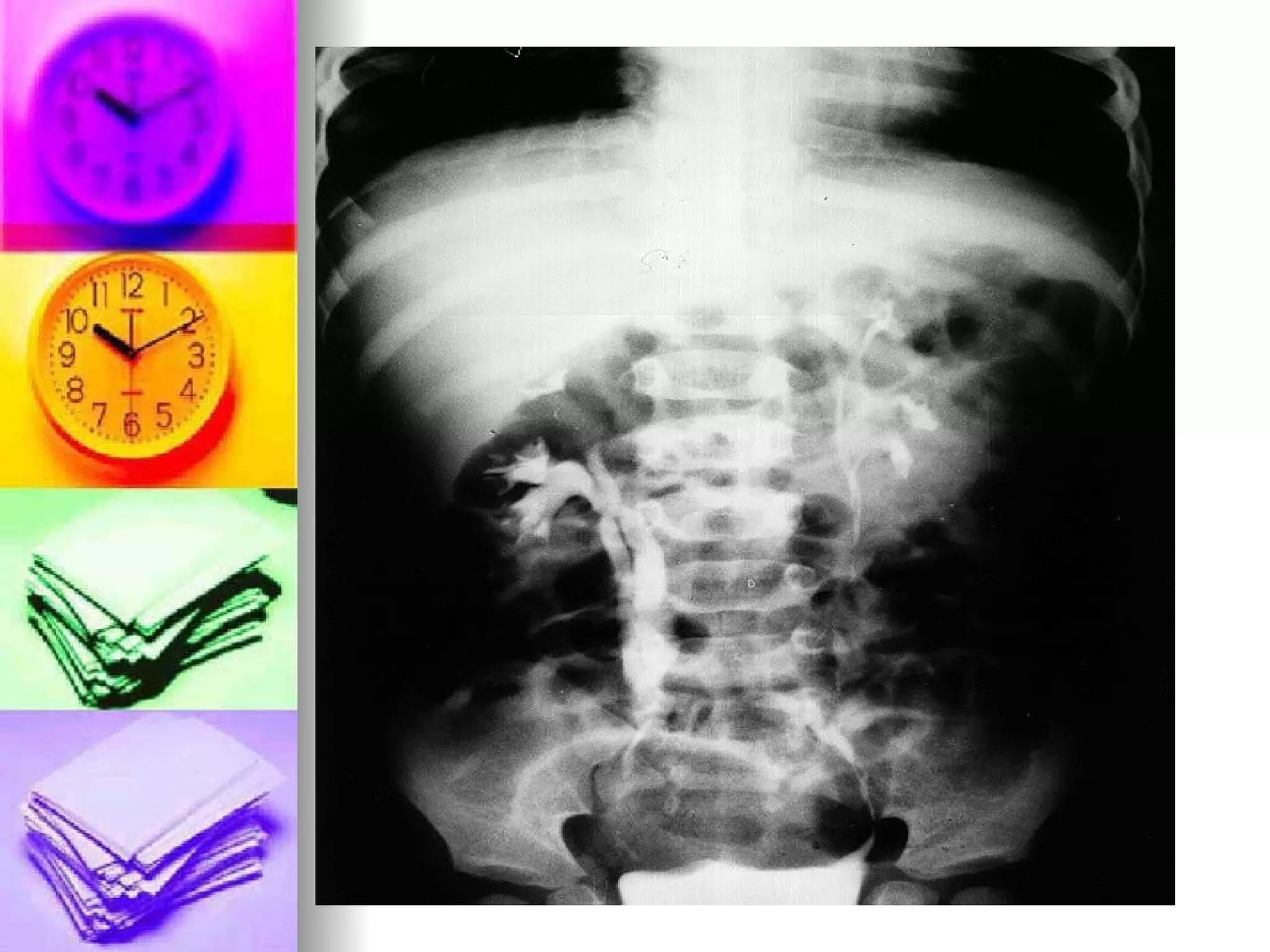
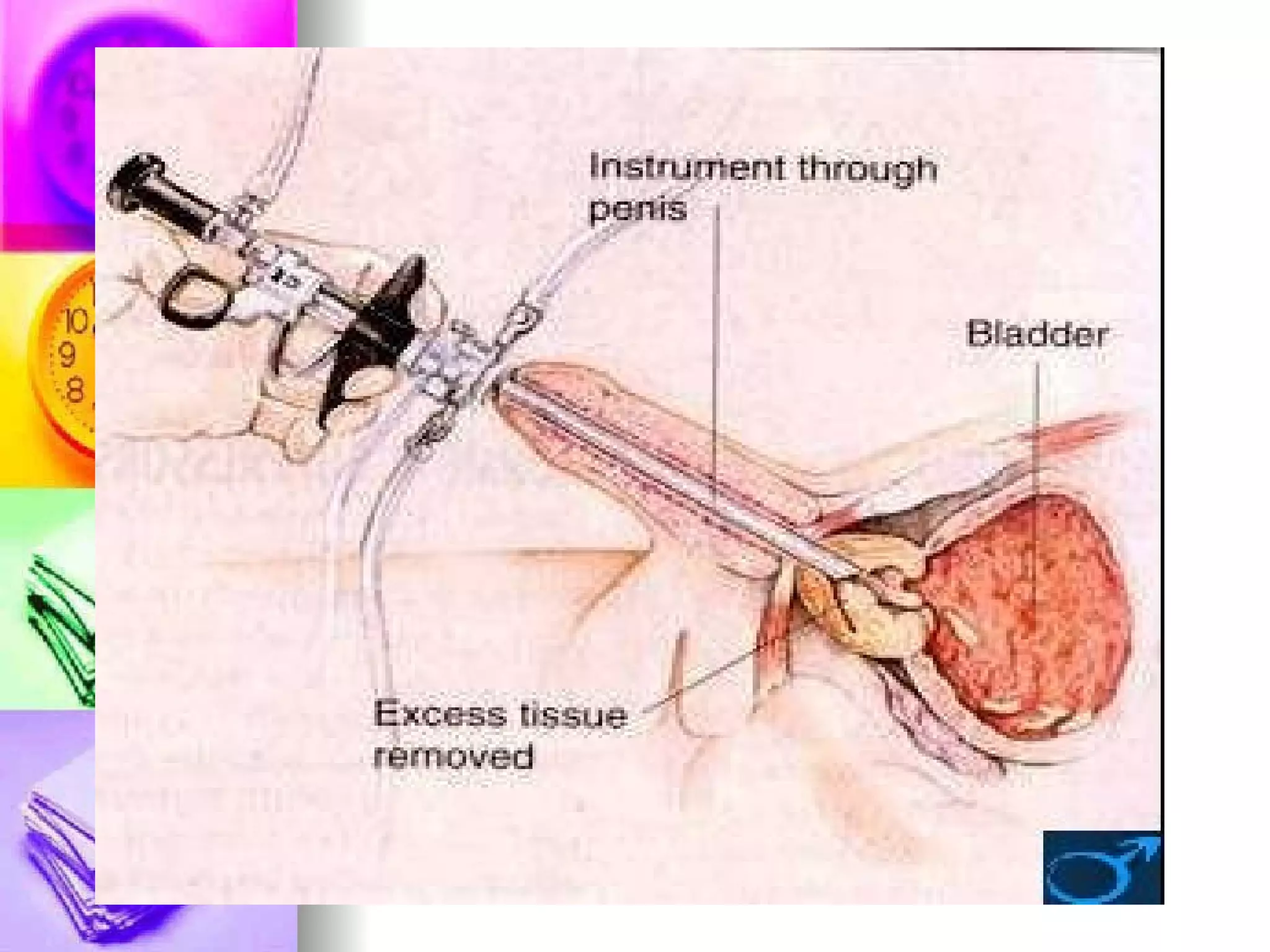
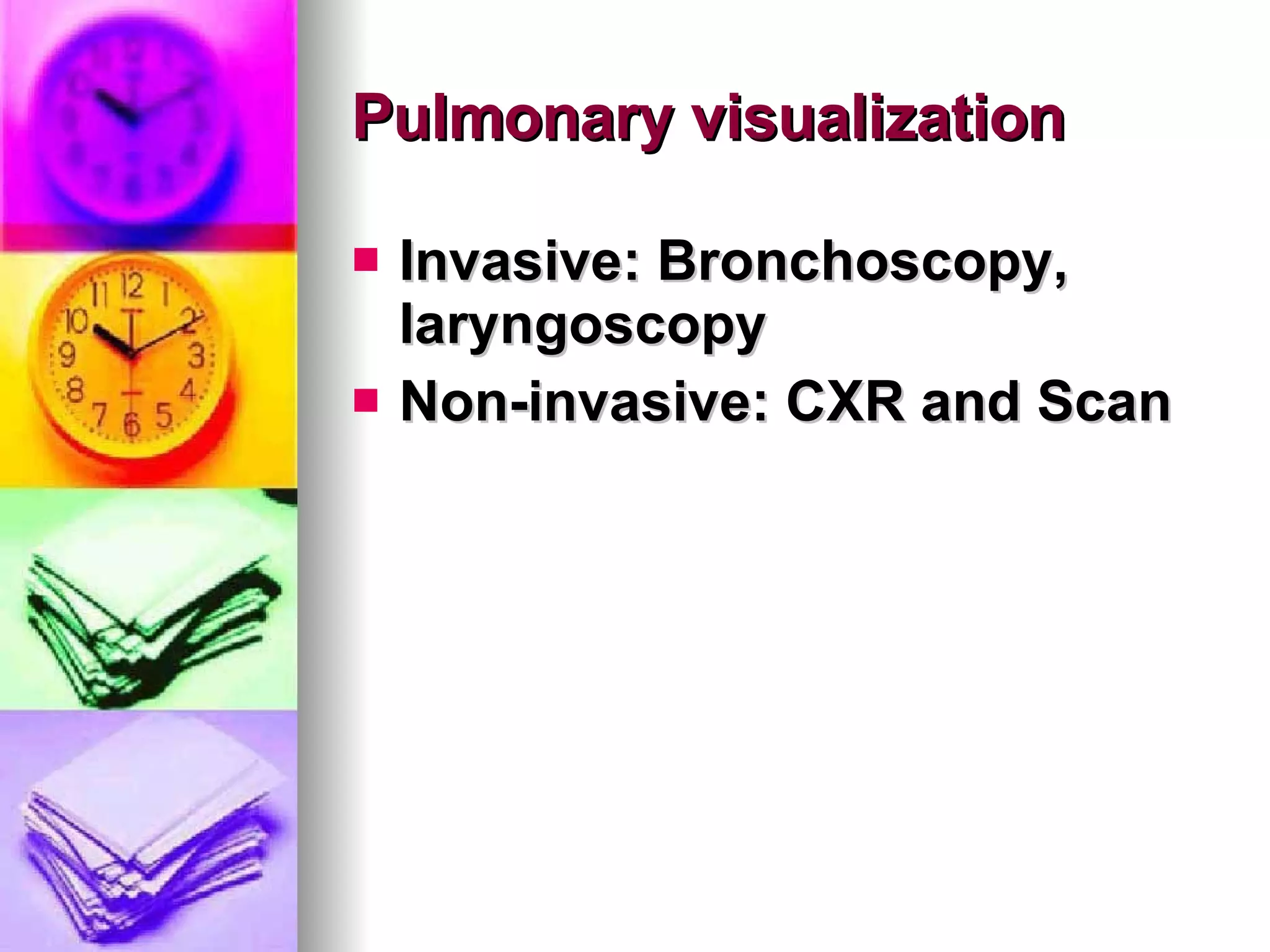
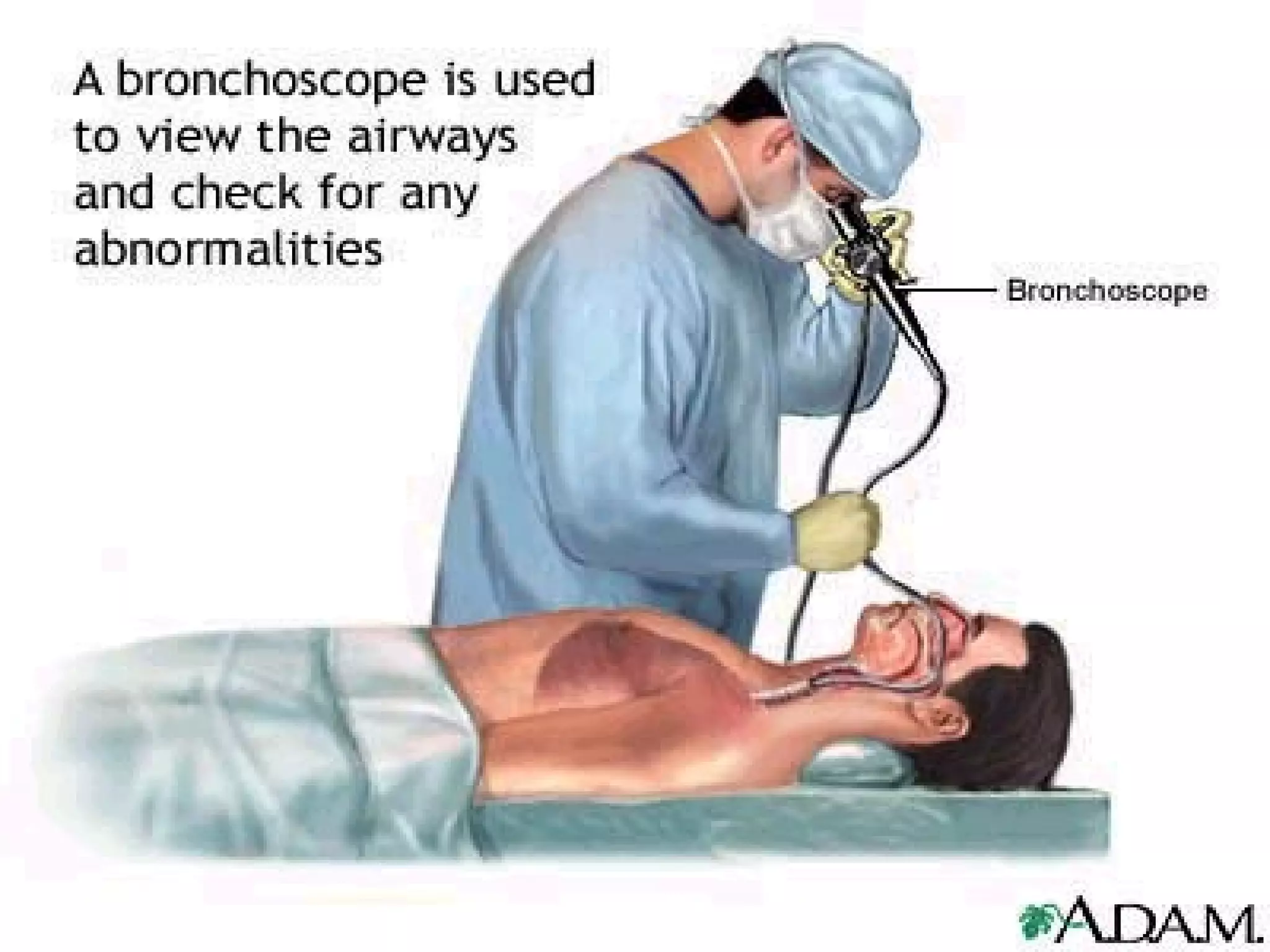
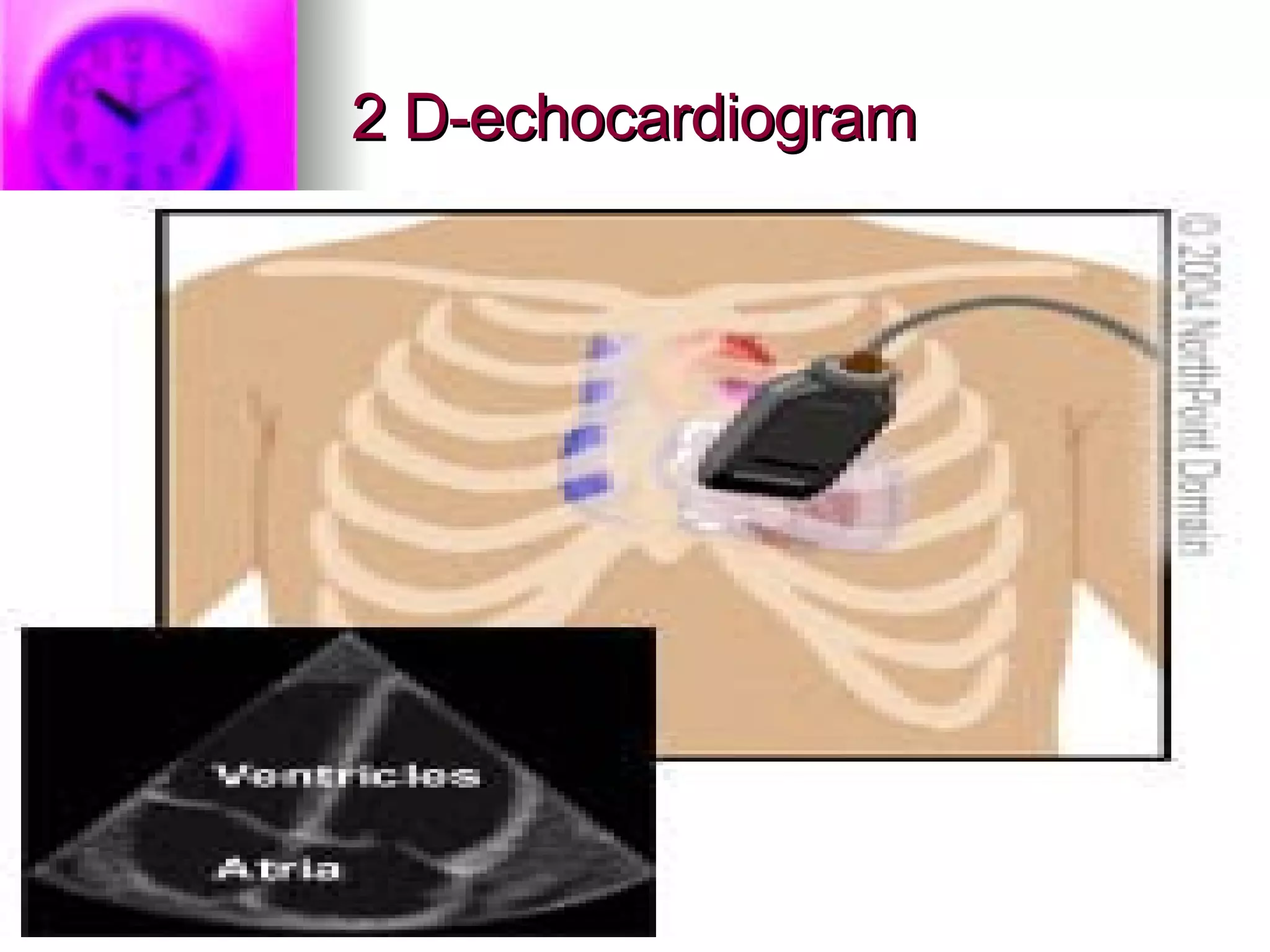
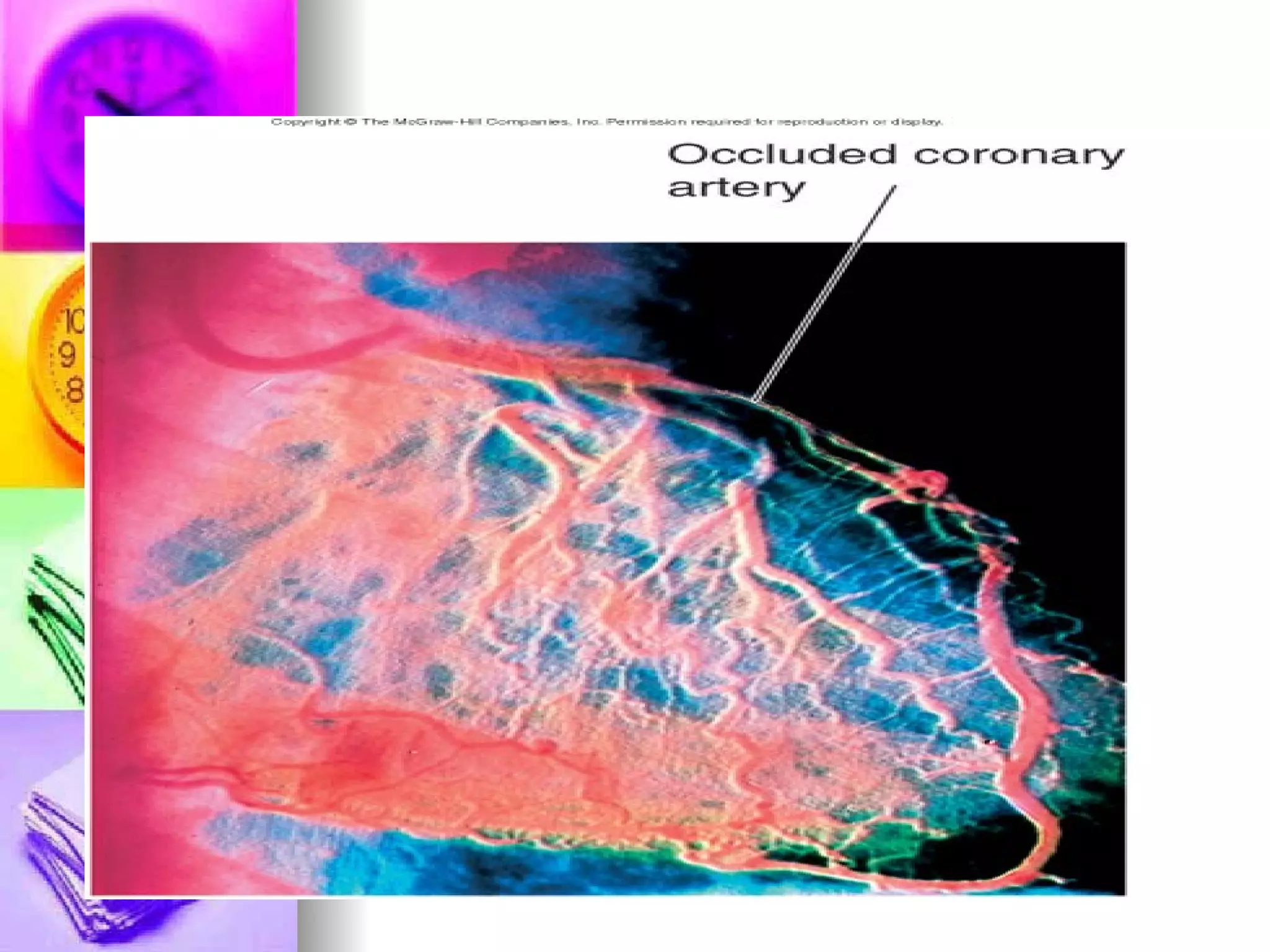
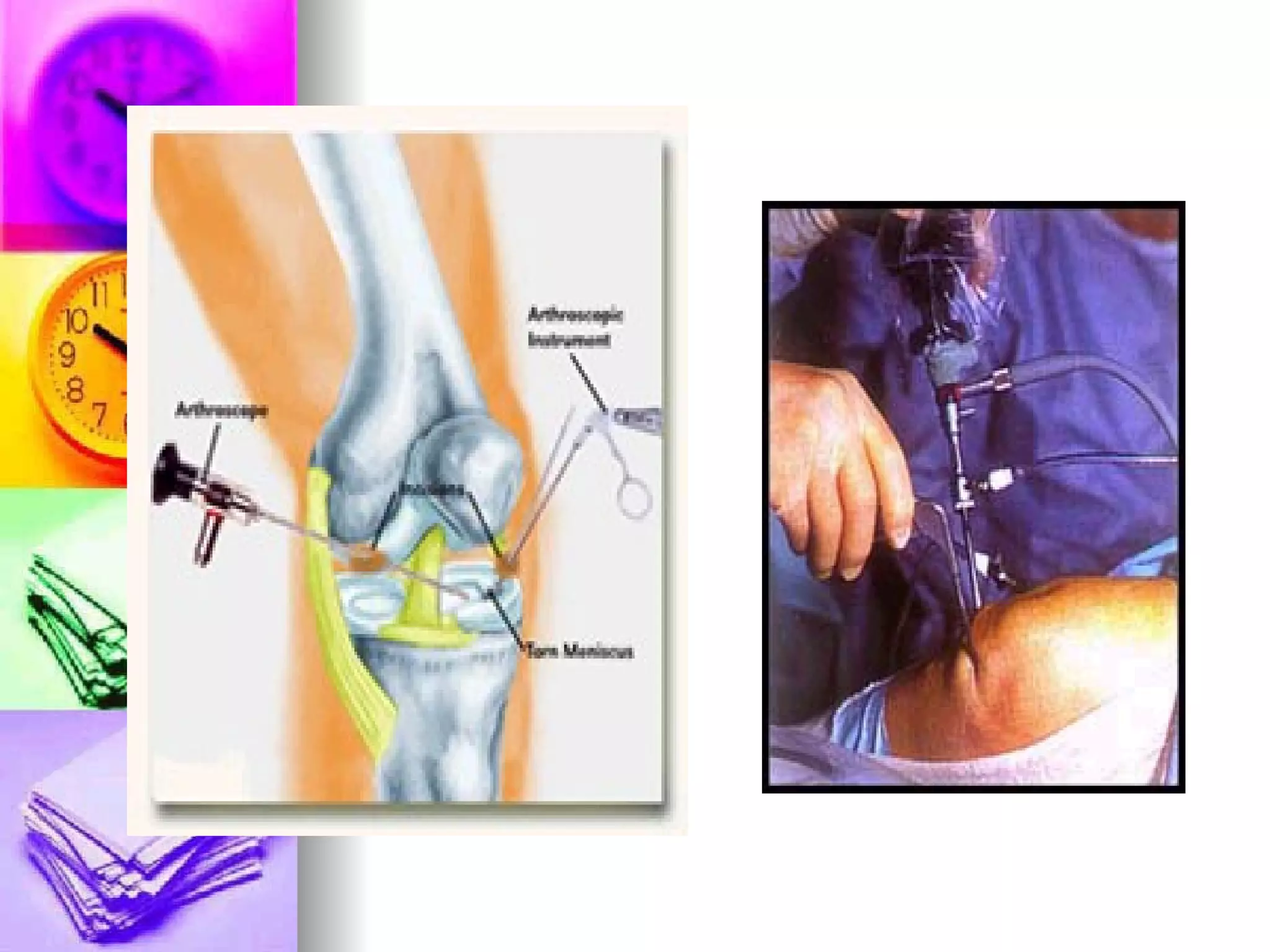
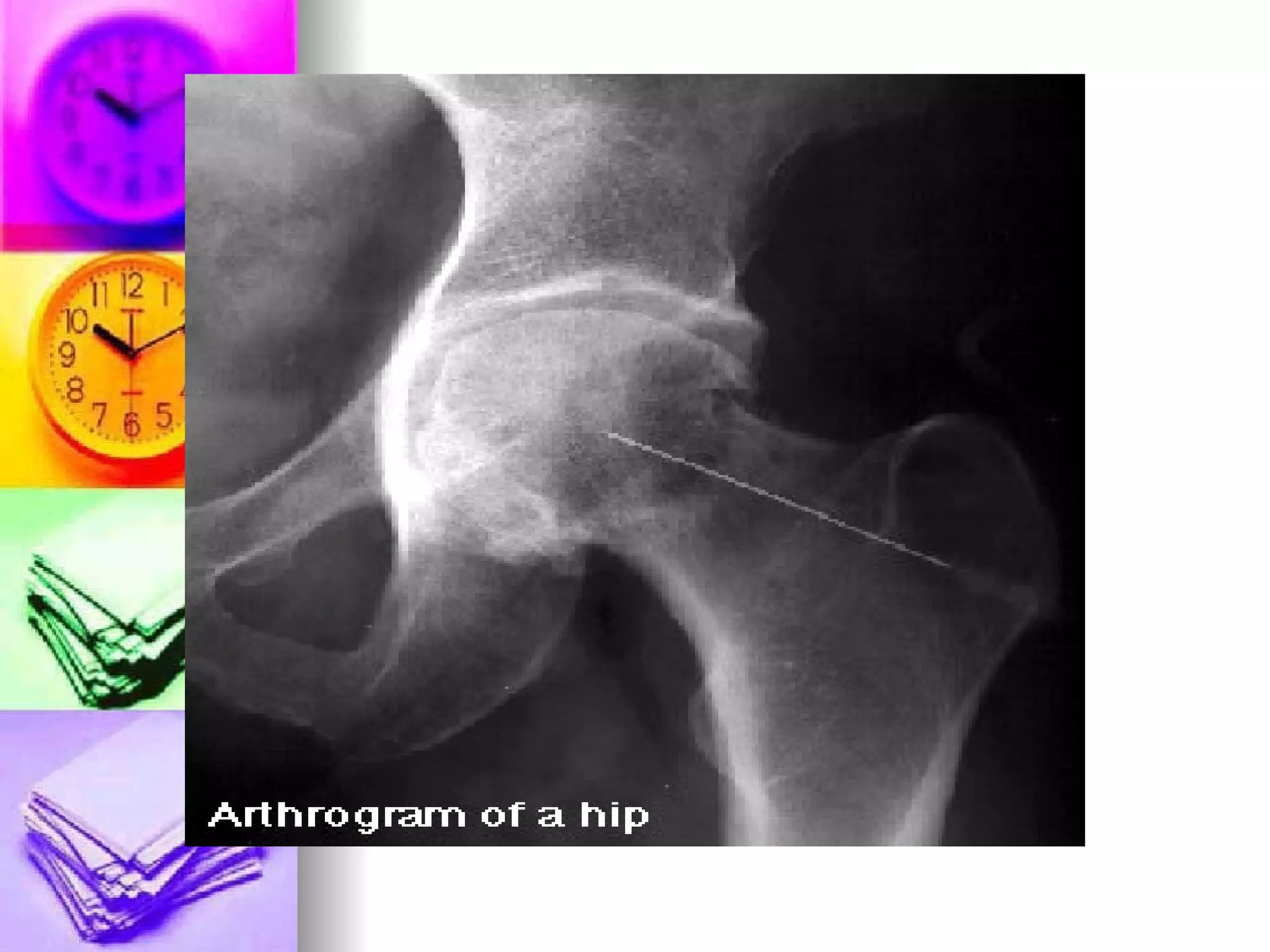
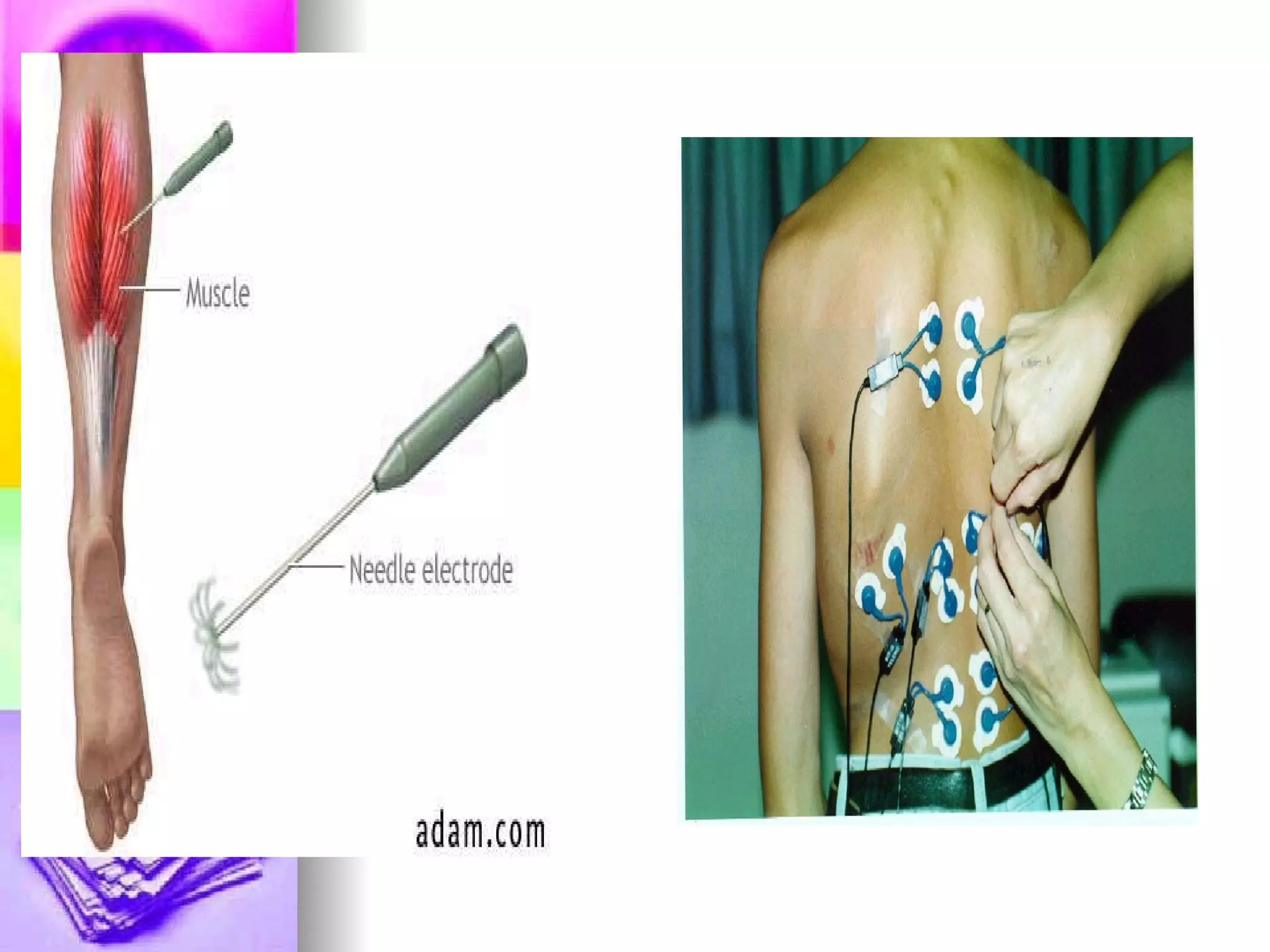
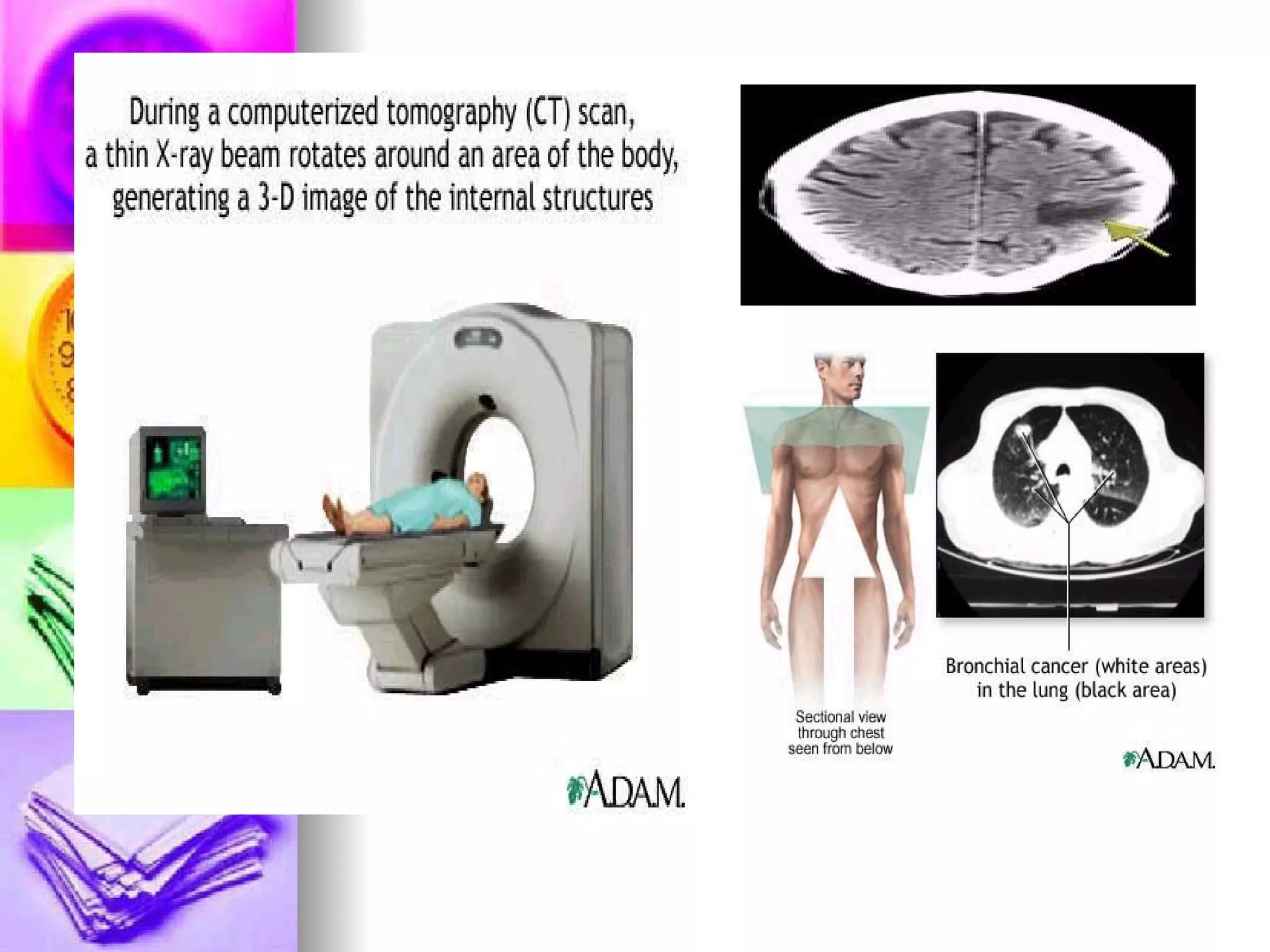
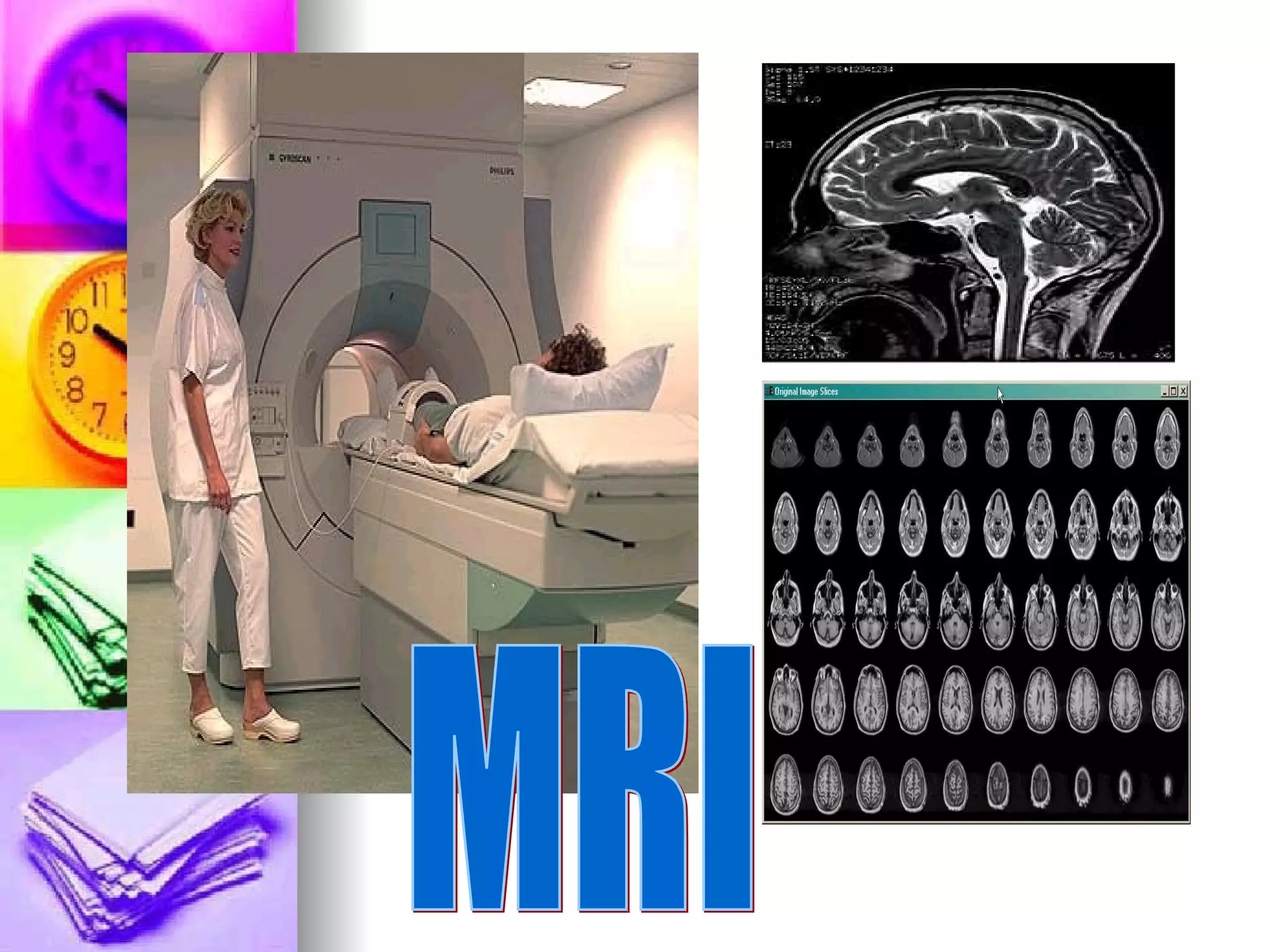
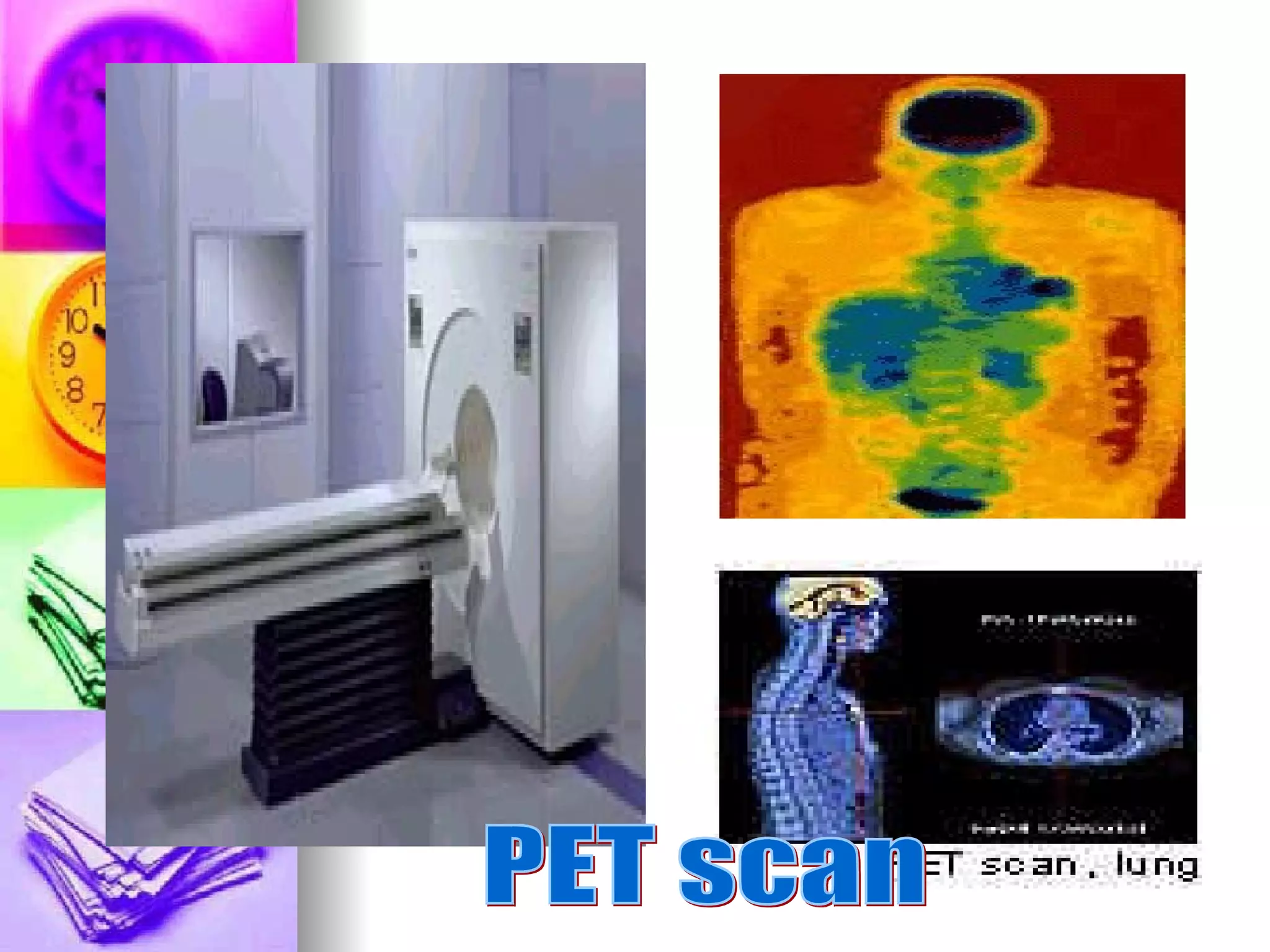
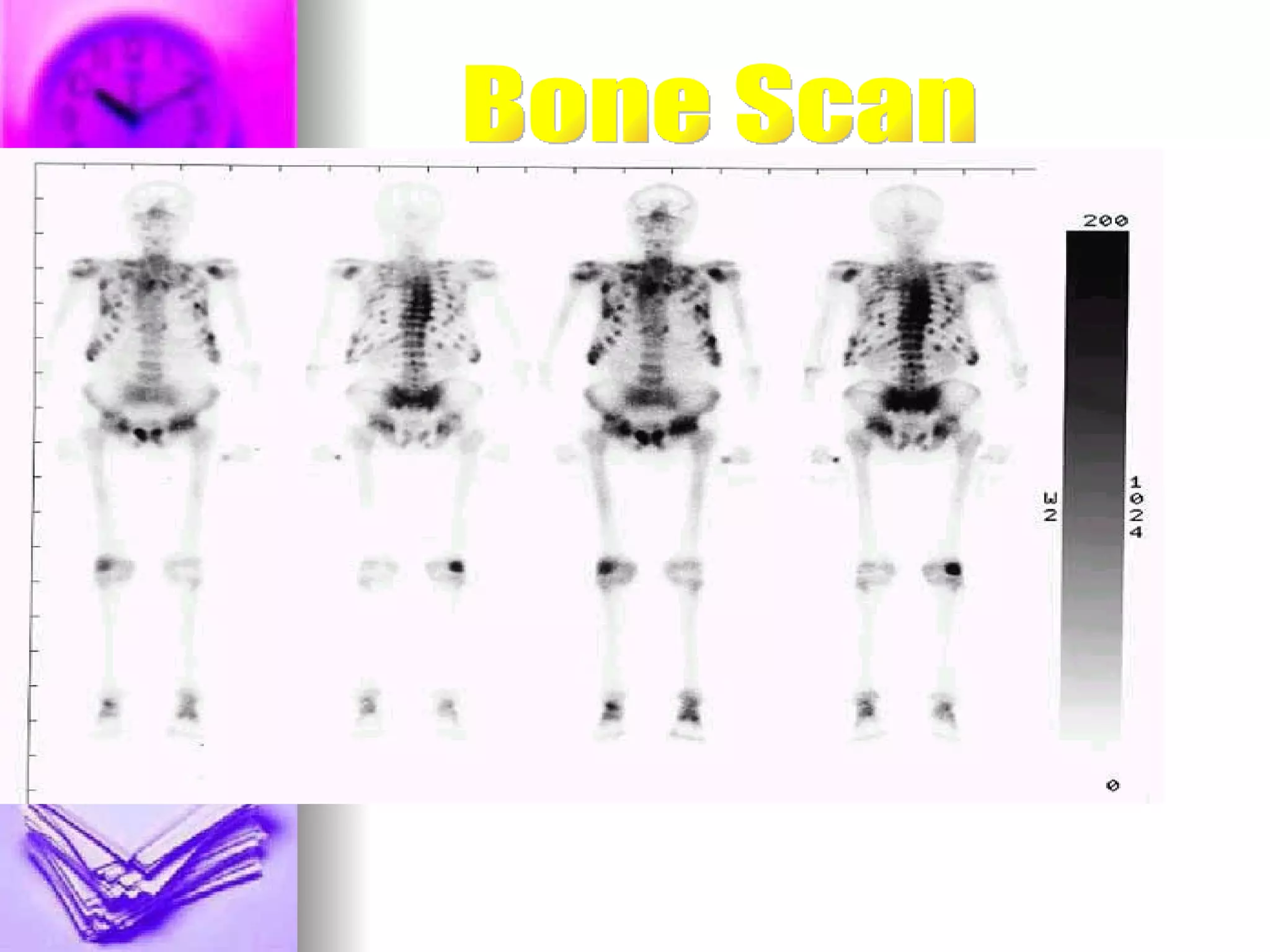
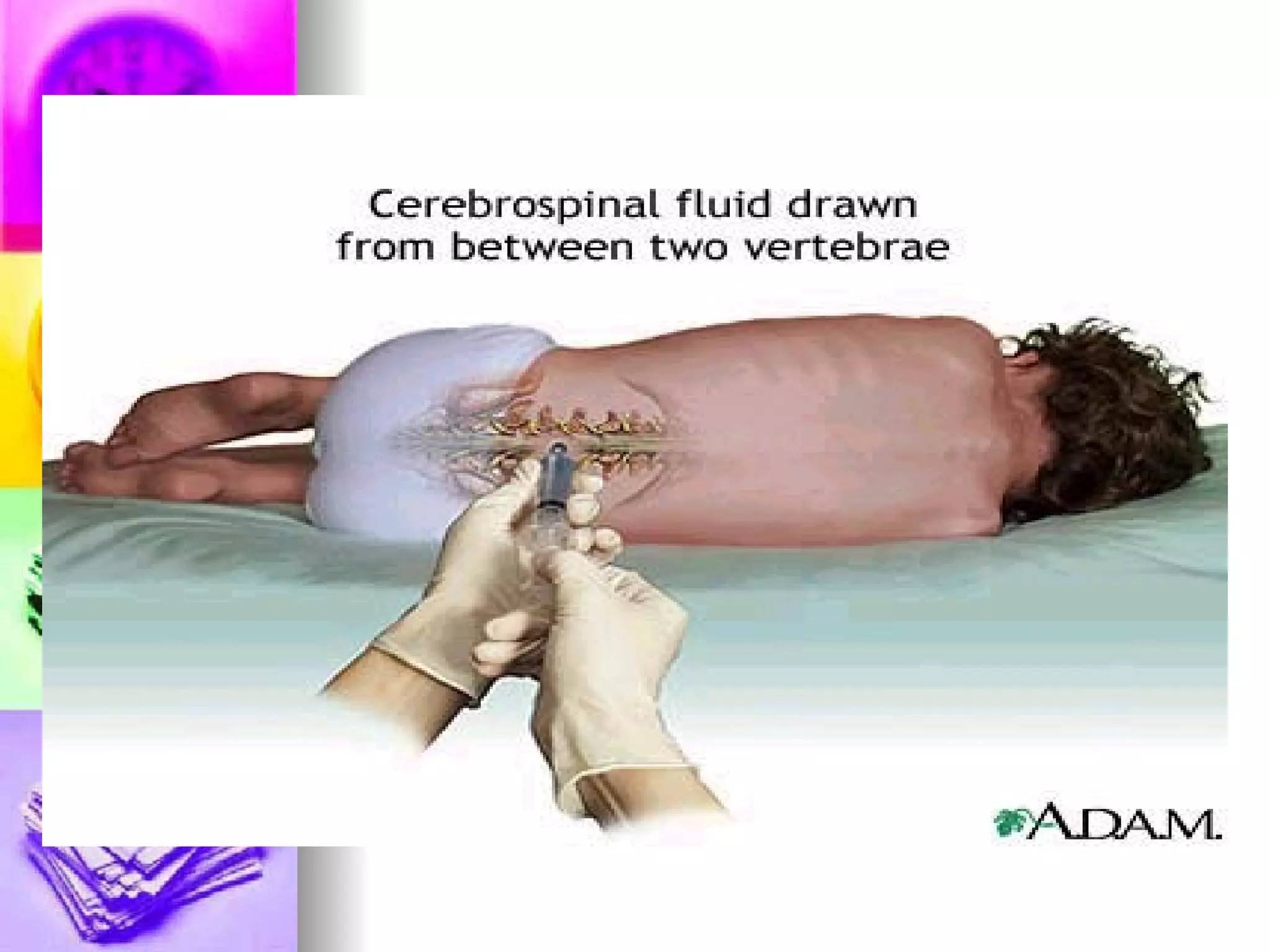
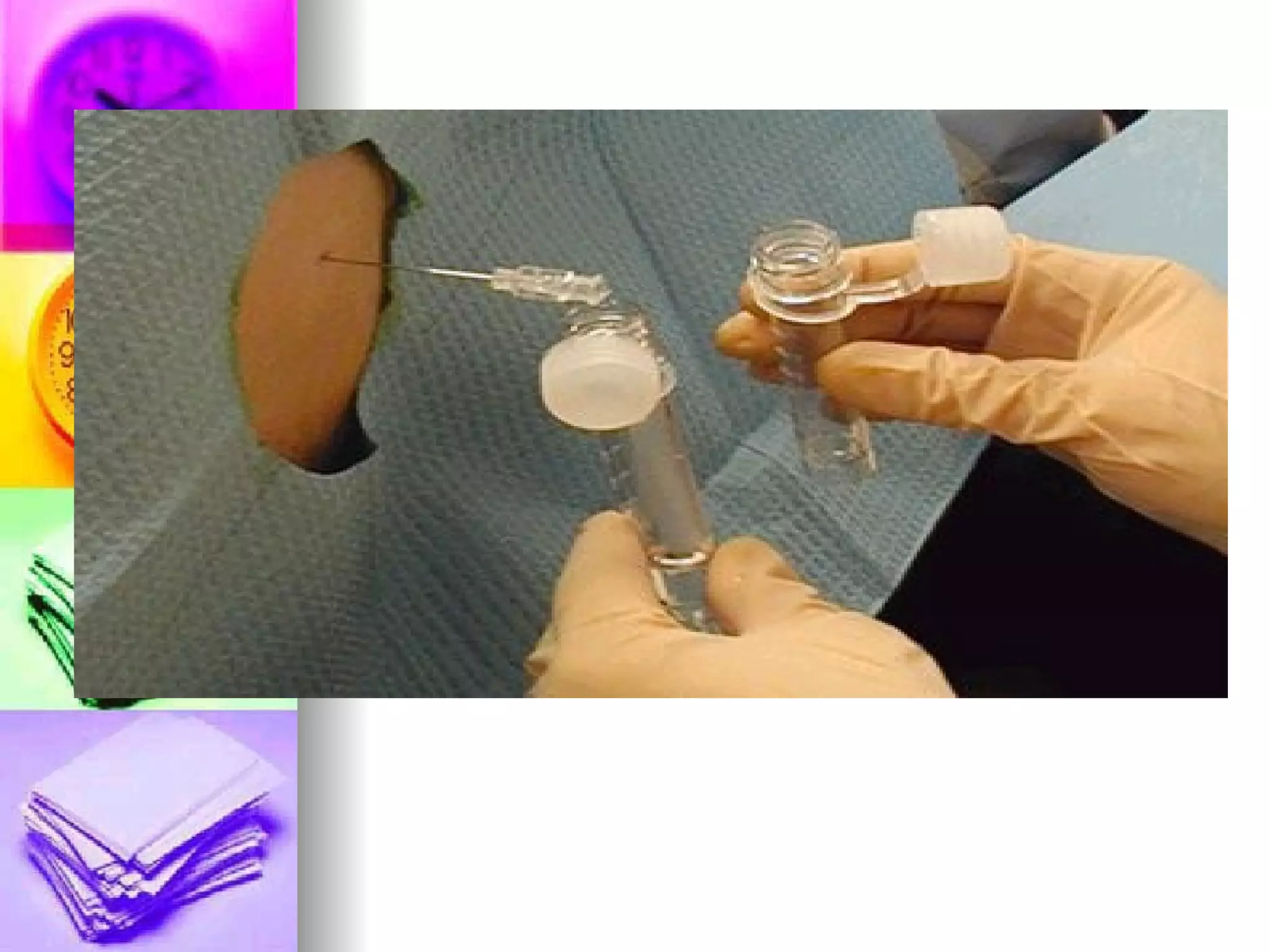
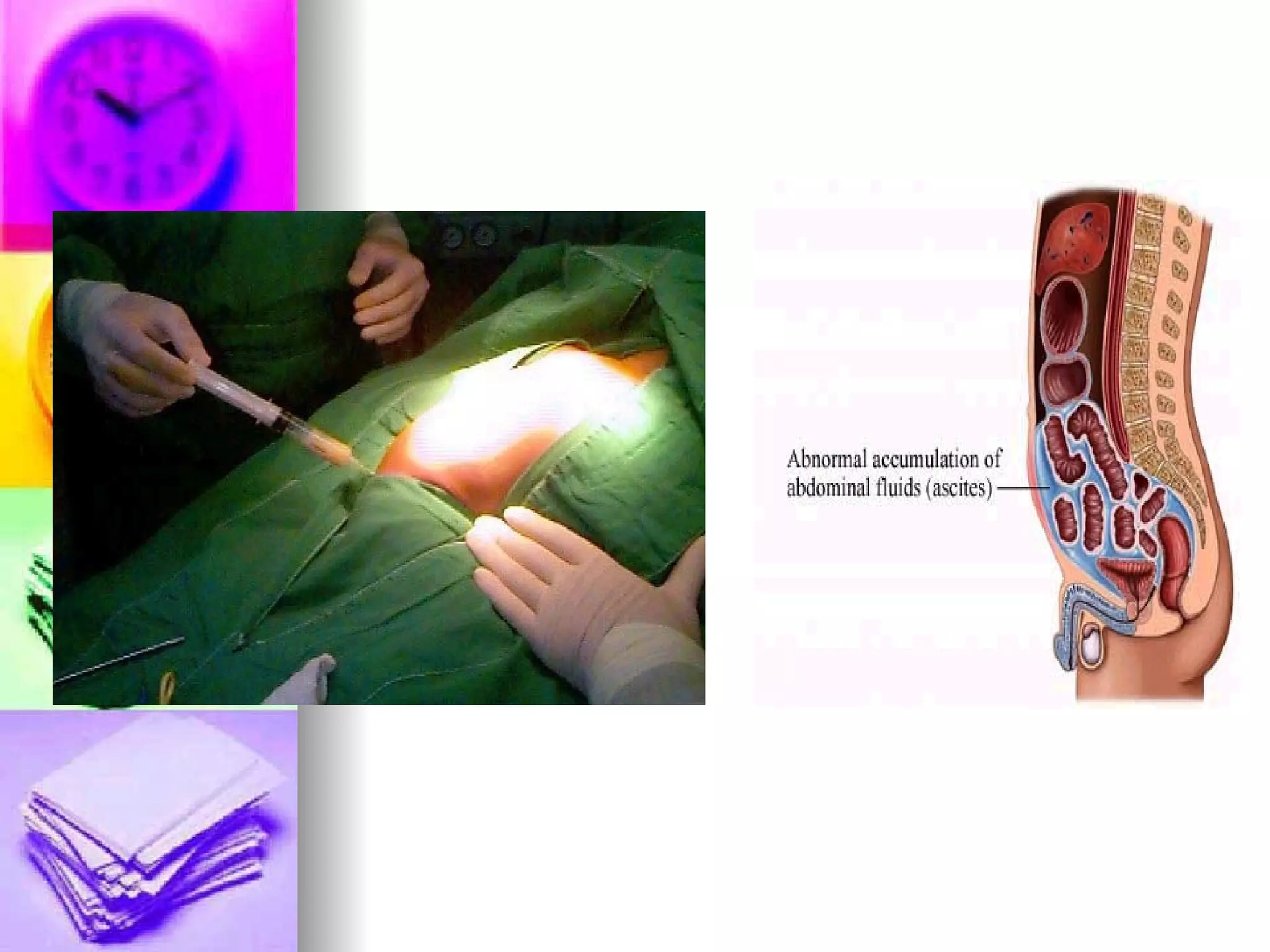
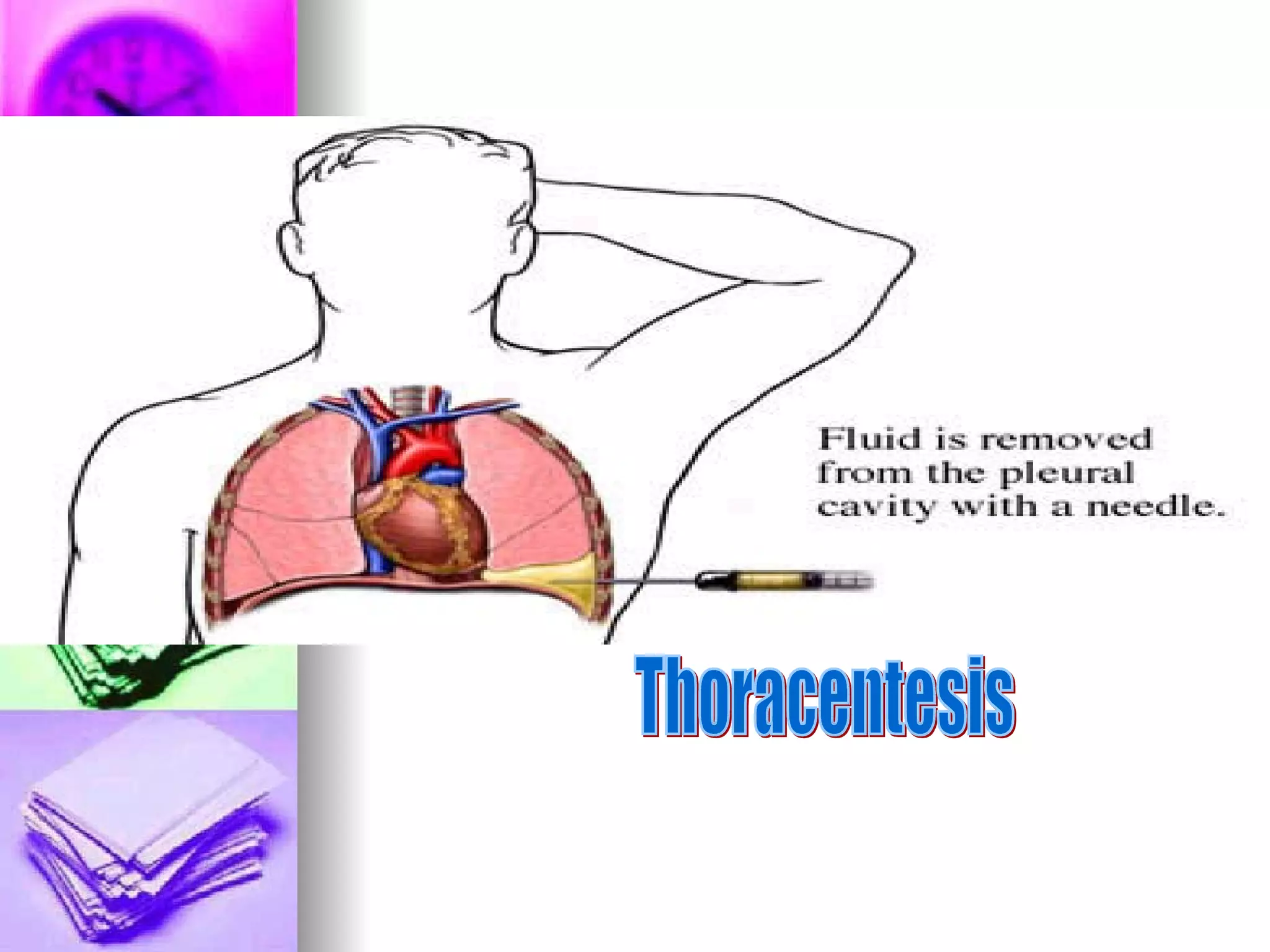
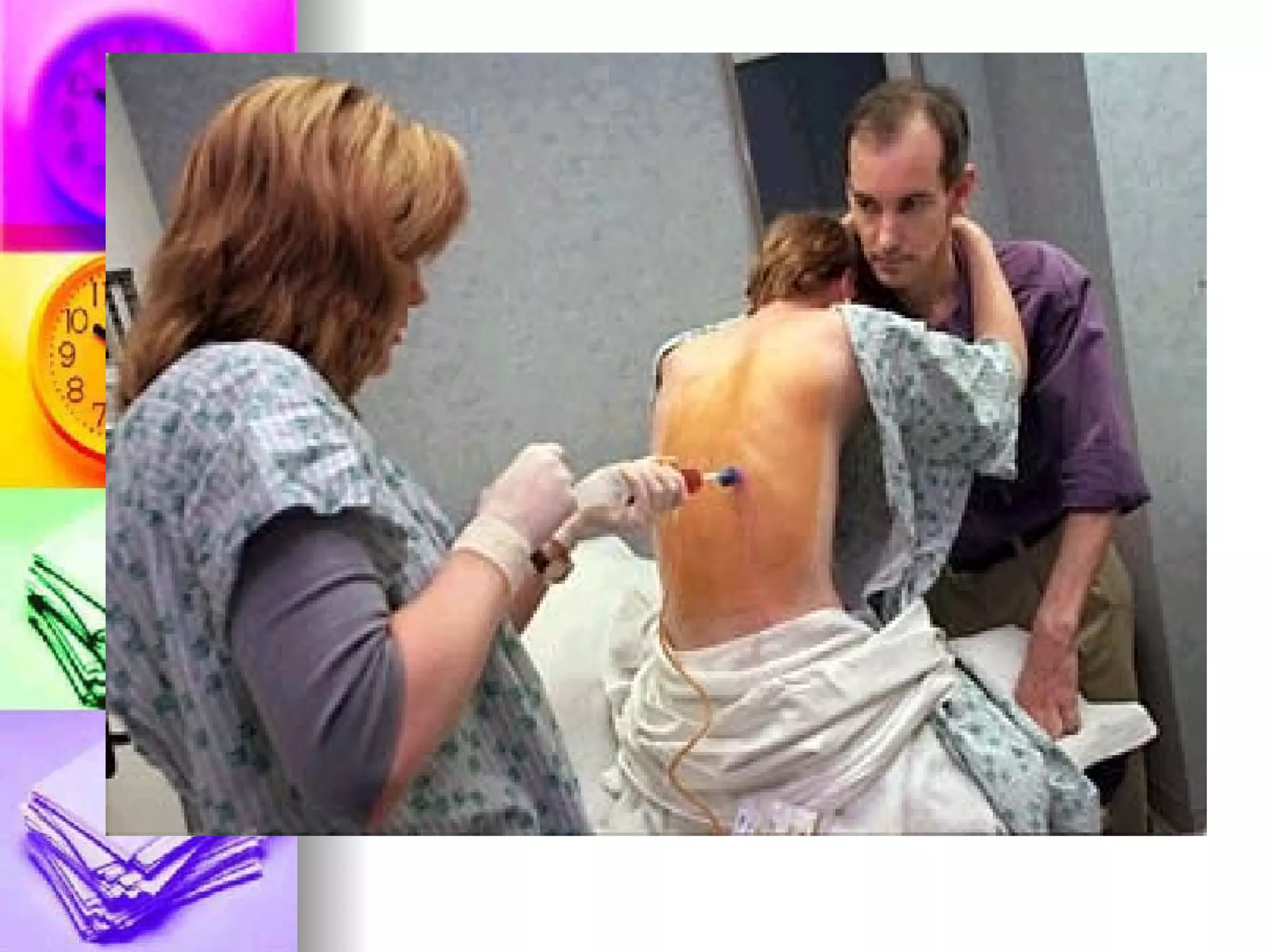
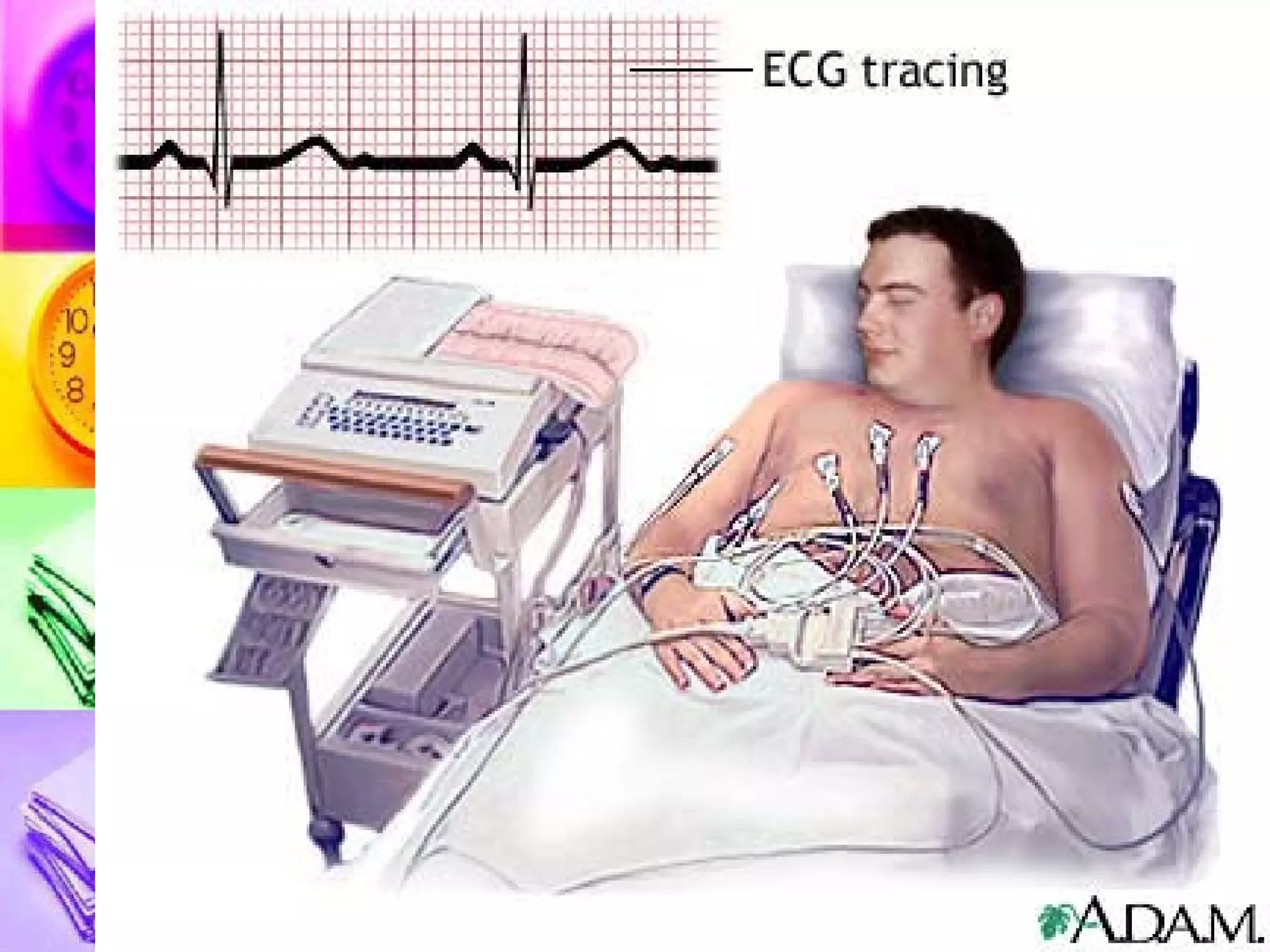
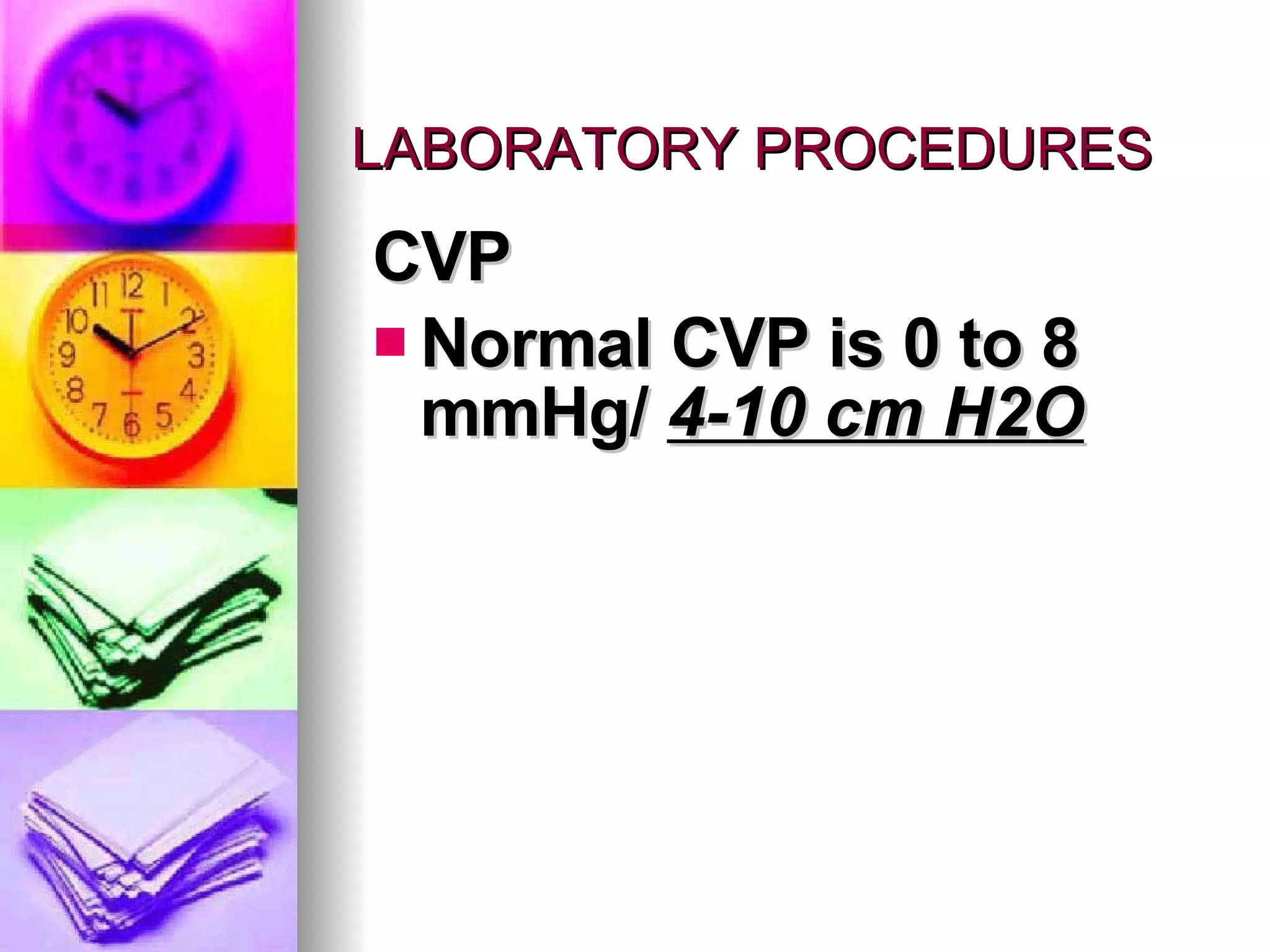
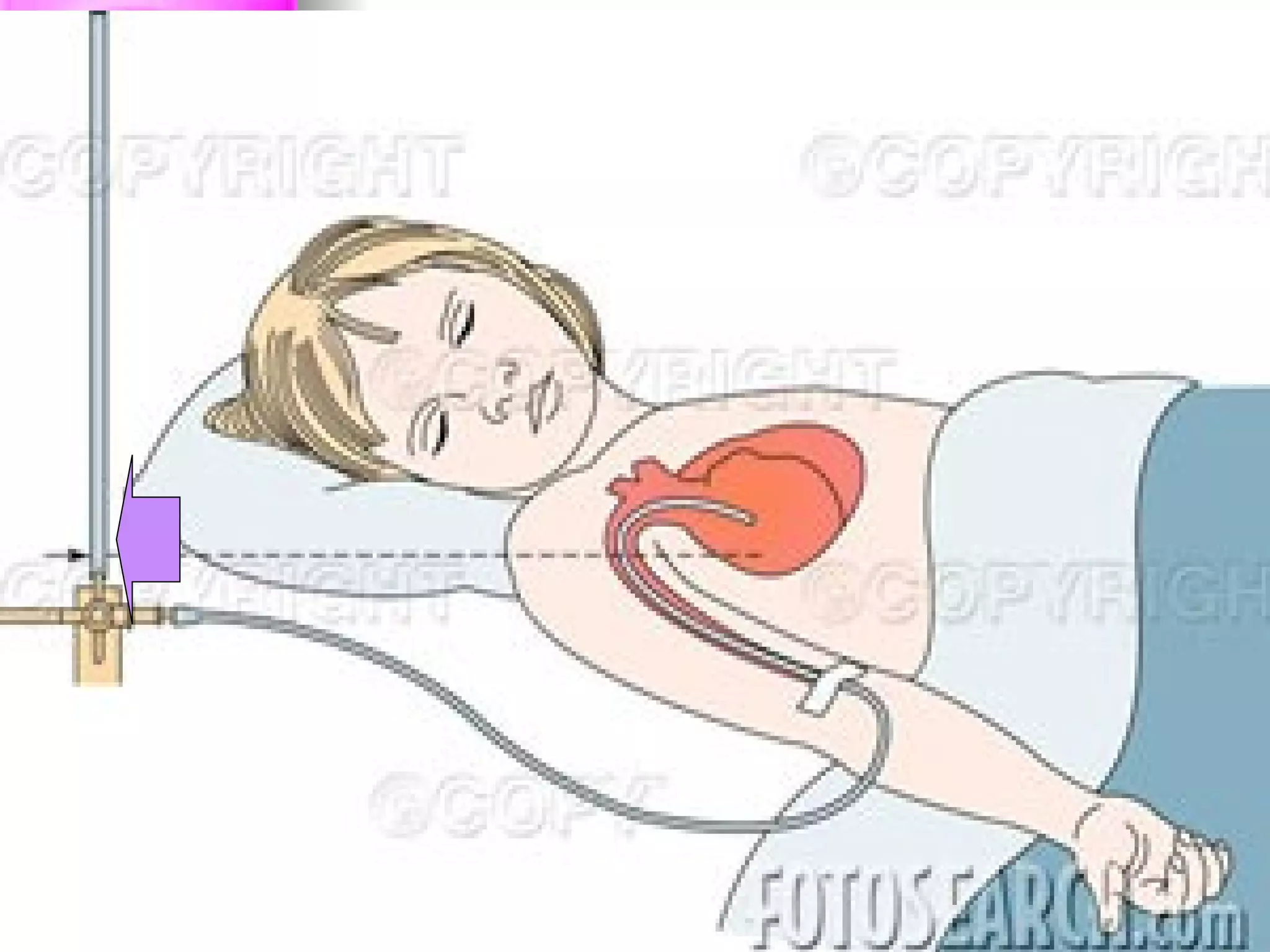
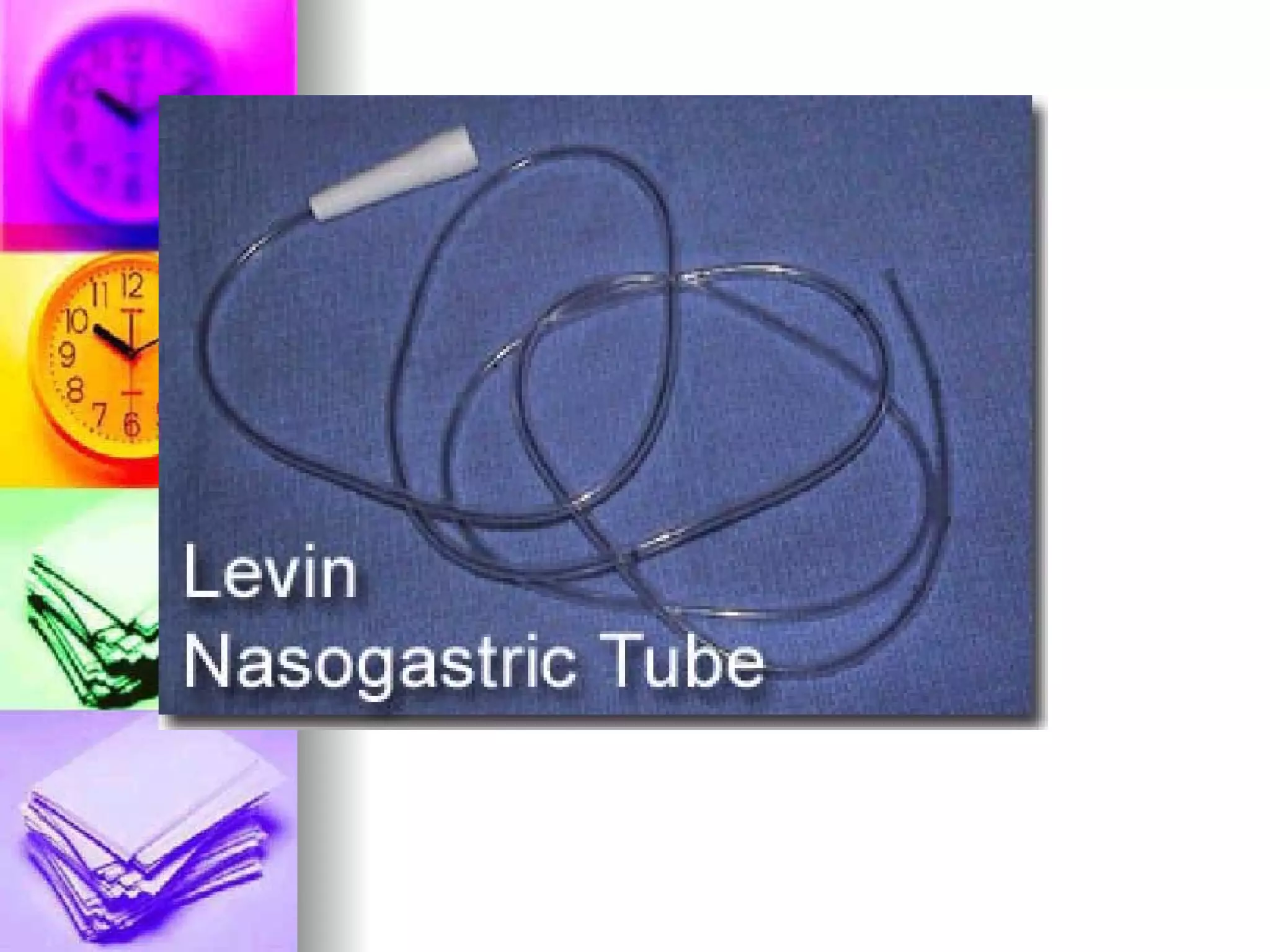
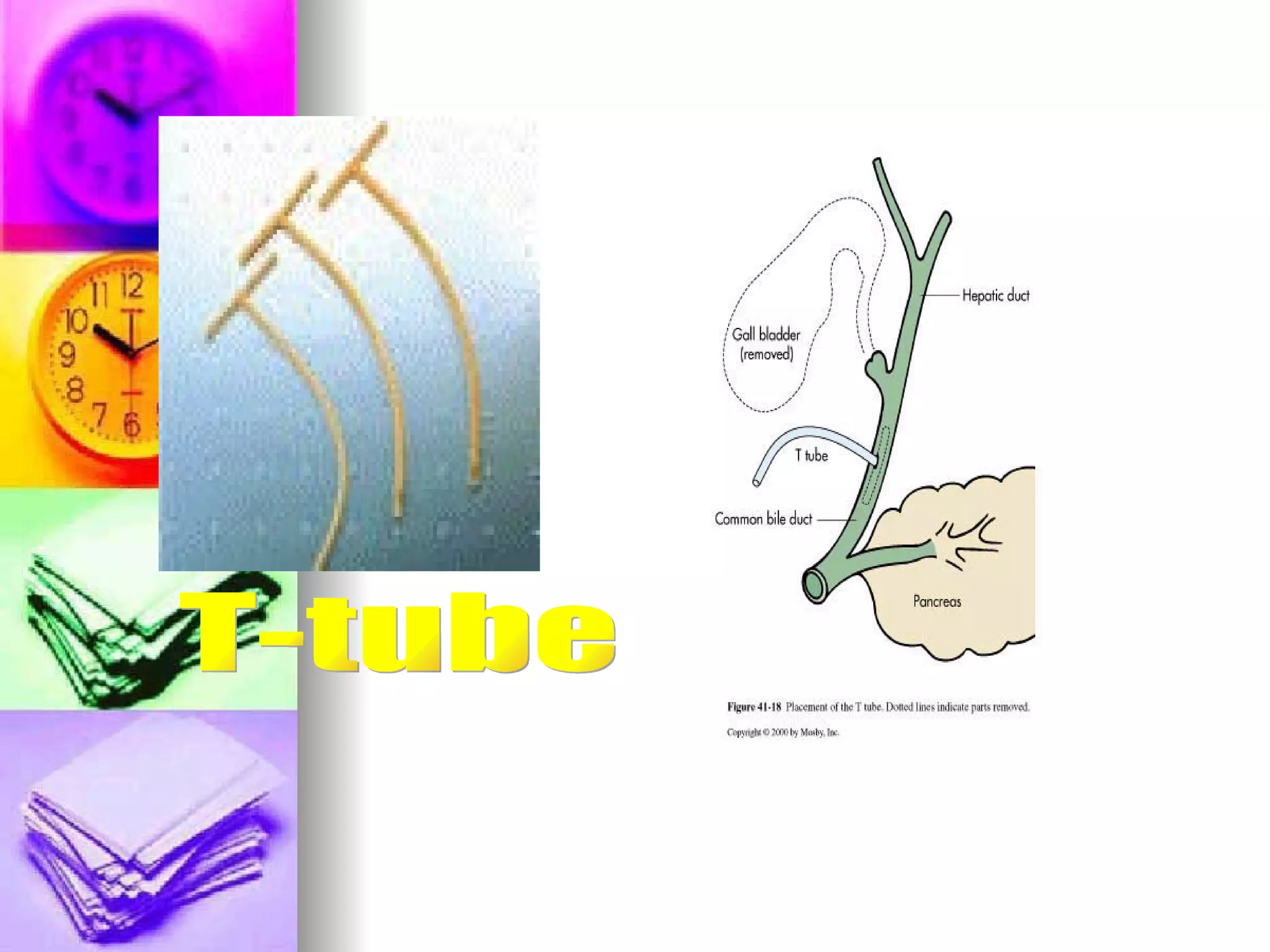
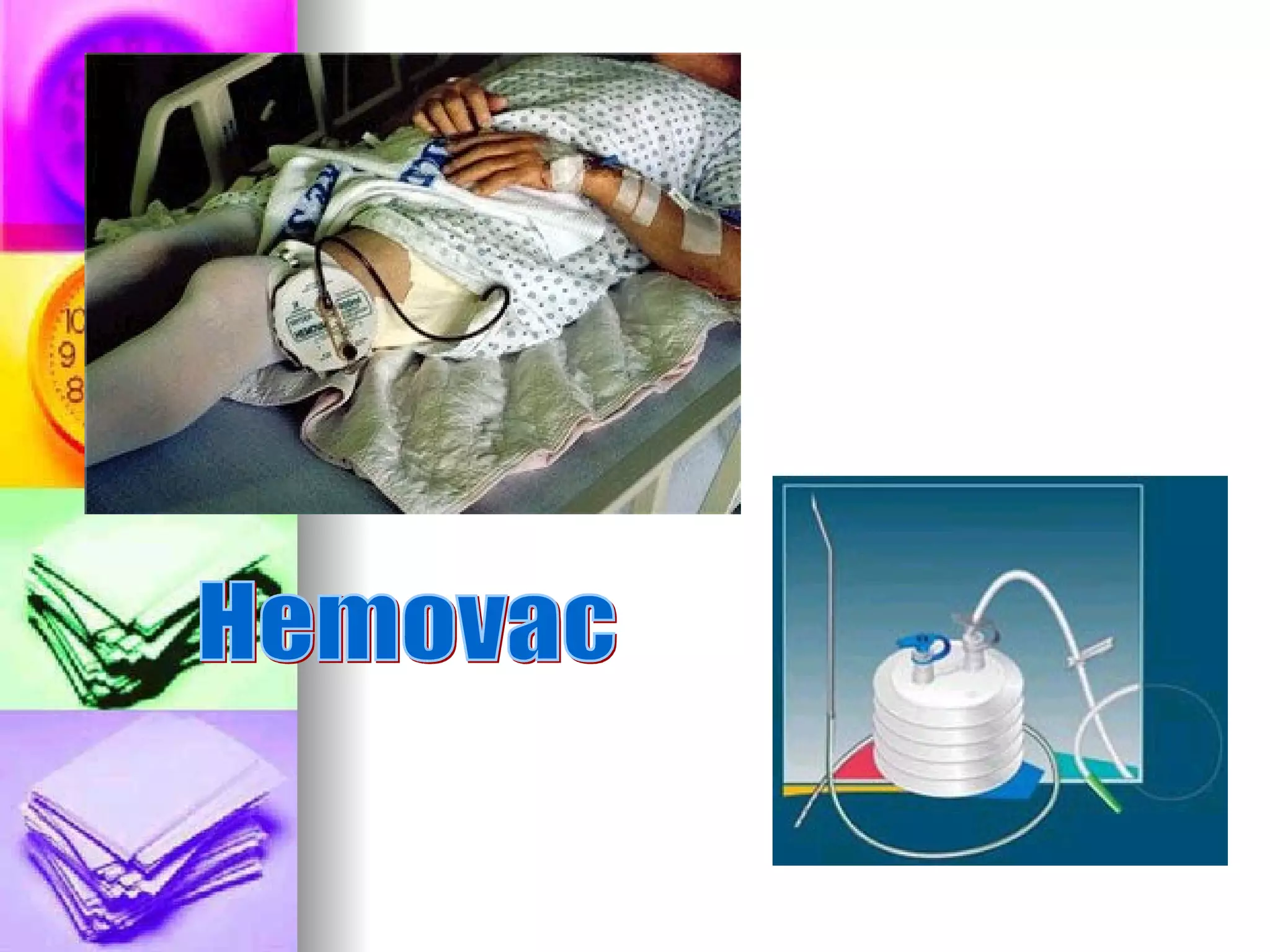
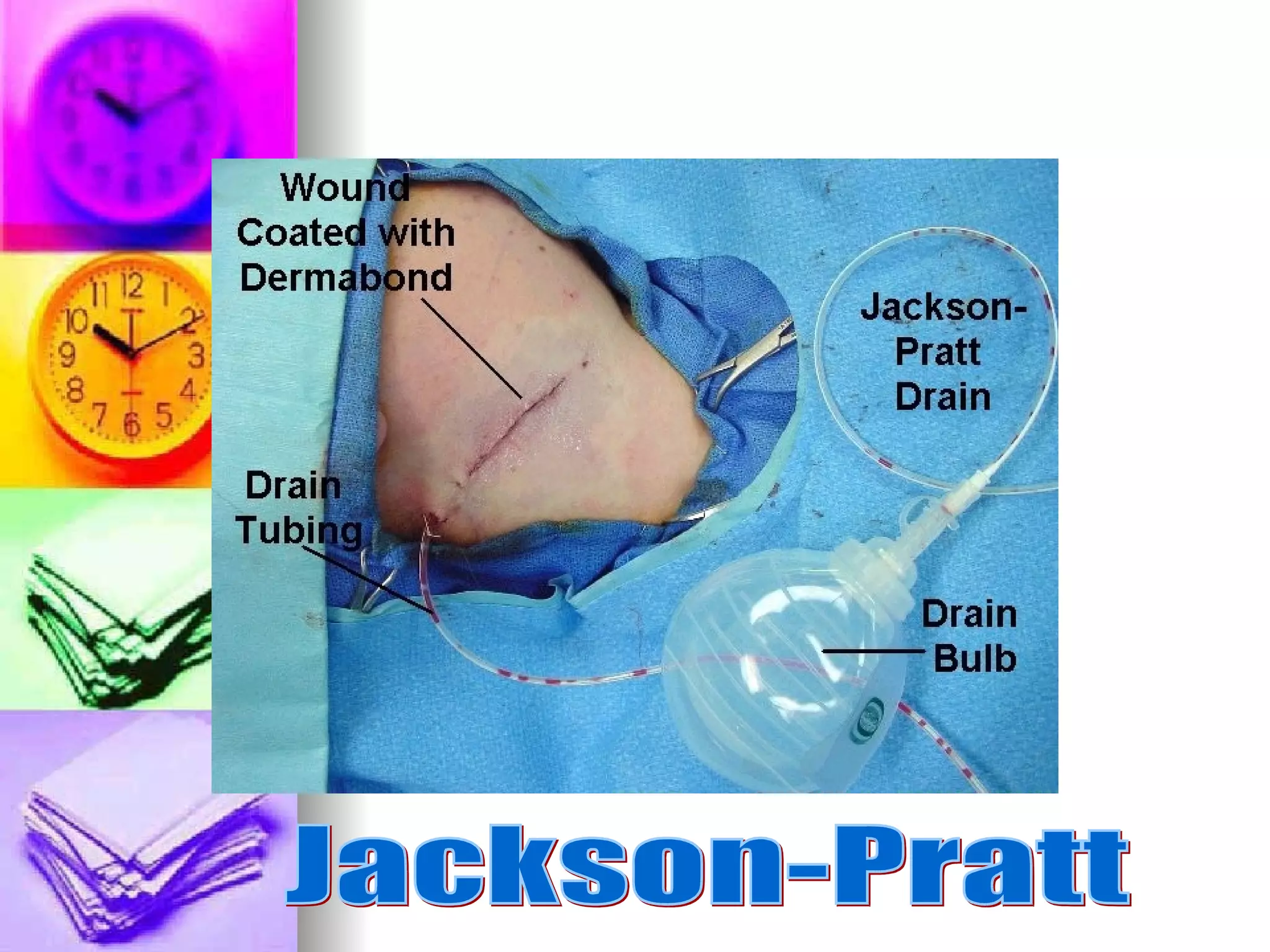
The document discusses common laboratory procedures and their nursing responsibilities. It covers blood tests like complete blood count and serum electrolytes. It also discusses urine, stool, sputum exams and various visualization procedures for the gastrointestinal, respiratory, cardiovascular and musculoskeletal systems. Procedures include imaging scans, endoscopies, biopsies and more. Pre-test, intra-test and post-test nursing responsibilities are provided for each procedure.