This document discusses several types of secondary plant metabolites:
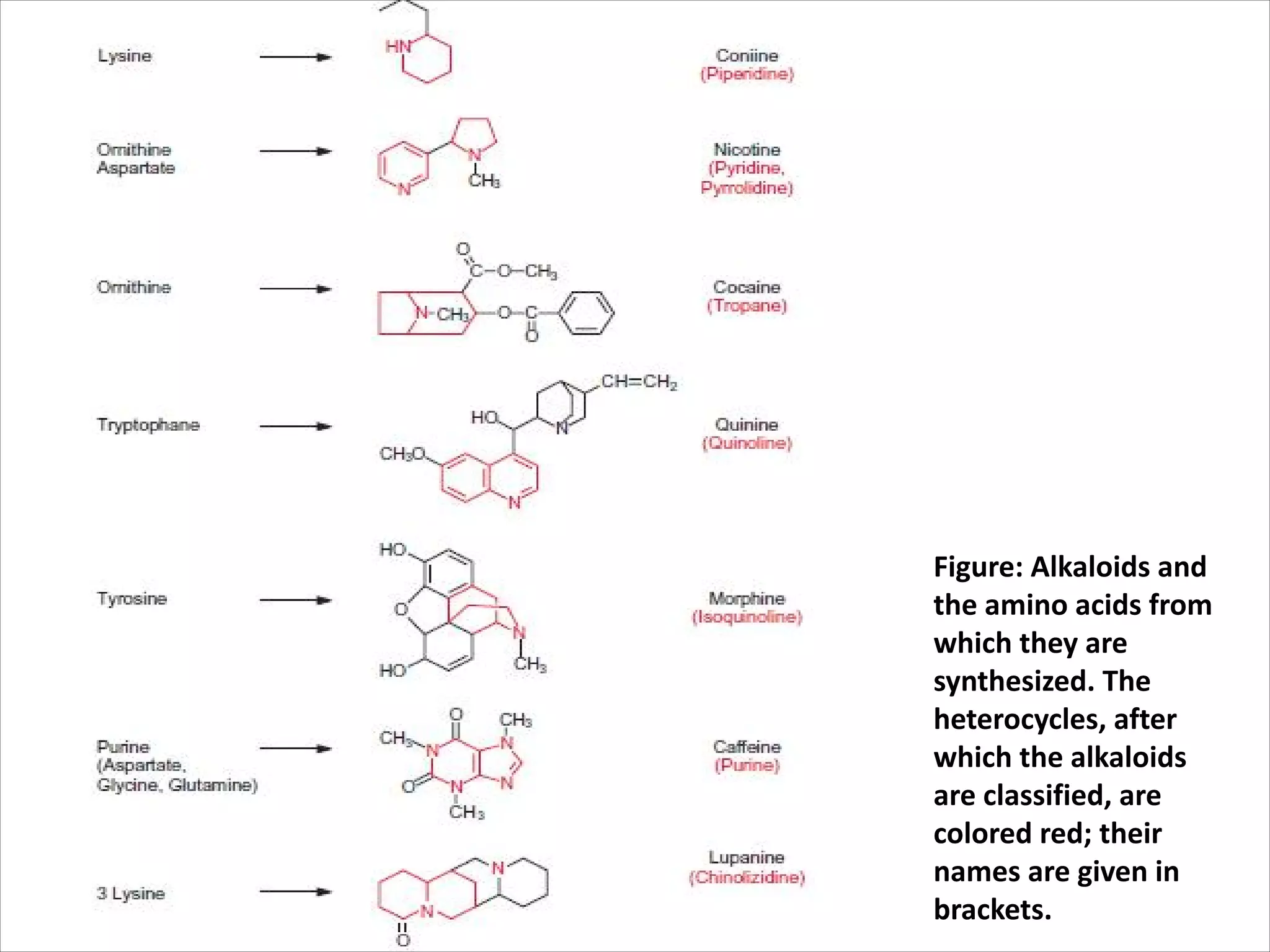
1. Alkaloids, which are synthesized from amino acids and contain nitrogen heterocycles. Examples include nicotine, cocaine, and morphine.
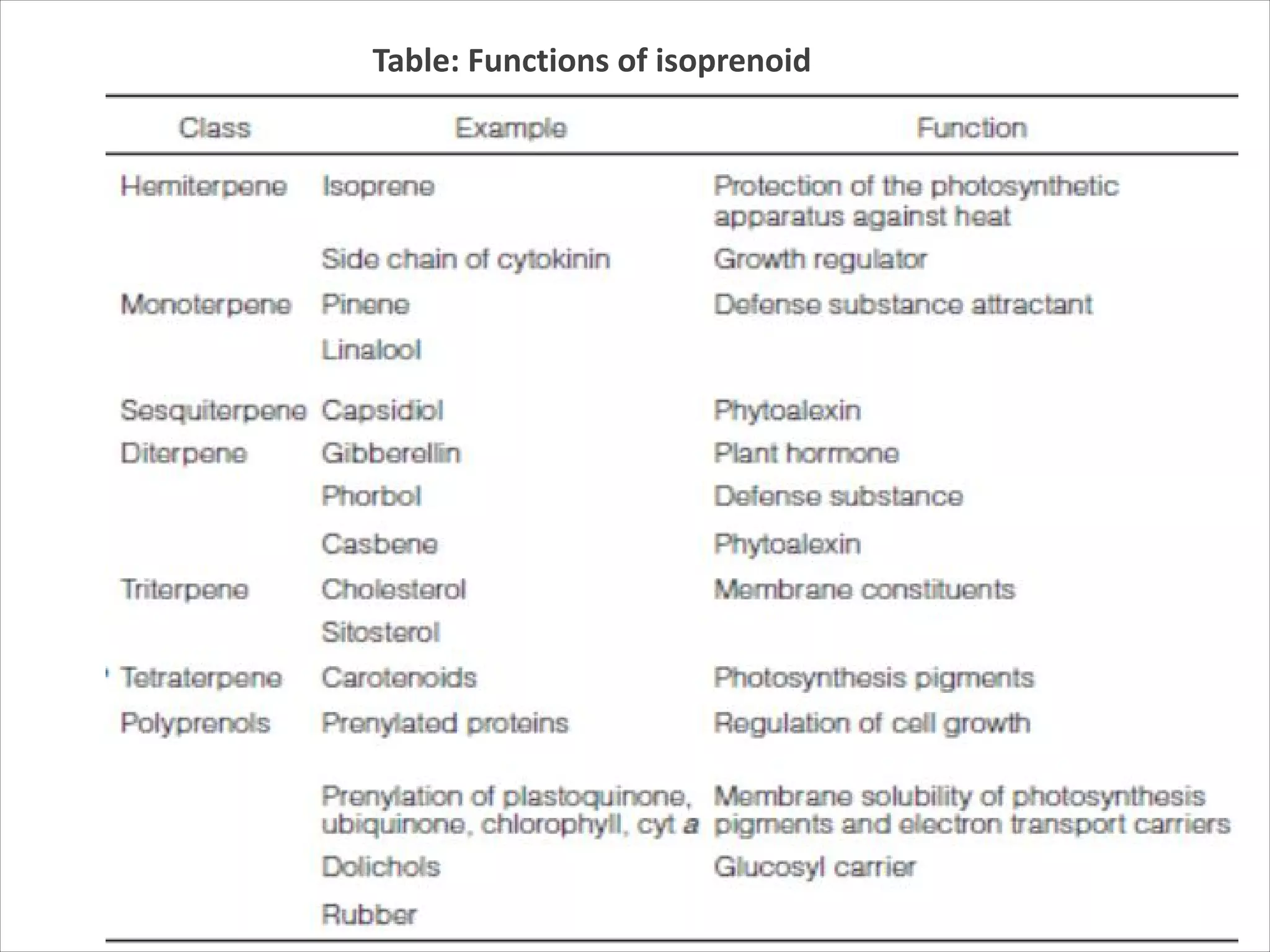
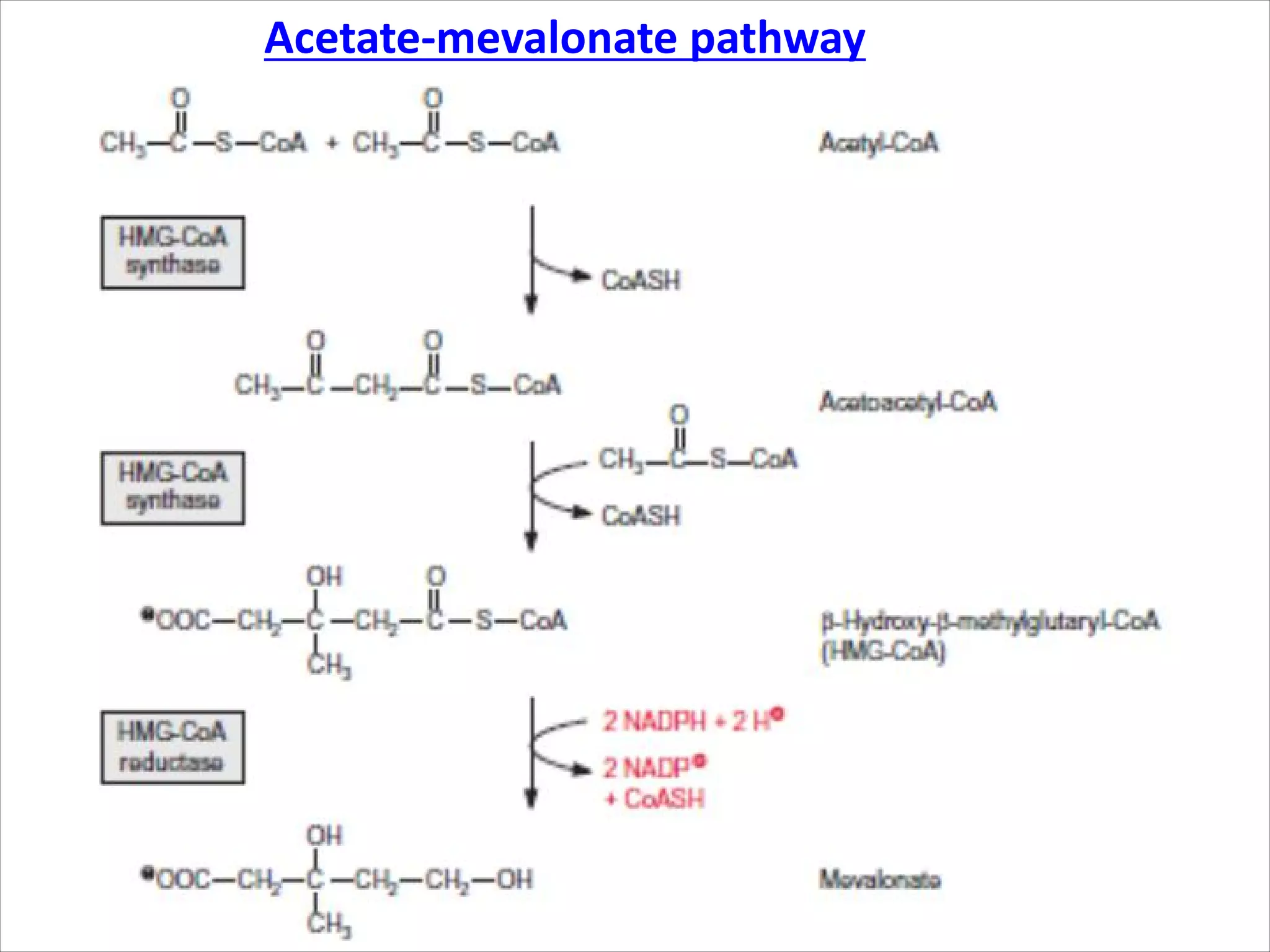
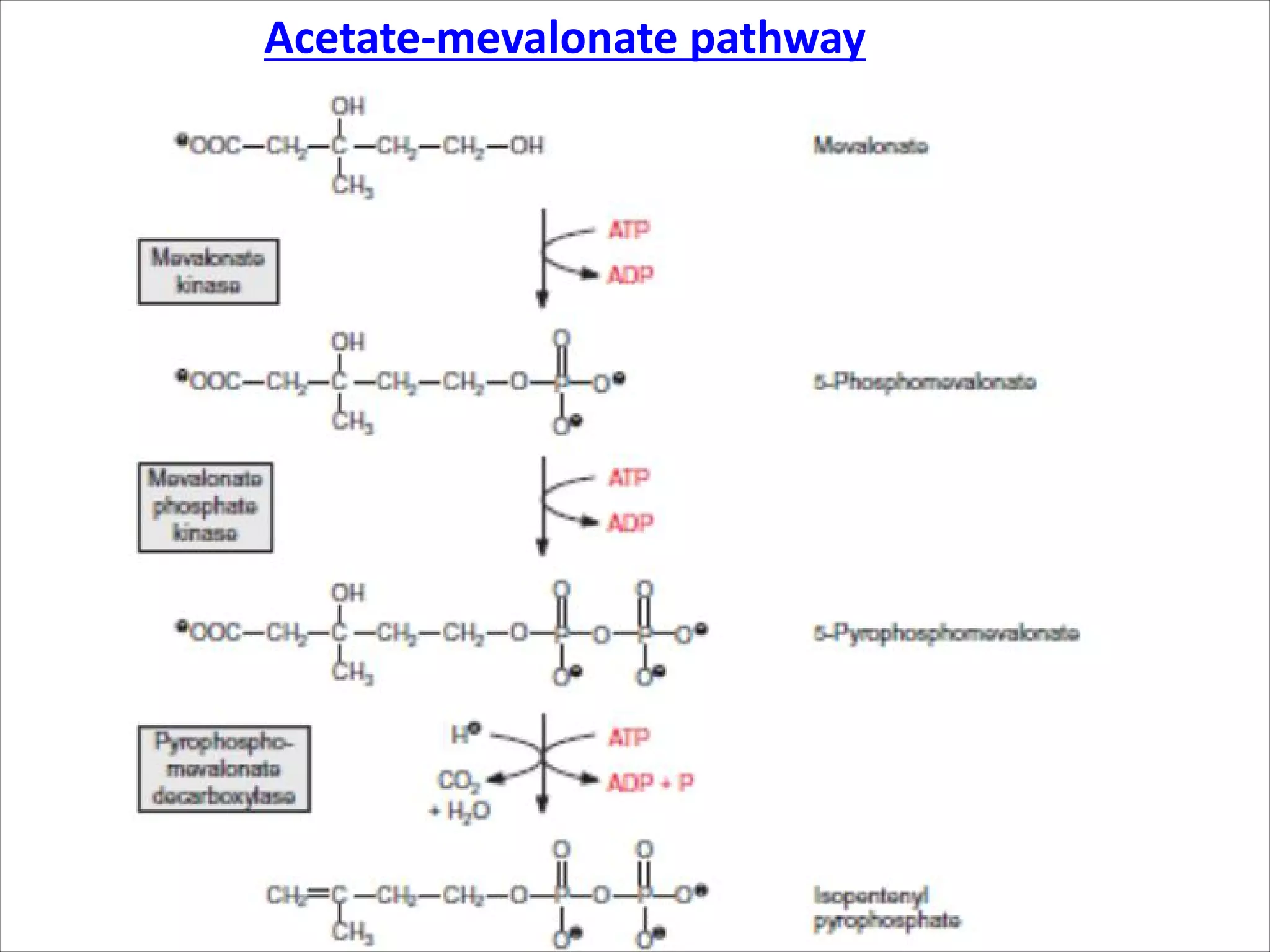
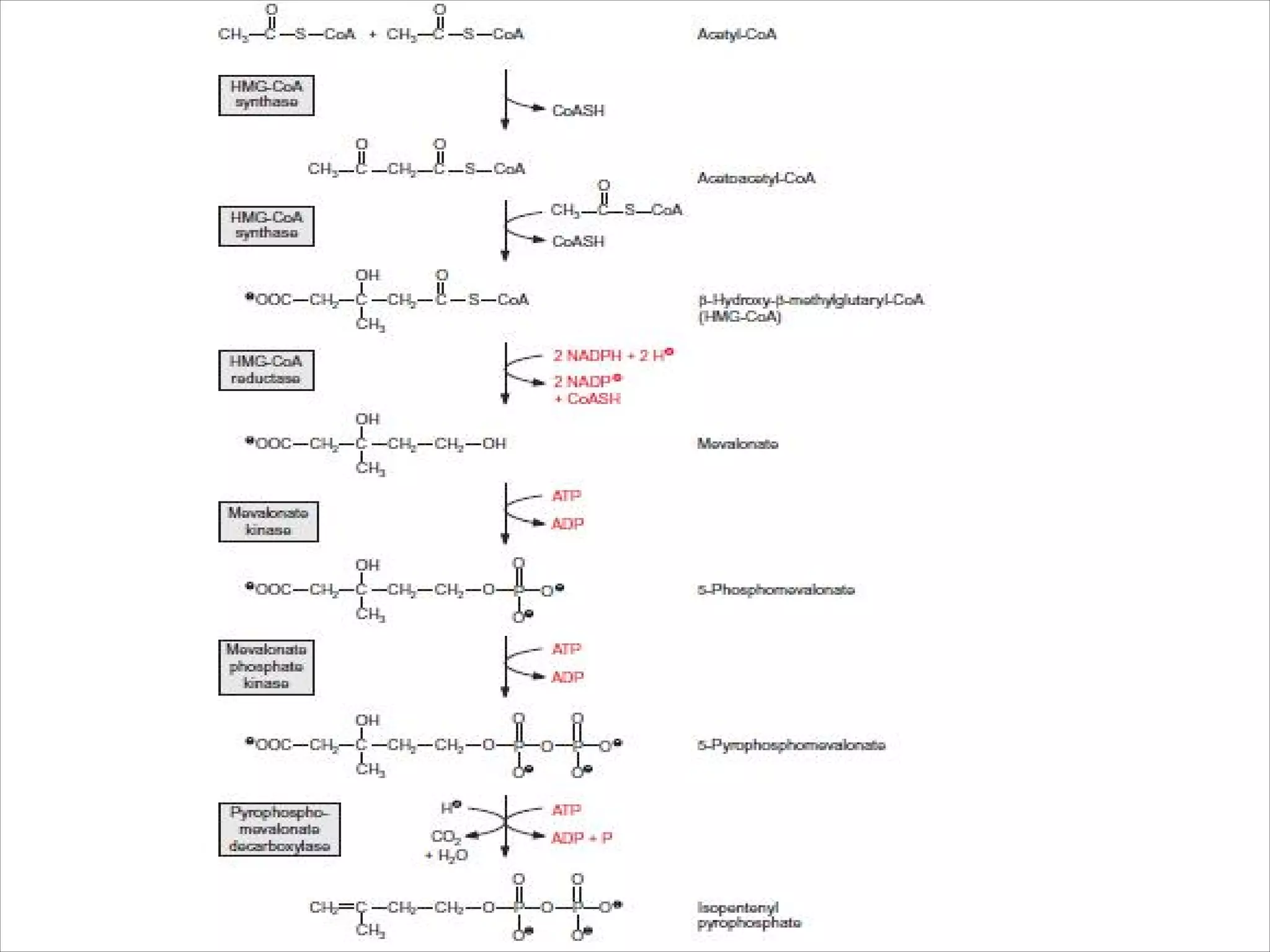
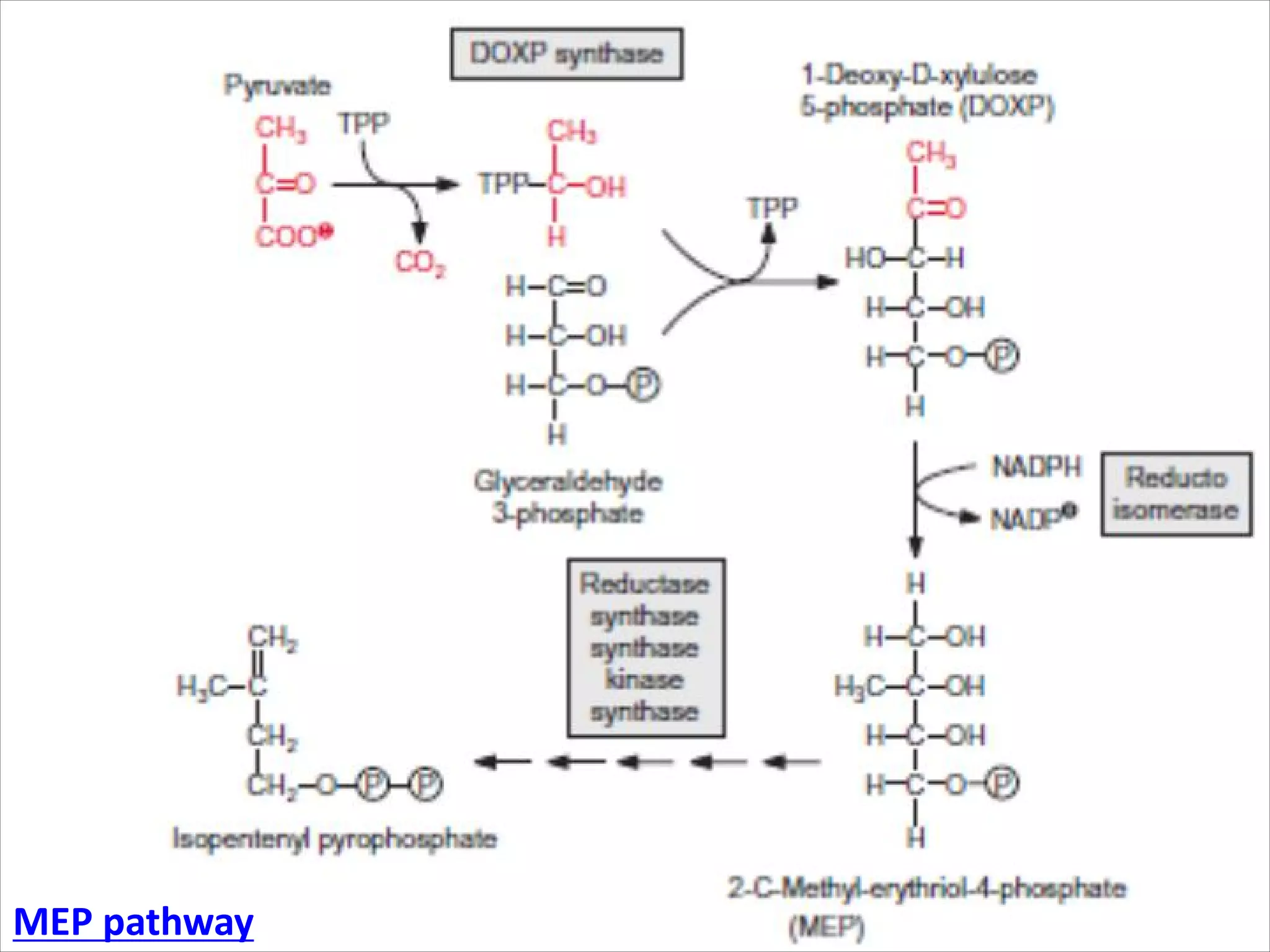
2. Isoprenoids, which are composed of repeating 5-carbon units and include terpenes, carotenoids, and rubber. They have important commercial and pharmaceutical uses.
3. Phenylpropanoids, which are derived from phenylalanine and include lignins, flavonoids, tannins, and stilbenes. Flavonoids have antioxidant and disease inhibitory properties.