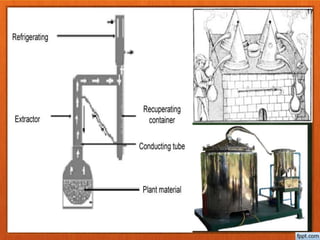
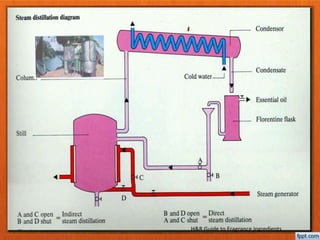
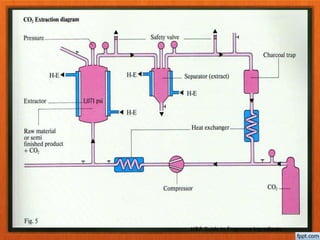
The document discusses various methods for extracting oils from plants, including expression, steam distillation, solvent extraction, CO2 extraction, and enfleurage. Steam distillation involves bubbling steam through plant material to release and collect essential oils, while solvent extraction uses solvents like hexane to extract oils and produce absolutes. CO2 extraction uses supercritical carbon dioxide to extract oils without heat or solvent residues. Each method has advantages and potential effects on the extracted oils.