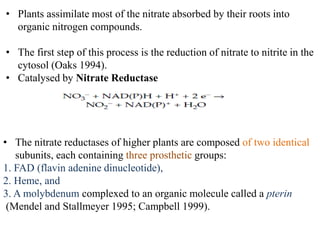
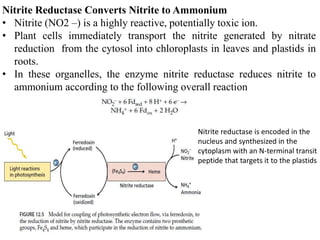
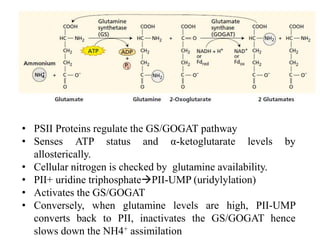
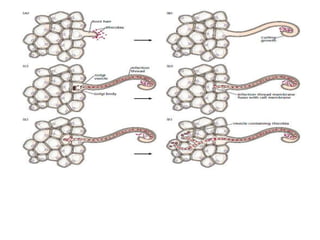
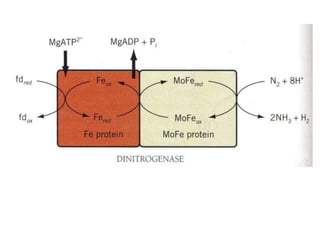
The document summarizes key steps in nitrate assimilation by plants. It discusses how plants reduce nitrate to nitrite and then to ammonium within cells. The ammonium is assimilated through the glutamine synthetase/glutamate synthase pathway to produce glutamine and other organic nitrogen compounds. Biological nitrogen fixation by symbiotic bacteria is also summarized, including the signaling and nodulation processes that allow nitrogen-fixing bacteria to interact with plant hosts.