Embed presentation
Downloaded 114 times






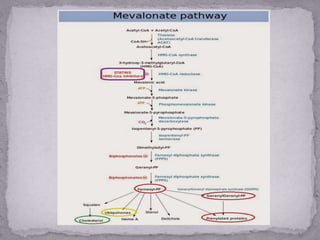

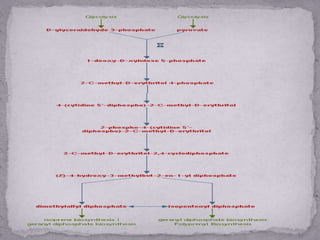
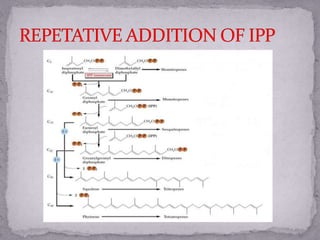

Terpenes are a large class of secondary metabolites produced by plants that are built from isoprene units. They are hydrocarbons or oxygenated derivatives that are synthesized in plants through two pathways: the mevalonate pathway which occurs in the cytosol and is regulated by the enzyme HMG-CoA reductase, and the methylerythritol phosphate pathway which occurs in the leucoplast and is regulated by DXP reductase. Terpenes were first termed by Kekule in 1866 and are derived from the German word for turpentine.










