This document discusses the technology of draw frame autolevellers used in textile manufacturing. It covers the following key points:
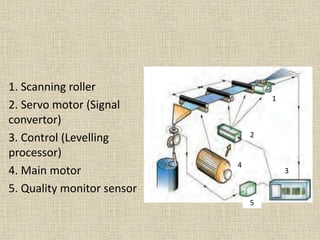
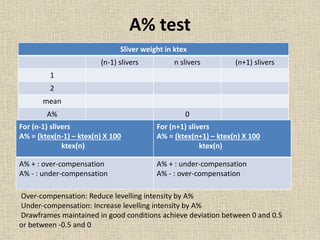
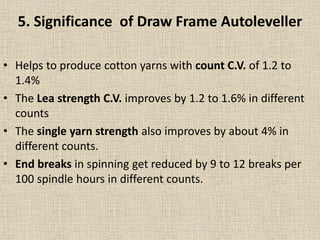
1. Draw frame autolevellers help improve yarn quality by monitoring sliver thickness and adjusting the draft to maintain a consistent sliver thickness and count CV%. This helps produce yarn with less variation.
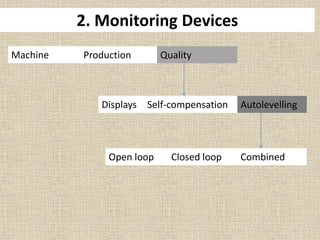
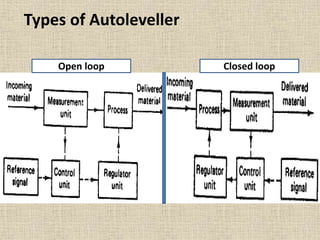
2. There are two main types of autolevellers - open loop and closed loop. Closed loop systems are better for correcting long-term variations.
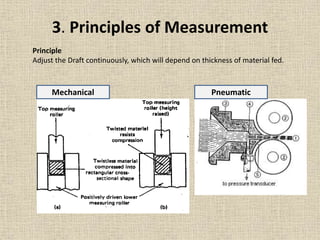
3. Important parameters for quality leveling include the leveling intensity, which determines how much the draft is adjusted, and the leveling action point, which is where corrections are applied along the production process.









![References
[1] TRUTZSCHLER auto leveller Draw Frame TD 03 –
Manual
[2] RIETER auto leveller Draw Frame RSB D – 40 – Manual
[3] GALILEO auto leveller Draw Frame DFR1 - Manual
[4] Sanjay R. Patel, Some Considerations in Designing
Autolevelling System for Conventional Draw frames
(Textile Machinery), Central Instrumentation (Mech.)
Faculity of Technology and Engineering, M.S.U. of Baroda
[5] Draw Frame Teaching Materials](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/technologyofdrawframeautolevellers-151021102508-lva1-app6891/85/Technology-of-draw-frame-autolevellers-16-320.jpg)