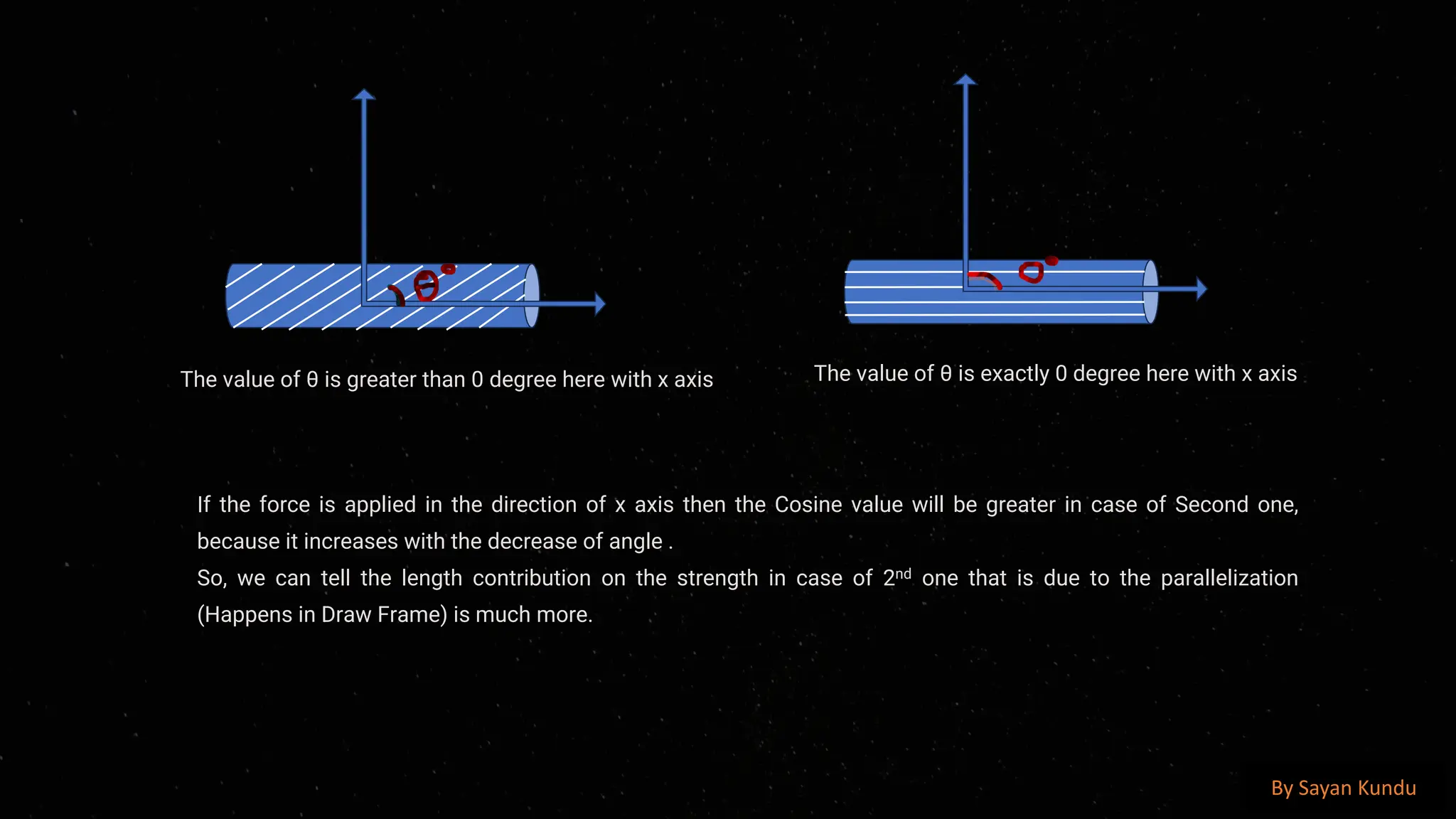
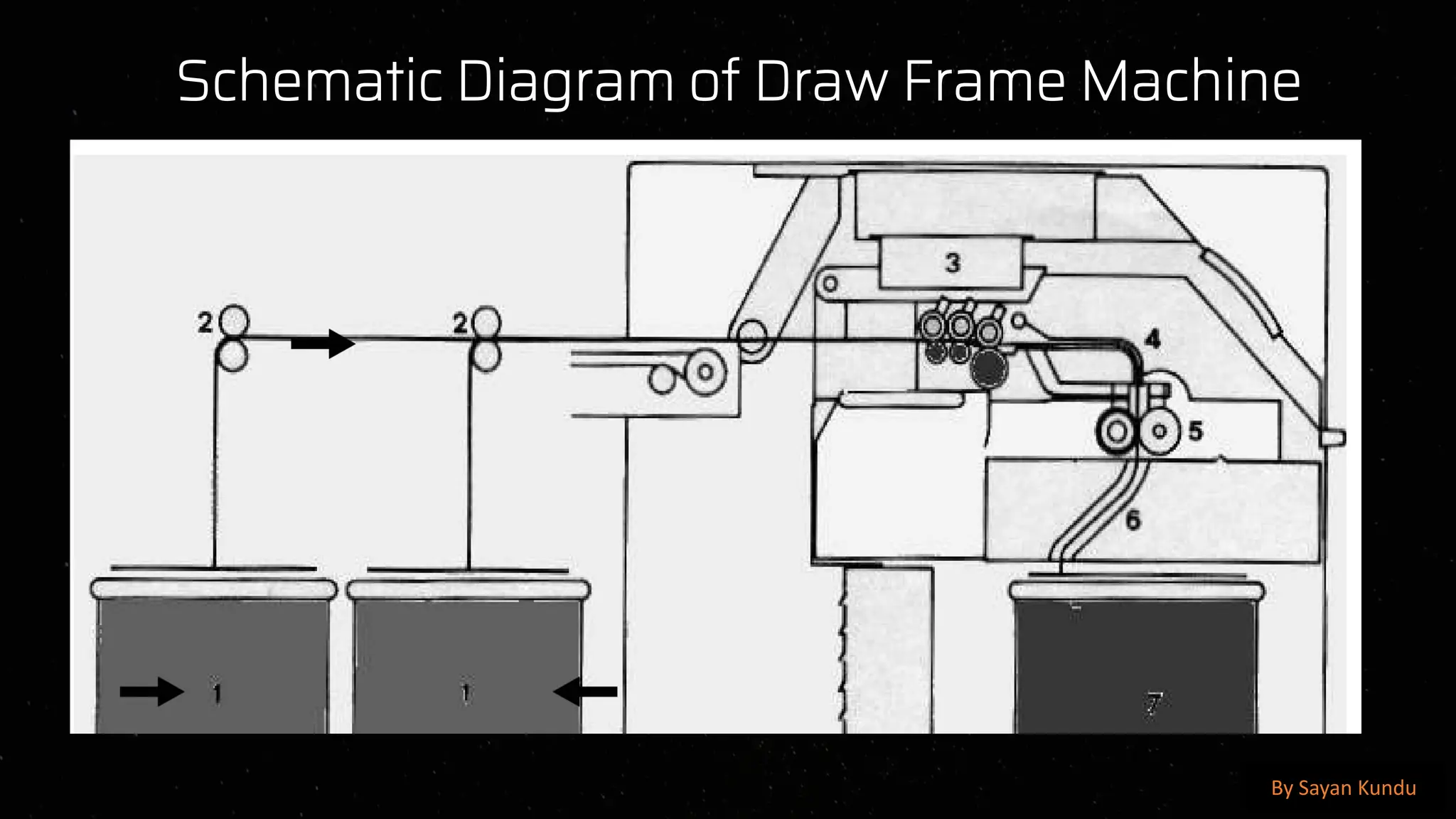
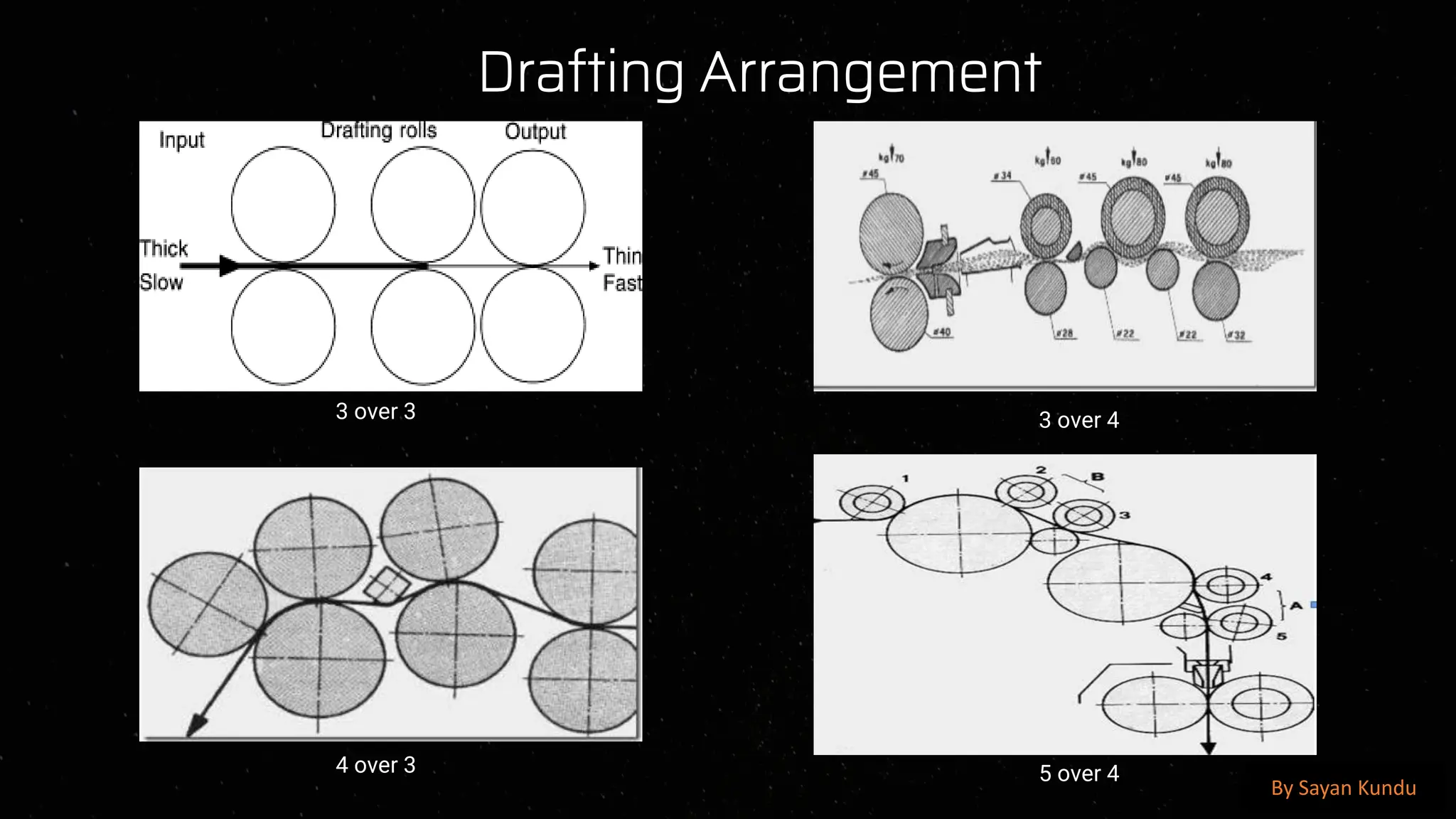
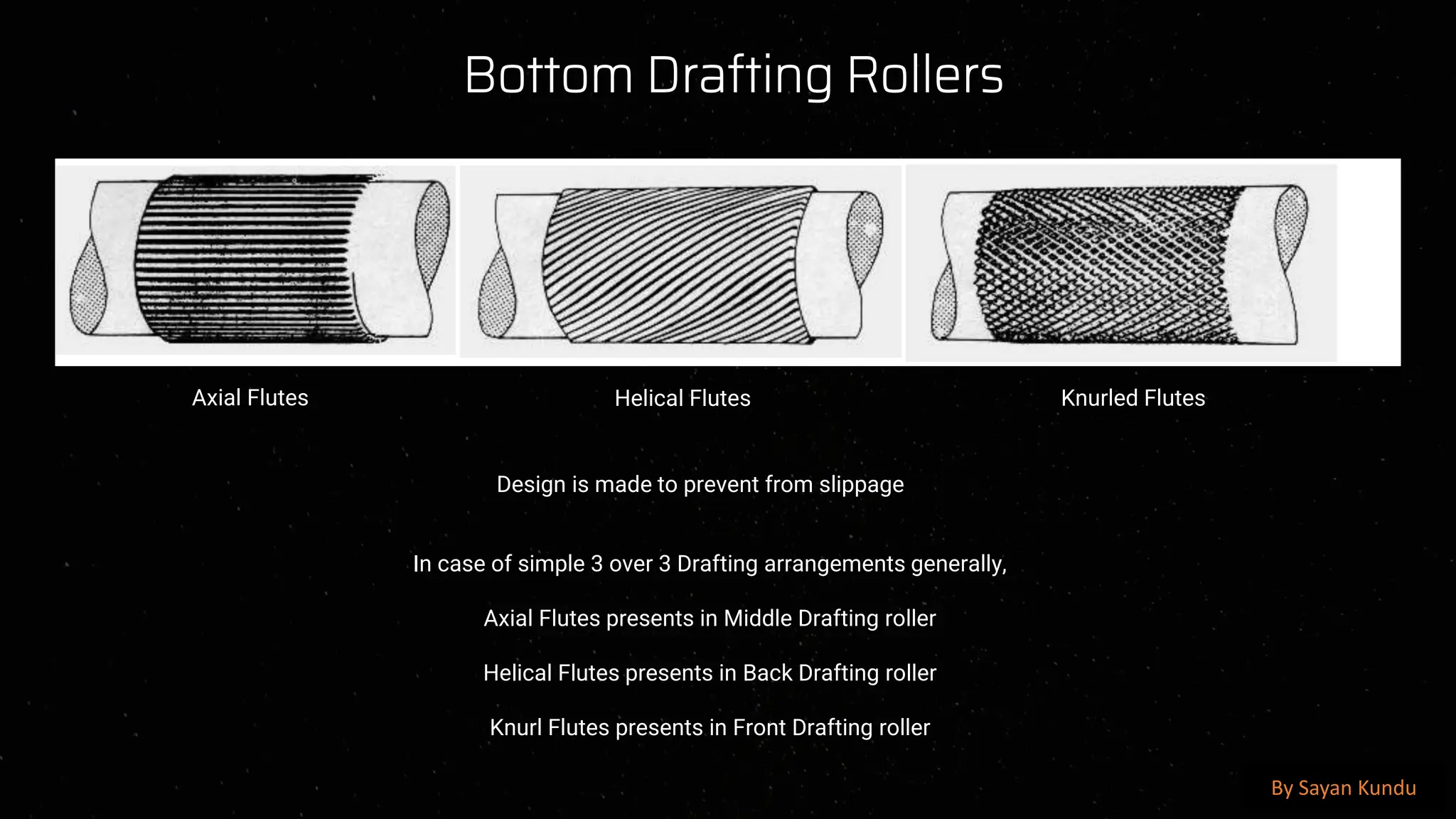
The draw frame is a crucial machine in the textile manufacturing process, primarily used in the spinning sector to improve the quality of sliver by doubling, drafting, and aligning the fibers to ensure uniformity and consistency before the roving and spinning stages. It plays a significant role in enhancing the evenness, strength, and parallelization of fibers, ultimately affecting the quality of the final yarn. The draw frame typically operates by taking multiple slivers from the carding or combing process and passing them through a series of drafting rollers, which reduce the thickness of the sliver while increasing its length. This process is essential to reduce fiber irregularities and improve the uniformity of the mass distribution, which helps prevent weak spots and defects in the yarn. The drafting mechanism, consisting of multiple roller pairs with different speeds, stretches the fiber bundle to achieve the desired fineness. Modern draw frames are equipped with auto-leveling devices that continuously monitor and correct the sliver’s linear density, ensuring that variations in weight per unit length are minimized, thus maintaining consistency. Additionally, the slivers are passed through coilers, which neatly deposit the processed sliver into cans for further processing. The key functions of a draw frame include straightening the fibers, removing short fibers, improving blending efficiency, and enhancing fiber cohesion, all of which are critical in producing high-quality yarns with superior tensile strength, reduced hairiness, and better evenness. Various factors affect the efficiency and performance of the draw frame, including roller settings, drafting zone temperature and humidity, fiber type, and machine speed. Proper maintenance, including regular cleaning of drafting rollers and aprons, lubrication of moving parts, and checking of sensors and auto-leveling devices, is essential to ensure smooth operation. The introduction of computerized and high-speed draw frames has significantly improved productivity and efficiency in modern textile mills, allowing for real-time monitoring of sliver quality, fault detection, and reduced waste generation. Furthermore, advanced draw frames now integrate optical and capacitive sensors to detect and correct irregularities, ensuring higher accuracy and quality consistency in sliver formation. In cotton spinning, the draw frame is often positioned after the carding machine, while in worsted spinning systems, it follows the combing process to further refine the fiber arrangement. The doubling process in draw frames, where multiple slivers are combined and drafted, helps in averaging out inconsistencies from the previous processes, thus reducing mass variations. The ratio of input to output slivers, known as the doubling factor, varies based on the fiber type and yarn specifications, typically ranging from four to eight.