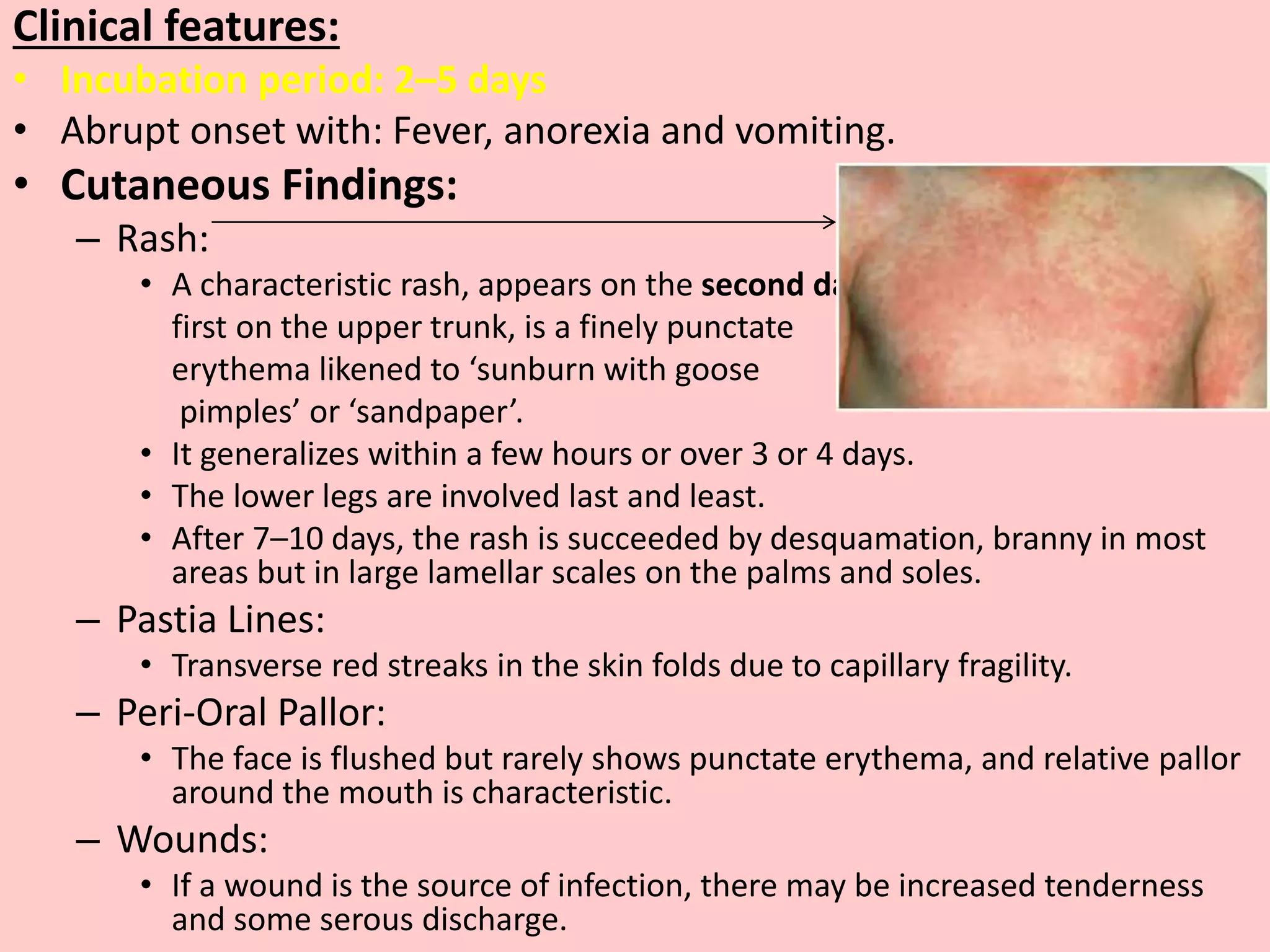
Scarlet fever is a bacterial disease caused by toxin-producing group A beta-hemolytic streptococci, primarily affecting young children aged 5 to 15, with clinical features including a distinct scarlatiniform rash, pharyngitis, and fever. The condition has a good prognosis but can lead to complications like rheumatic fever and glomerulonephritis if not treated promptly, with penicillin being the primary treatment. The disease is infectious for up to 7 days before symptoms appear and until 24 hours after starting antibiotics.